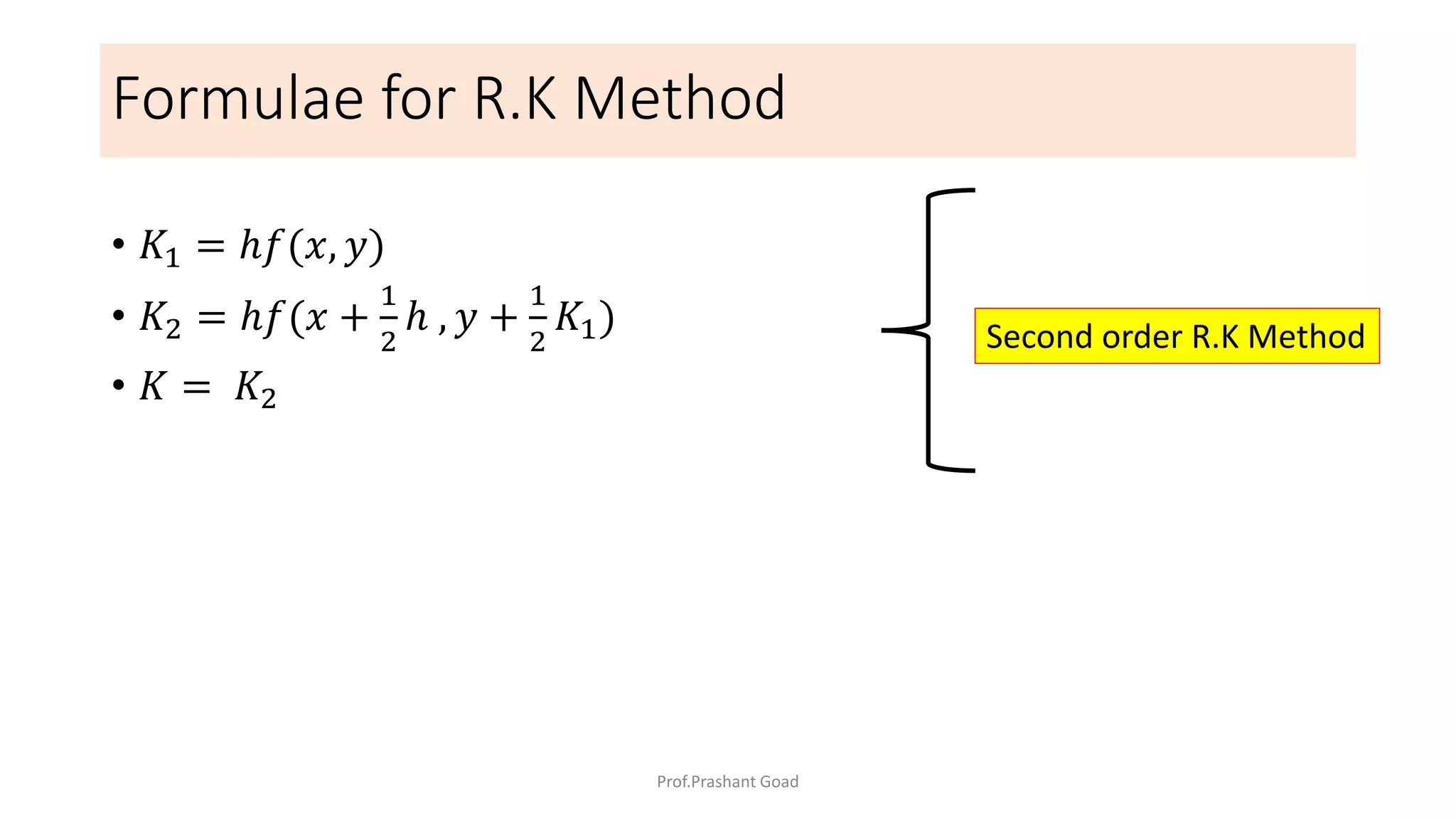
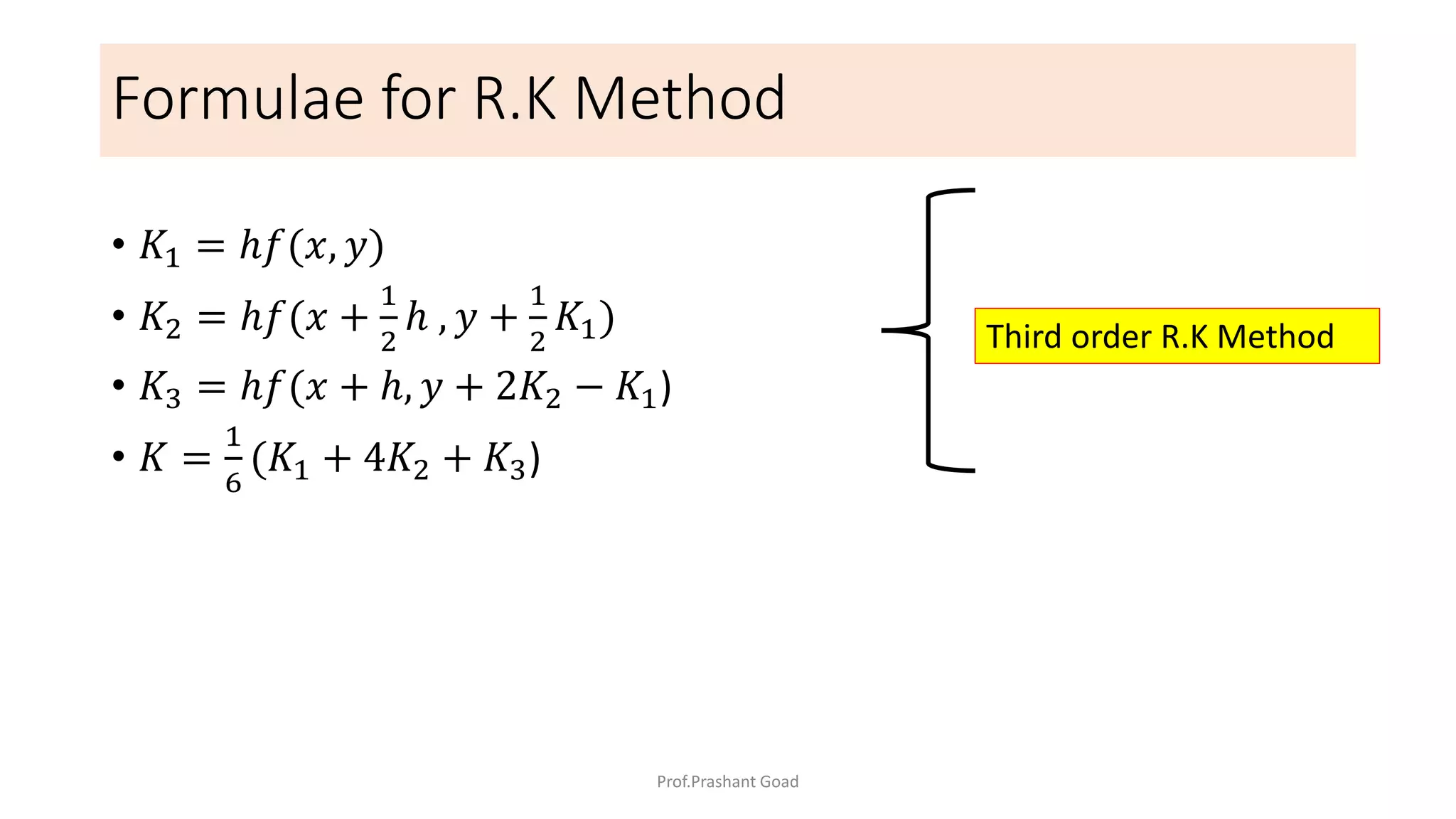
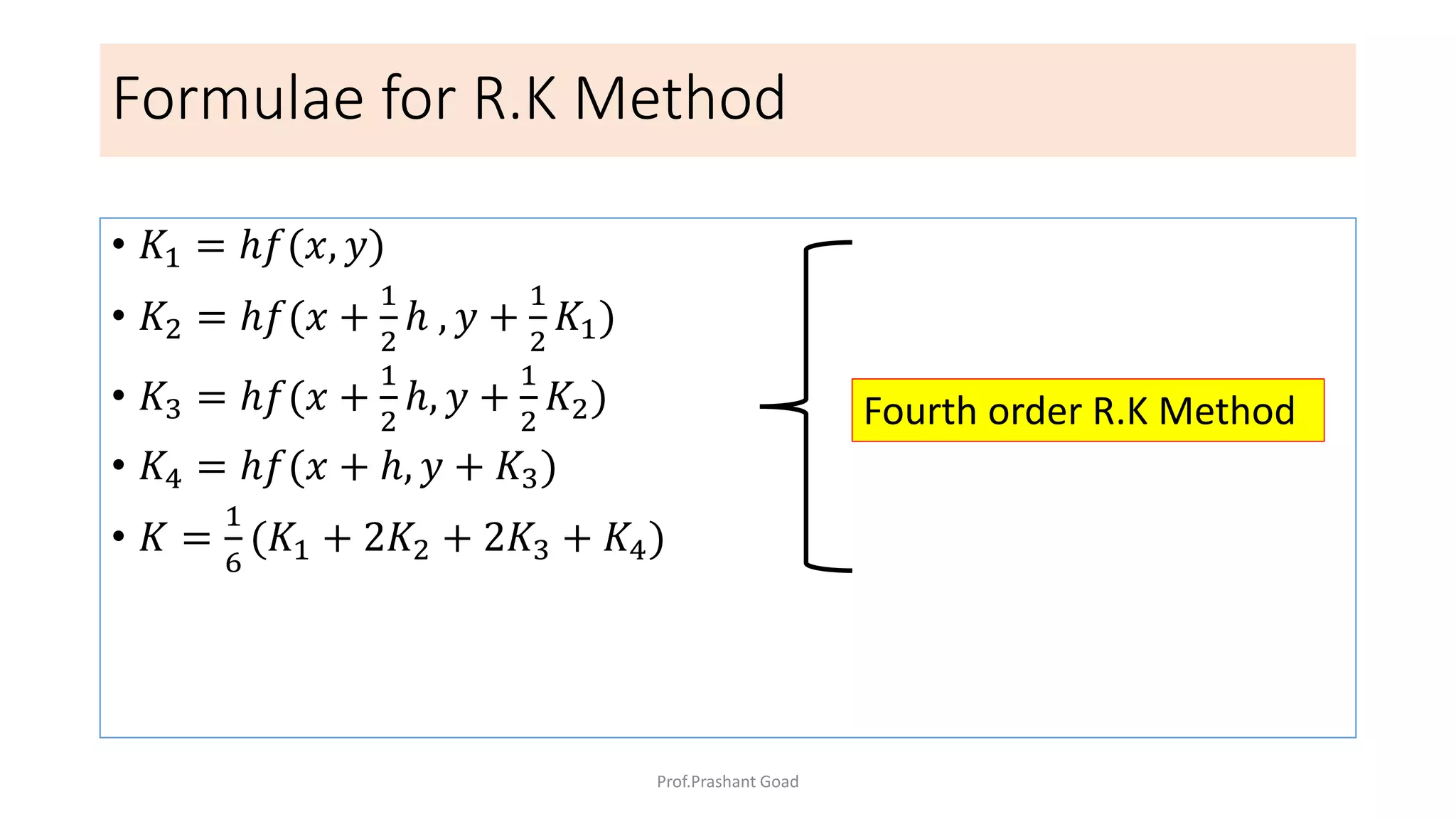
