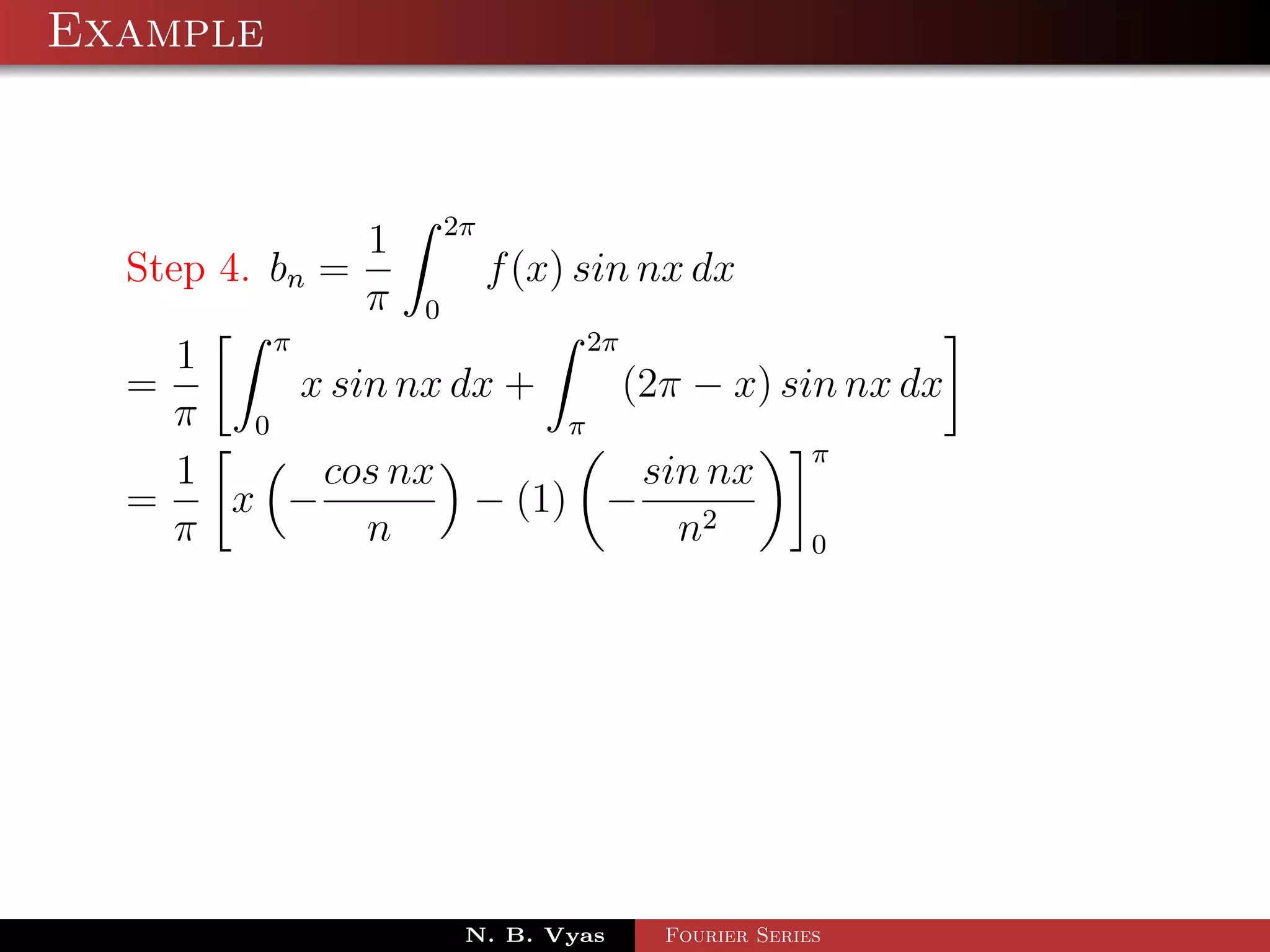
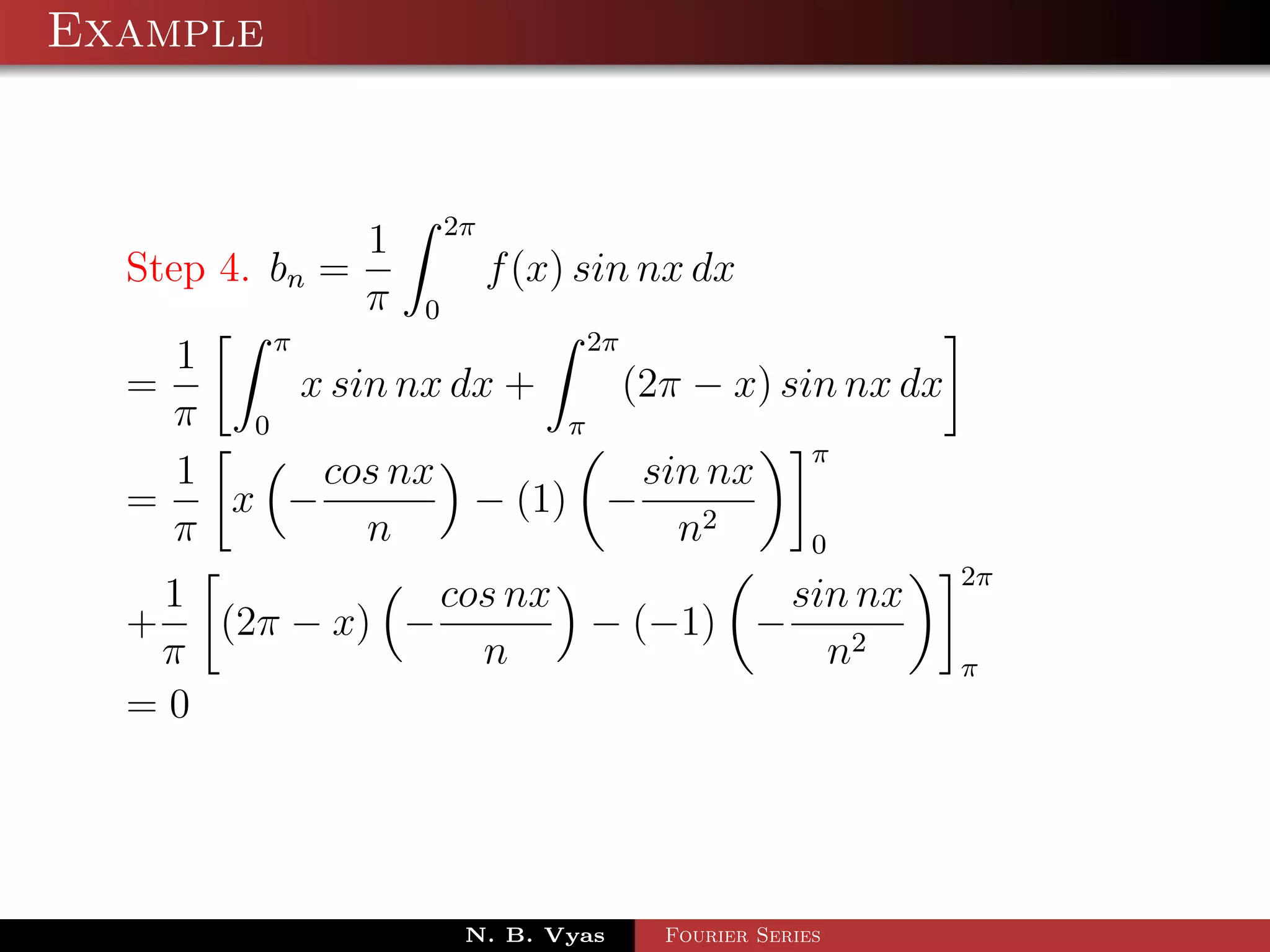
The document discusses periodic functions and their properties. The key points are:
- A periodic function f(x) satisfies f(x) = f(x + T) for some fixed period T and all real x.
