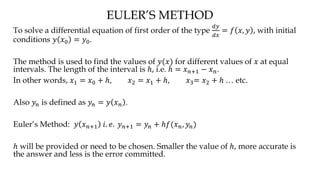
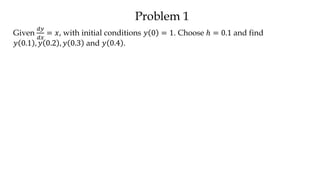
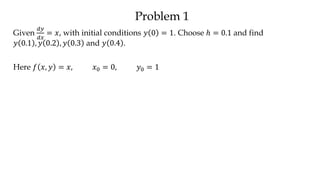
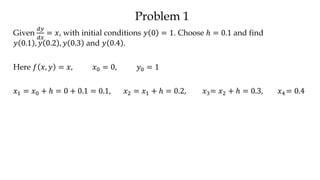
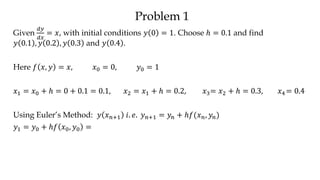
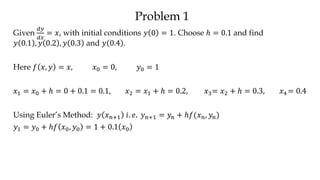
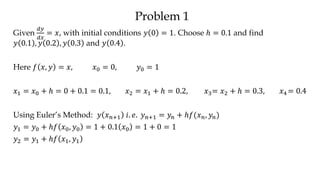
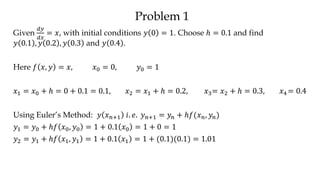
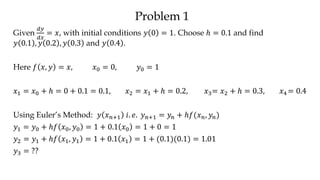
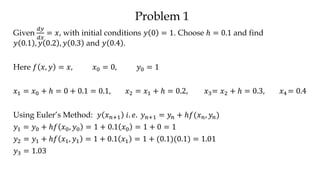
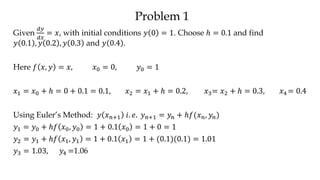
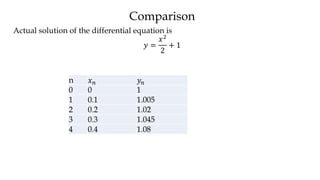
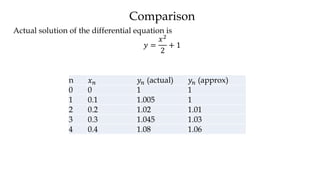
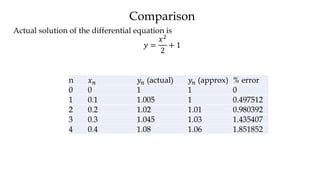
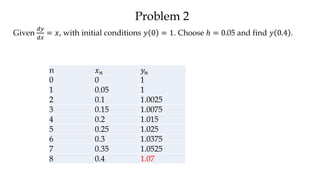
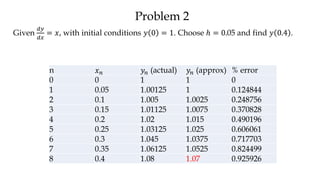
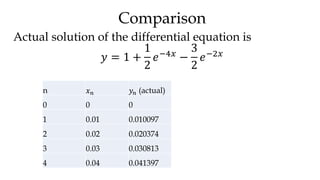
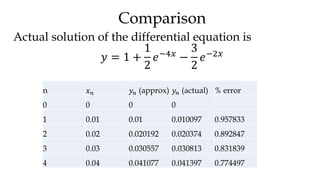
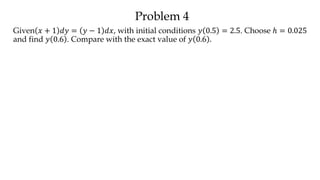
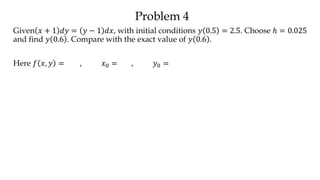
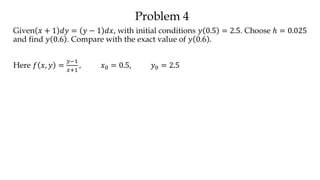
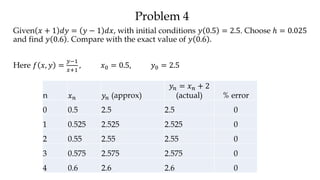
The document discusses initial value problems for first order differential equations and Euler's method for solving such problems numerically. It provides an example problem where Euler's method is used to find successive y-values for the differential equation dy/dx = x with the initial condition y(0) = 1. The y-values found using Euler's method are then compared to the actual solution, showing small errors that decrease as the step size h is reduced.