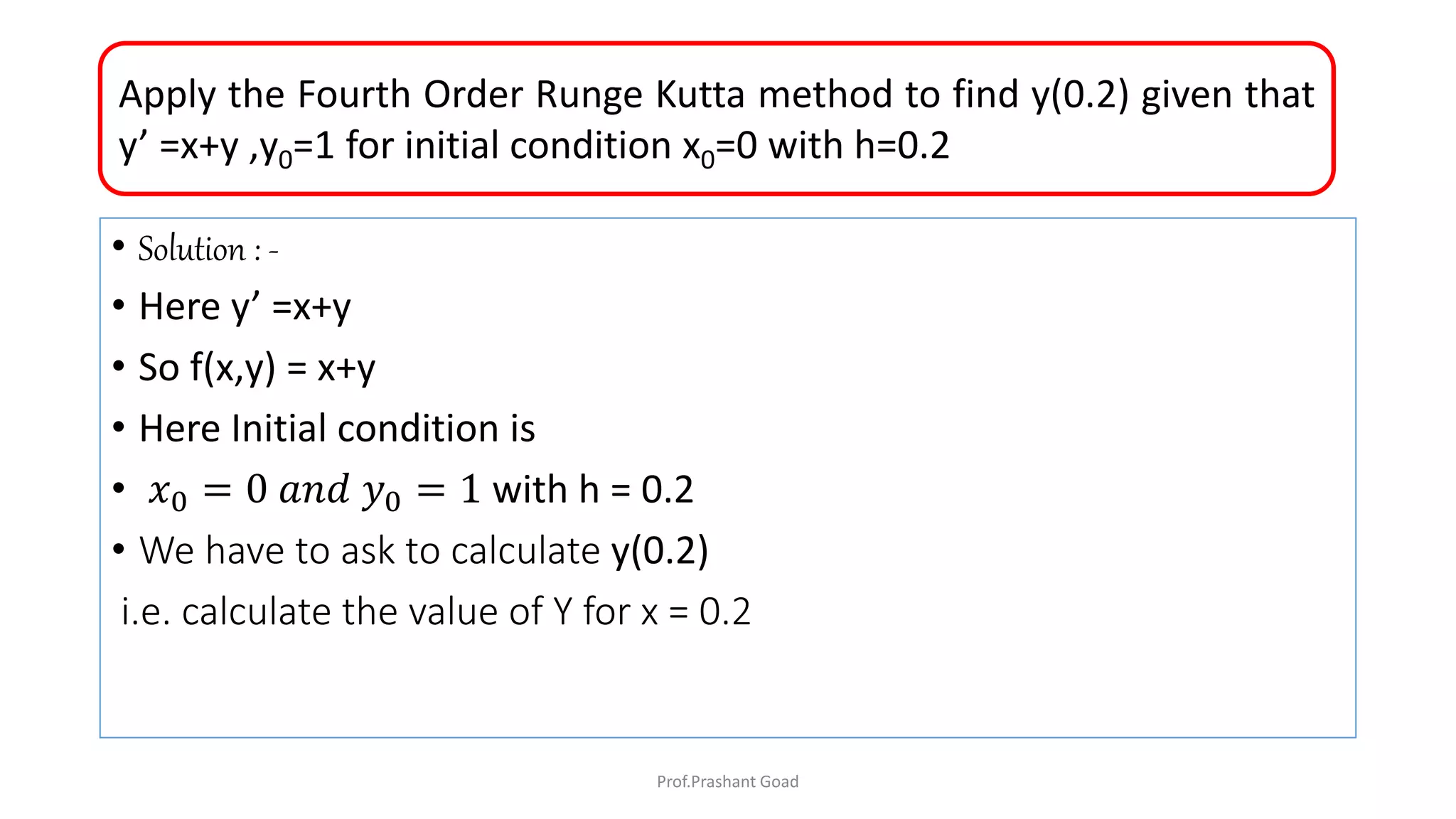
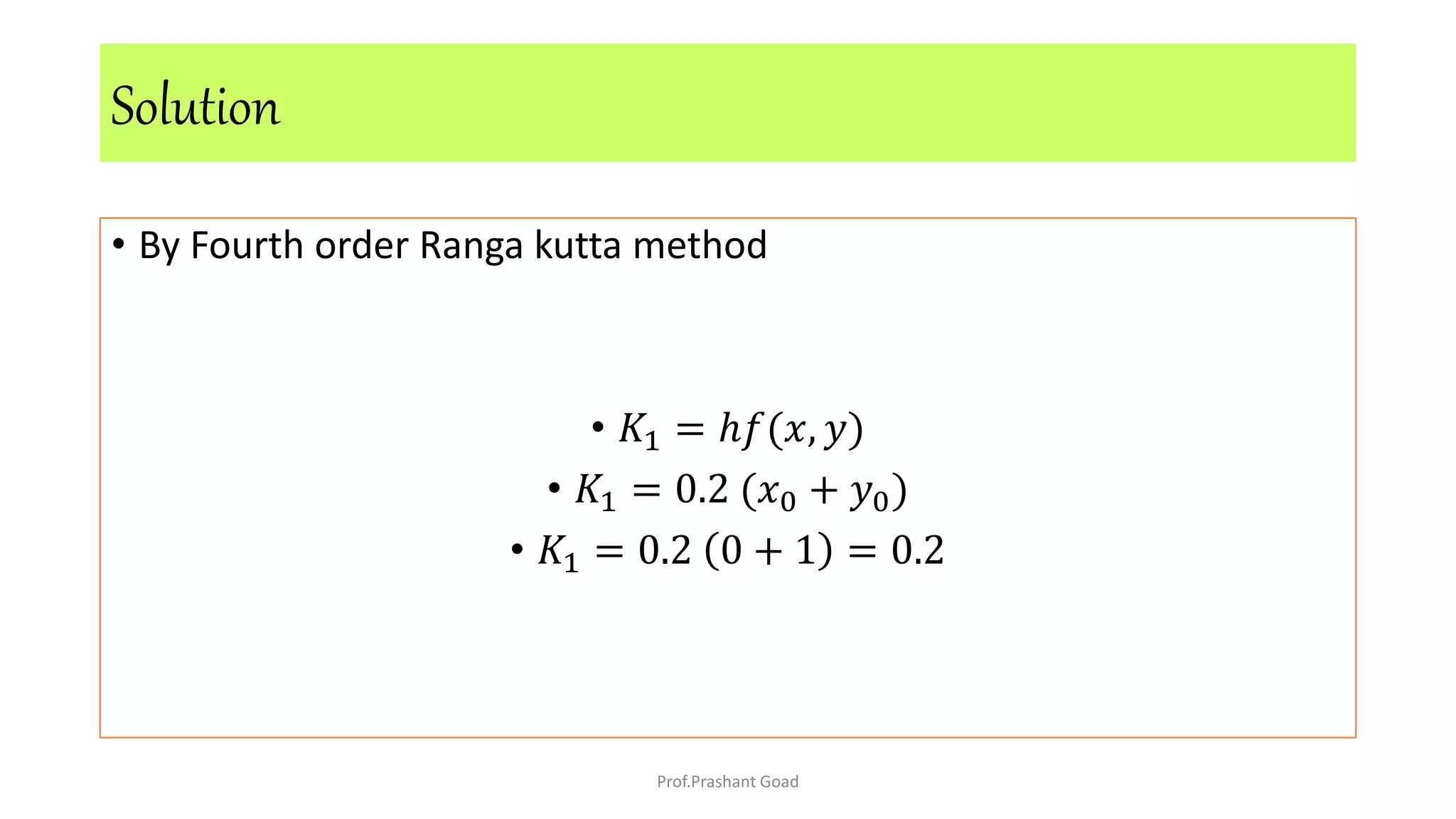
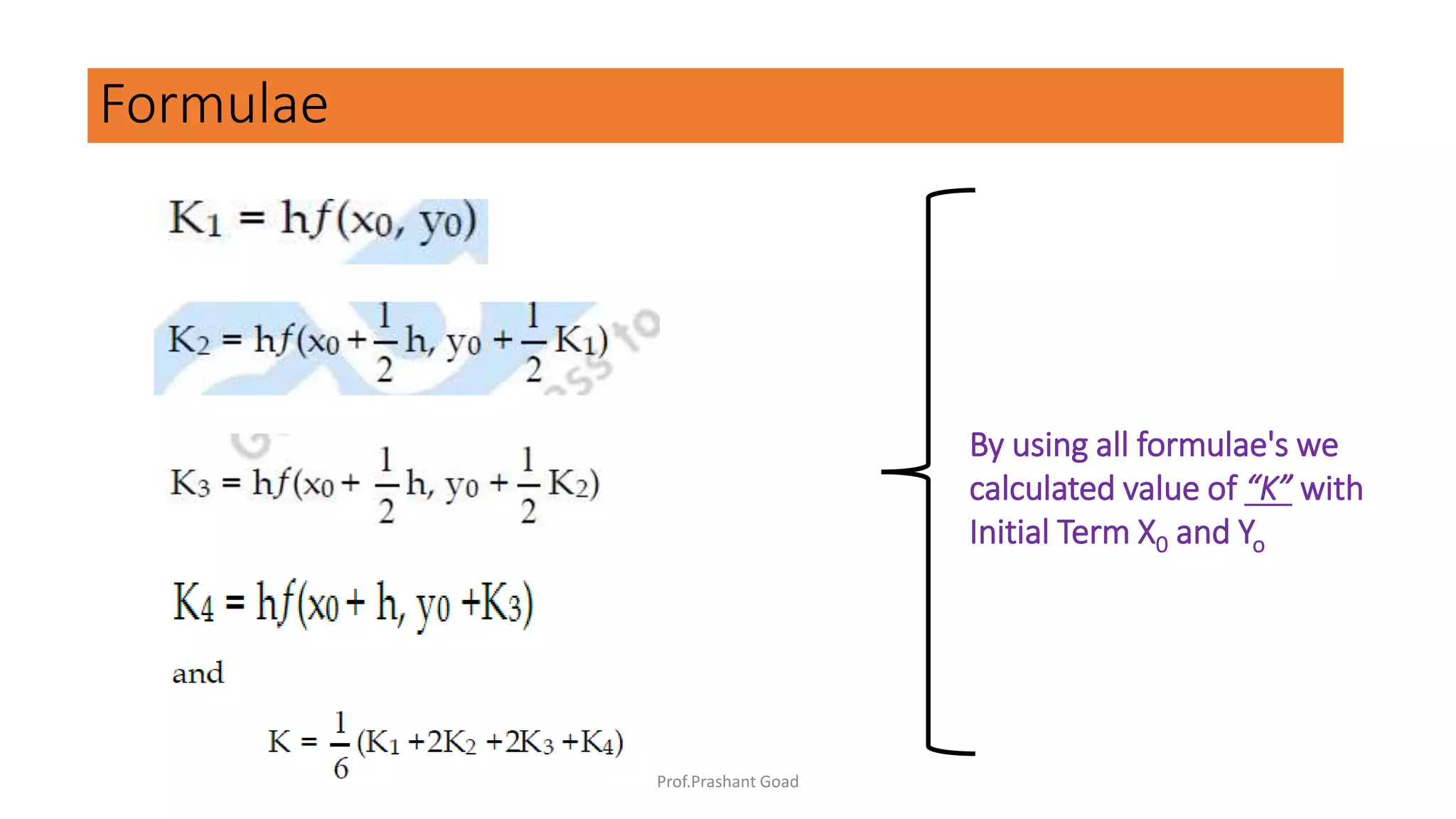
