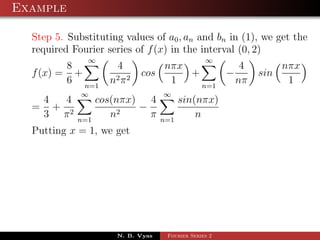
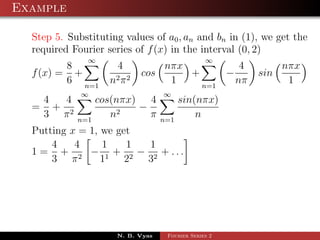
The document discusses the Fourier series representation of periodic functions with an arbitrary period. It provides the general form of the Fourier series for a function f(x) with period 2L, defined over the interval c < x < c + 2L. It also gives the specific forms when c = 0, -L, or L. An example of finding the Fourier series of the function f(x) = x^2 from 0 to 2 is worked out step-by-step.
































































![Fourier Cosine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-69-320.jpg)
![Fourier Cosine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
the Fourier cosine series expansion of f (x) on the half range
interval [0, l] is given by
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-70-320.jpg)
![Fourier Cosine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
the Fourier cosine series expansion of f (x) on the half range
interval [0, l] is given by
∞
ao nπx
f (x) = + an cos
2 n=1
l
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-71-320.jpg)
![Fourier Cosine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
the Fourier cosine series expansion of f (x) on the half range
interval [0, l] is given by
∞
ao nπx
f (x) = + an cos
2 n=1
l
l
2
where a0 = f (x) dx
l 0
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-72-320.jpg)
![Fourier Cosine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
the Fourier cosine series expansion of f (x) on the half range
interval [0, l] is given by
∞
ao nπx
f (x) = + an cos
2 n=1
l
l
2
where a0 = f (x) dx
l 0
l
2 nπx
an = f (x) cos dx
l 0 l
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-73-320.jpg)
![Fourier Sine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-74-320.jpg)
![Fourier Sine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
the Fourier sine series expansion of f (x) on the half range
interval [0, l] is given by
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-75-320.jpg)
![Fourier Sine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
the Fourier sine series expansion of f (x) on the half range
interval [0, l] is given by
∞
nπx
f (x) = bn sin
n=1
l
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-76-320.jpg)
![Fourier Sine Series
Let f (x) be piecewise continuous on [o, l].
the Fourier sine series expansion of f (x) on the half range
interval [0, l] is given by
∞
nπx
f (x) = bn sin
n=1
l
l
2 nπx
bn = f (x) sin dx
l 0 l
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-77-320.jpg)








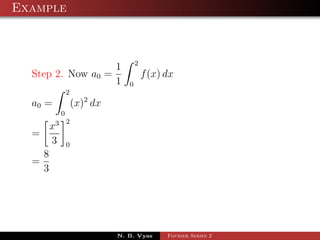
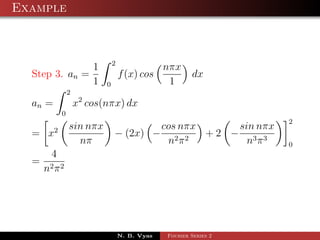
![Example
2
2
Step 2. a0 = f (x)dx
2 0
2
= 1dx = [x]2
0
0
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-86-320.jpg)
![Example
2
2
Step 2. a0 = f (x)dx
2 0
2
= 1dx = [x]2 = 2.
0
0
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries2-130124054331-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-2-87-320.jpg)








