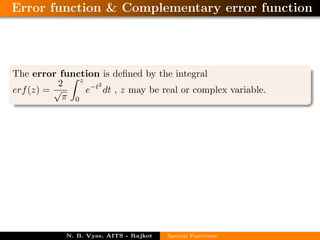
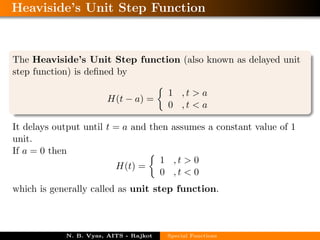
The document defines and provides equations for various special functions including the beta and gamma functions, Bessel function, error function, complementary error function, Heaviside's unit step function, pulse function, sinusoidal pulse, rectangle function, gate function, Dirac delta function, signum function, saw tooth wave function, triangular wave function, half-wave and full-wave rectified sinusoidal functions, and square wave function. The author is N. B. Vyas from the Department of Mathematics at Atmiya Institute of Tech. and Science in Rajkot, India.














![Signum Function
The signum function , denoted by sgn(t) , is defined by
sgn(t) =
1 , t > 0
−1 , t < 0
If H(t) is unit step function, then
H(t) =
1
2
[1 + sgn(t)]
and so
sgn(t) = 2H(t) − 1
N. B. Vyas, AITS - Rajkot Special Functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specialfunction-130701221925-phpapp01/85/Special-functions-17-320.jpg)