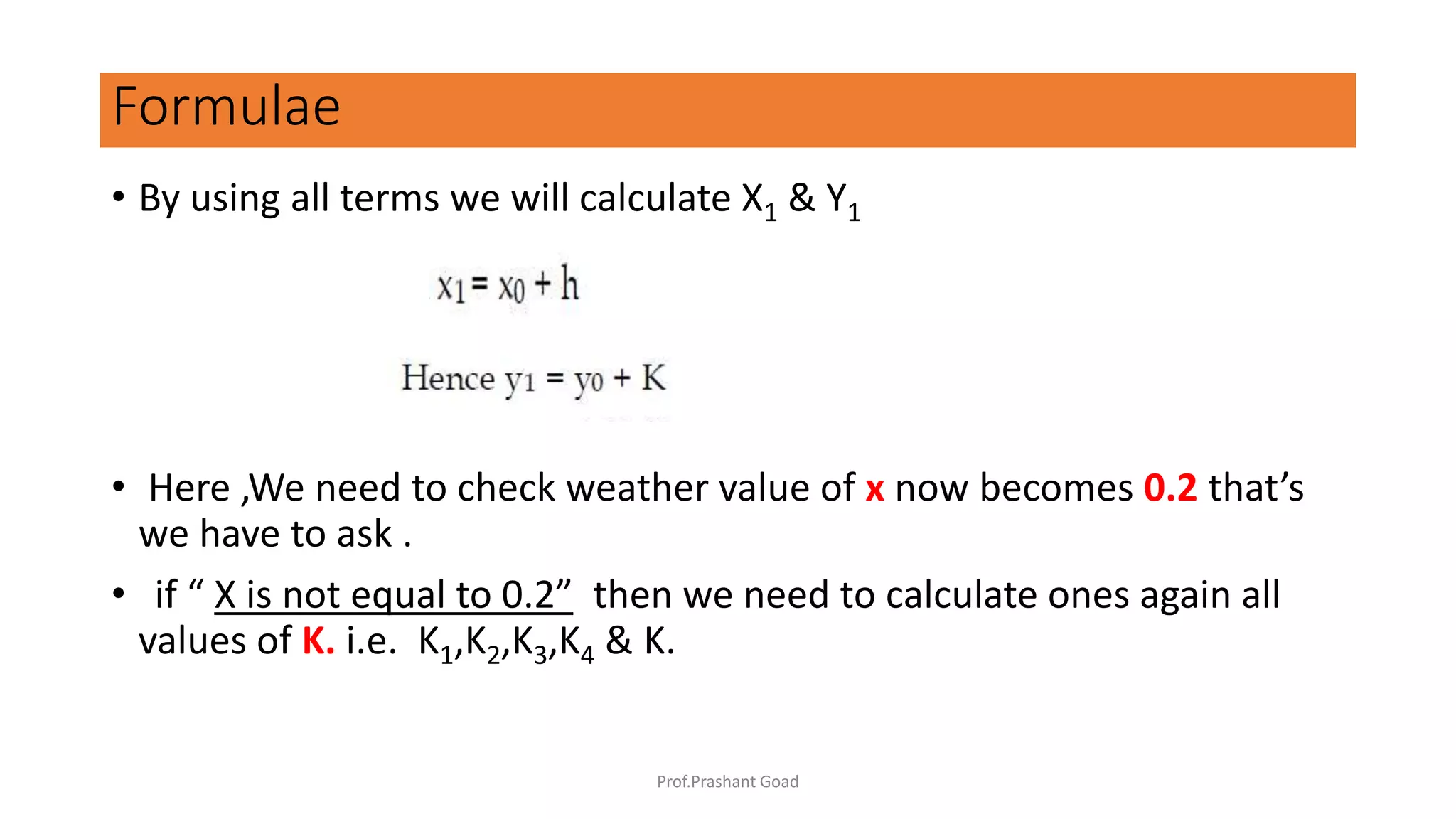
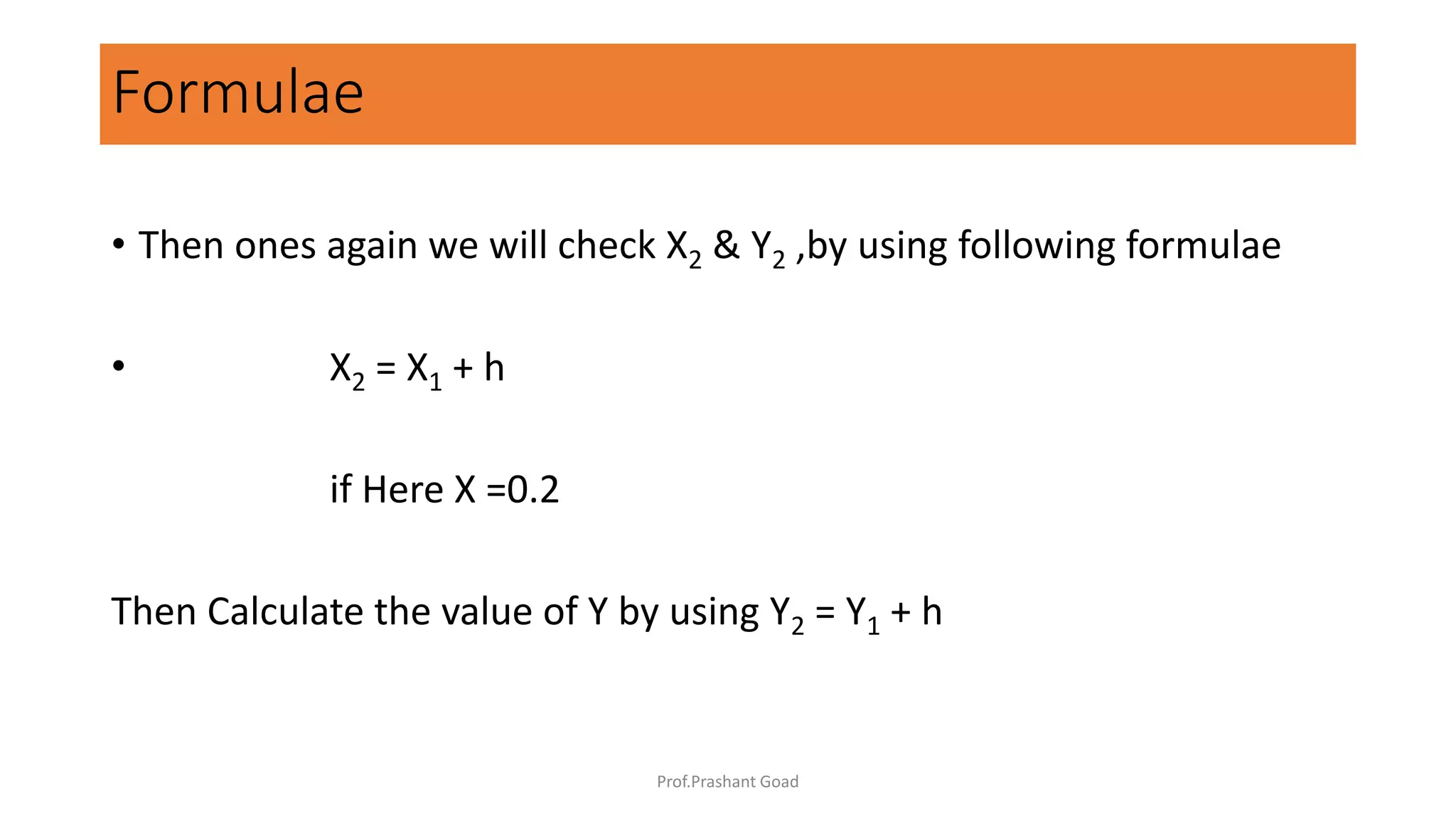
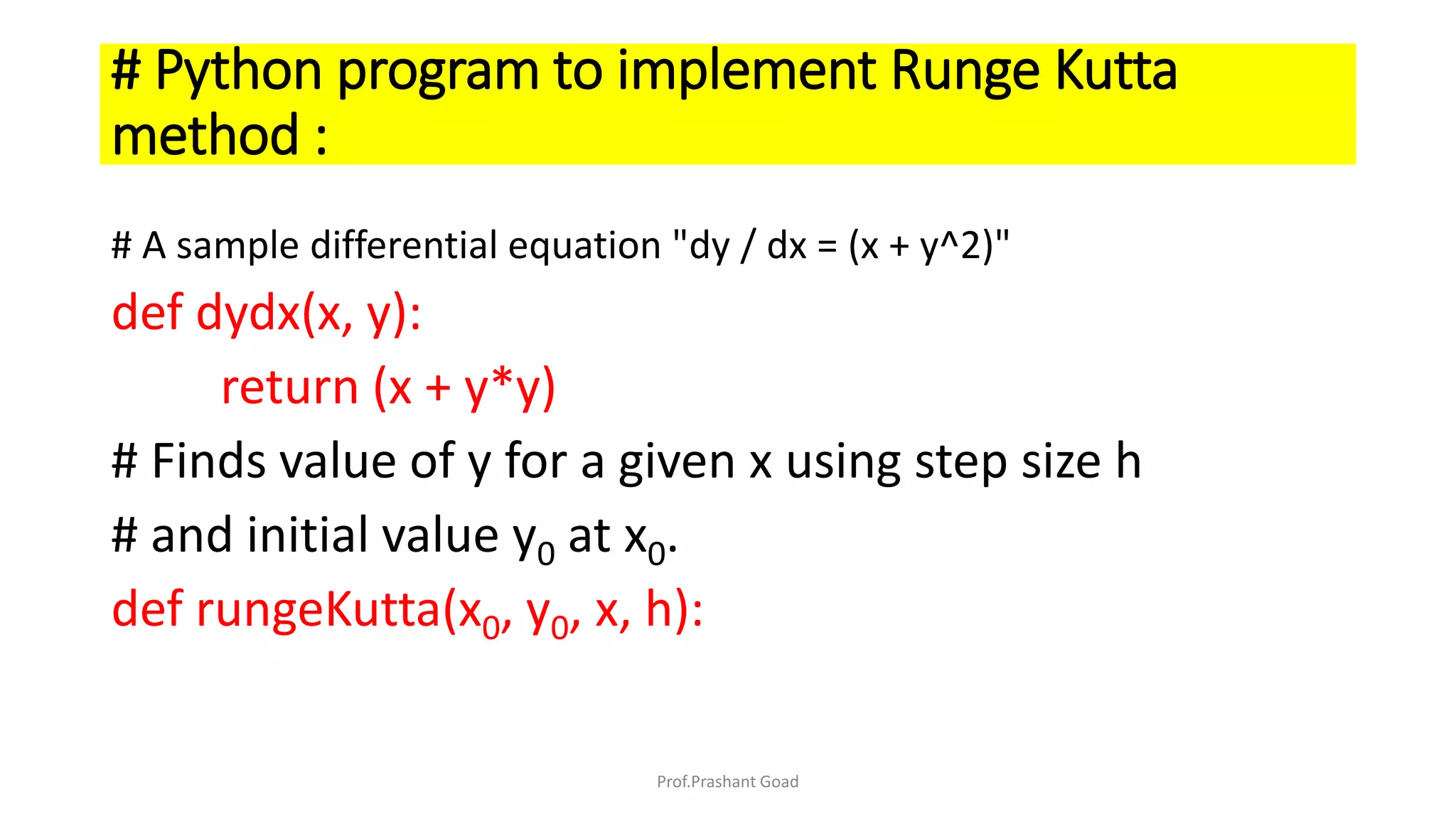
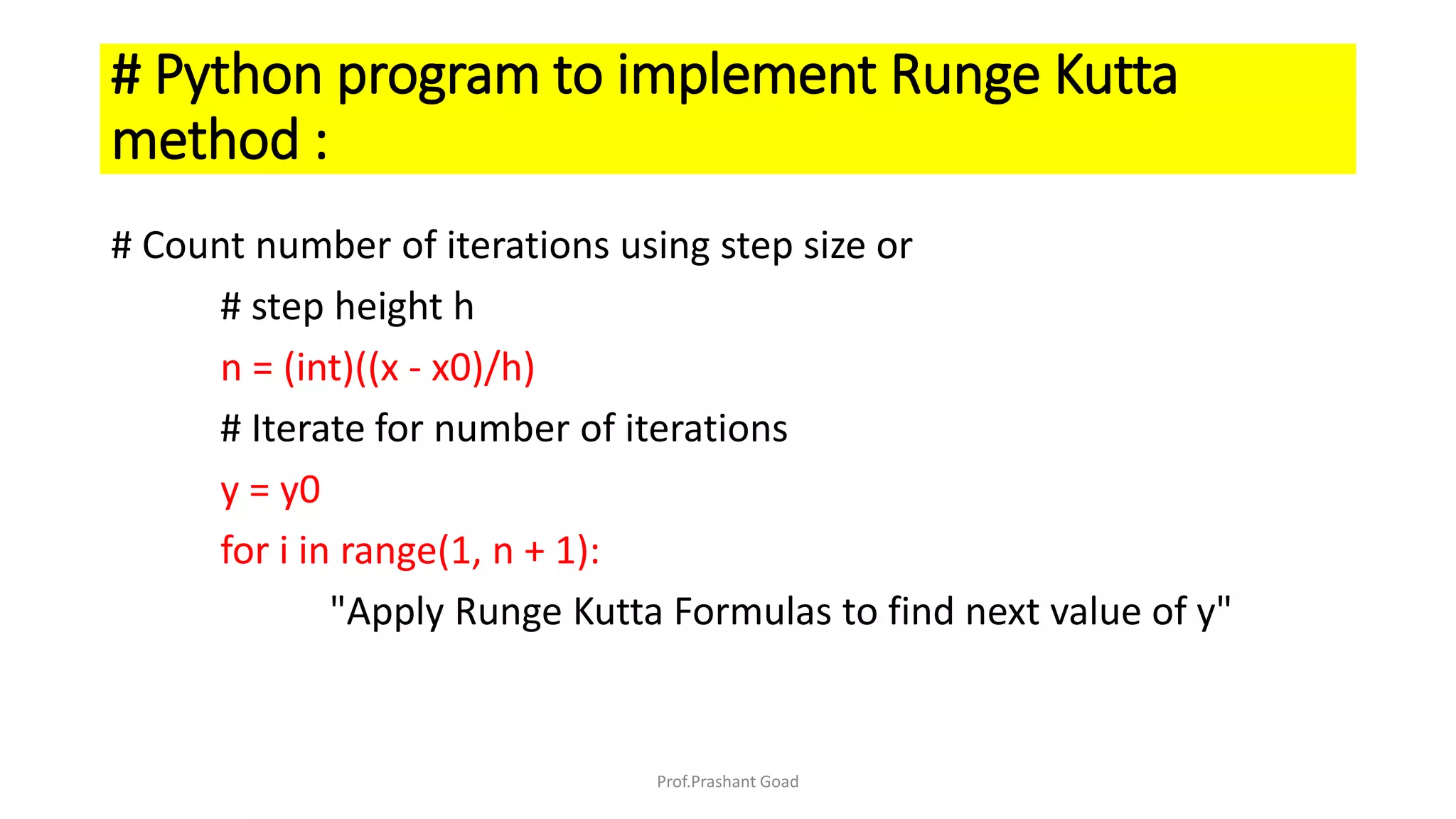
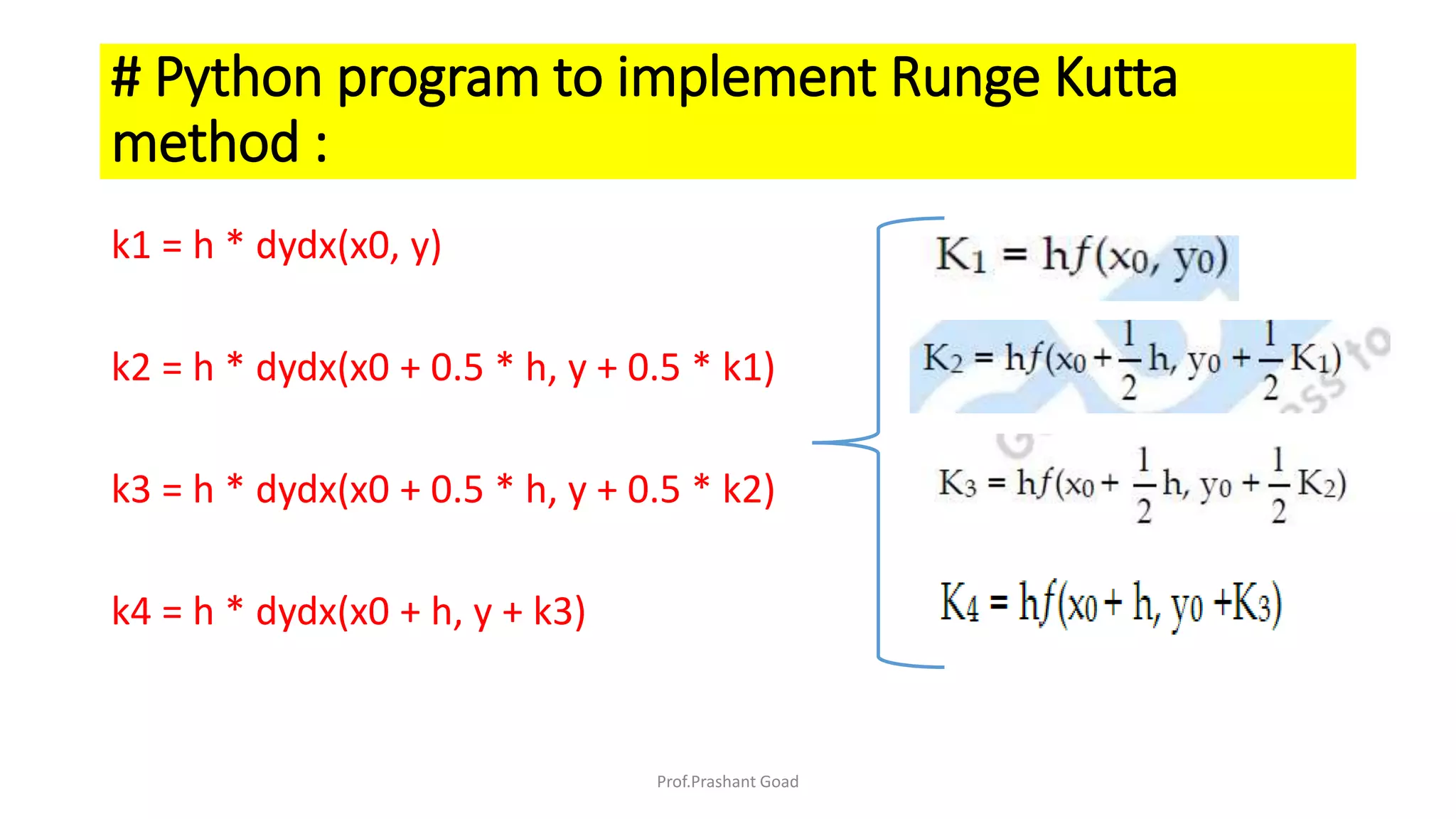
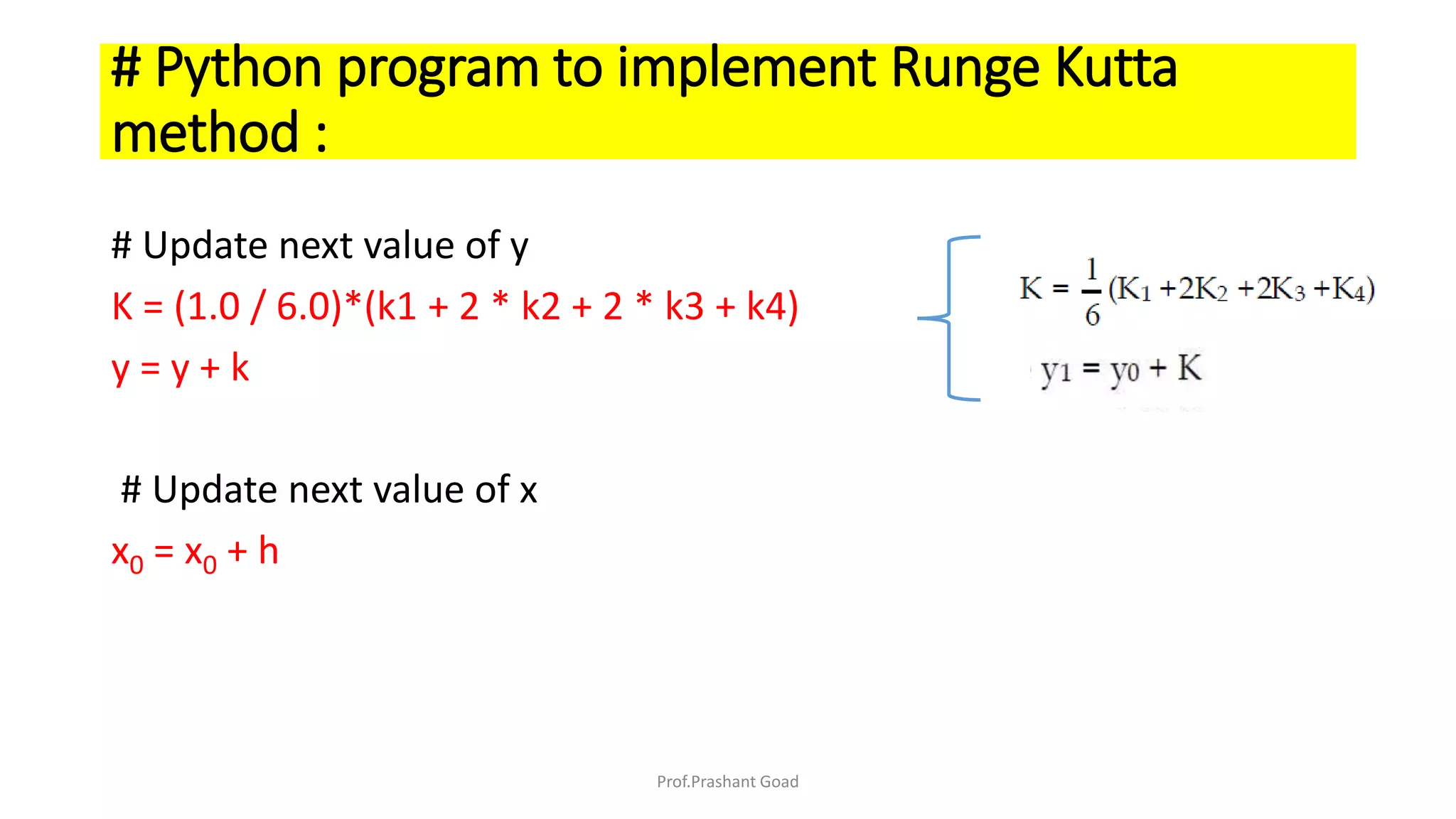
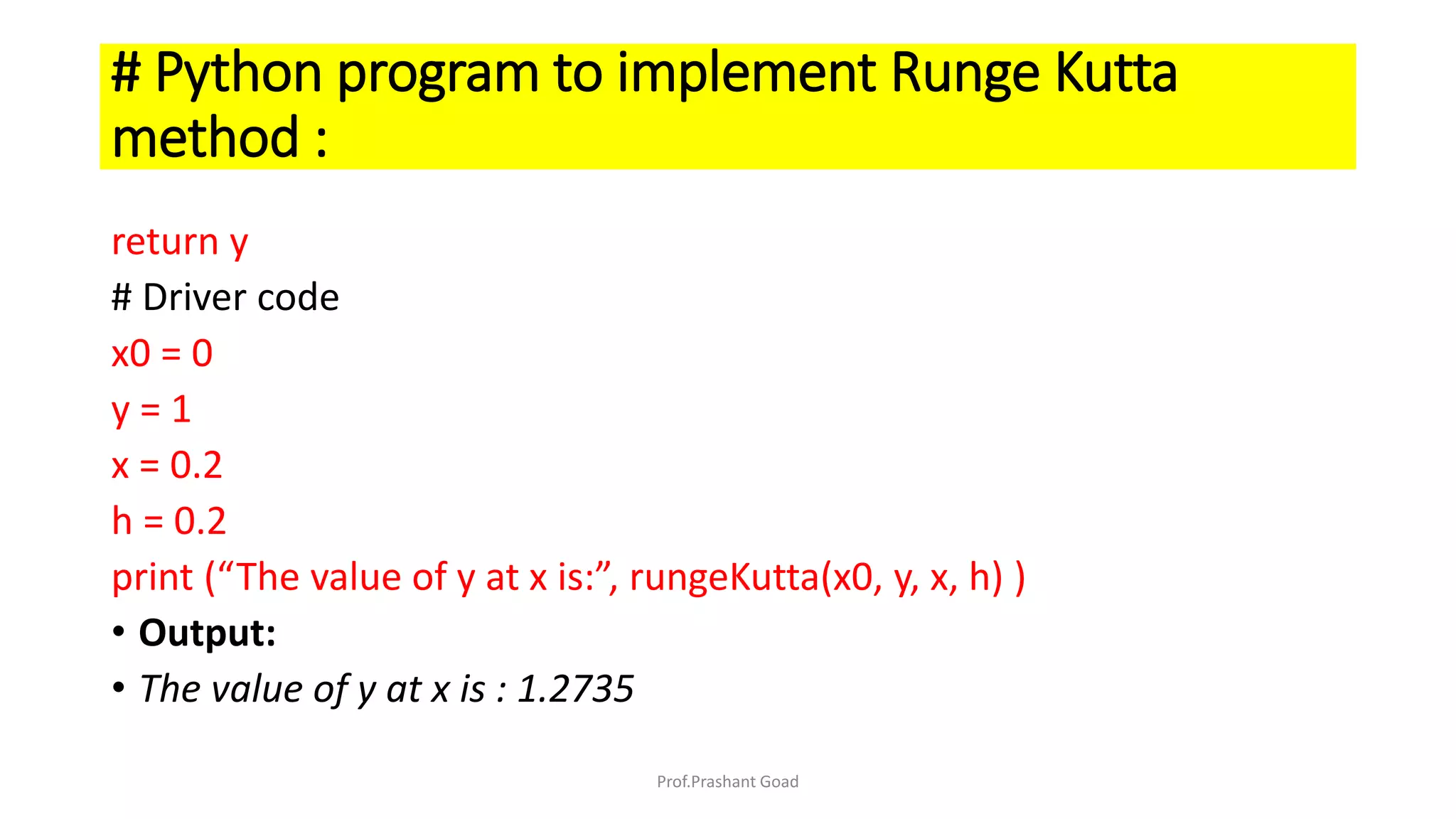
The document presents a program for the Runge-Kutta 4th order method, a technique for solving ordinary differential equations, specifically applied to calculate the behavior of a rocket in flight. It details the step-by-step calculations necessary to find the value of y at x=0.2, including the formulas for the method and a Python implementation. The final output of the program indicates the estimated value of y at the specified x value as 1.2735.