- Periodic functions repeat their values at intervals of their period, including integer multiples of the period.
- Functions are defined as even if f(-x) = f(x) and odd if f(-x) = -f(x).
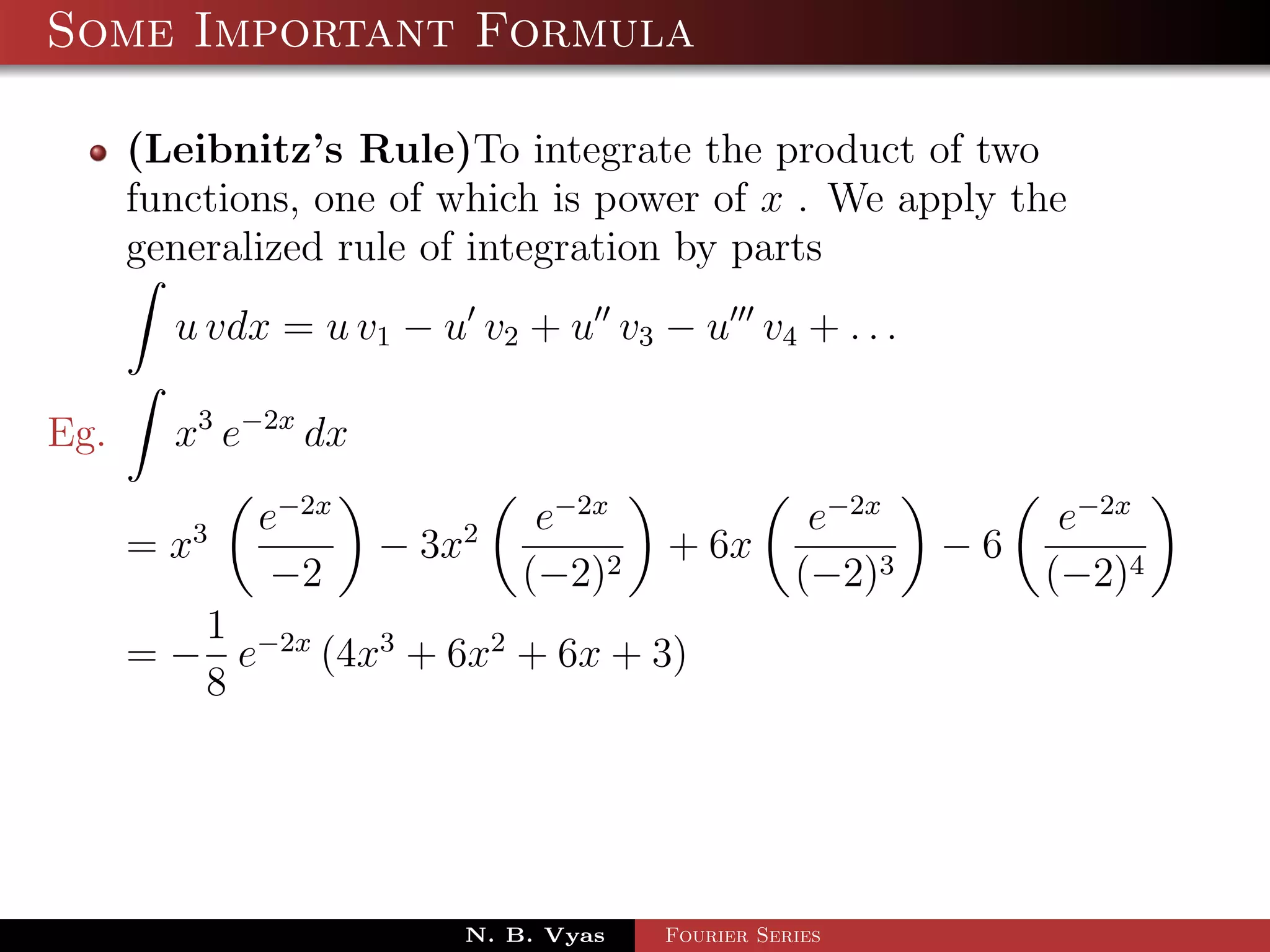
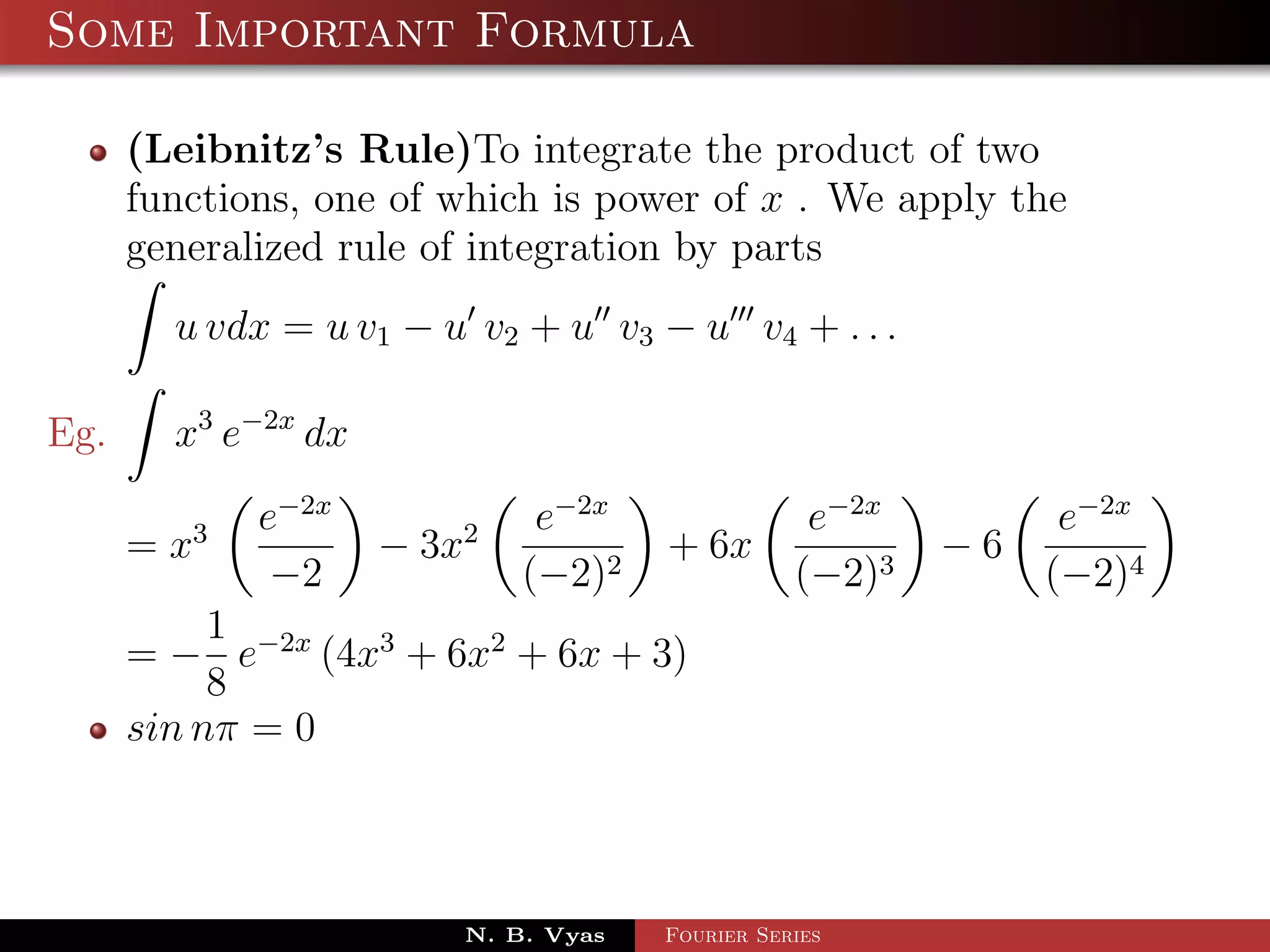
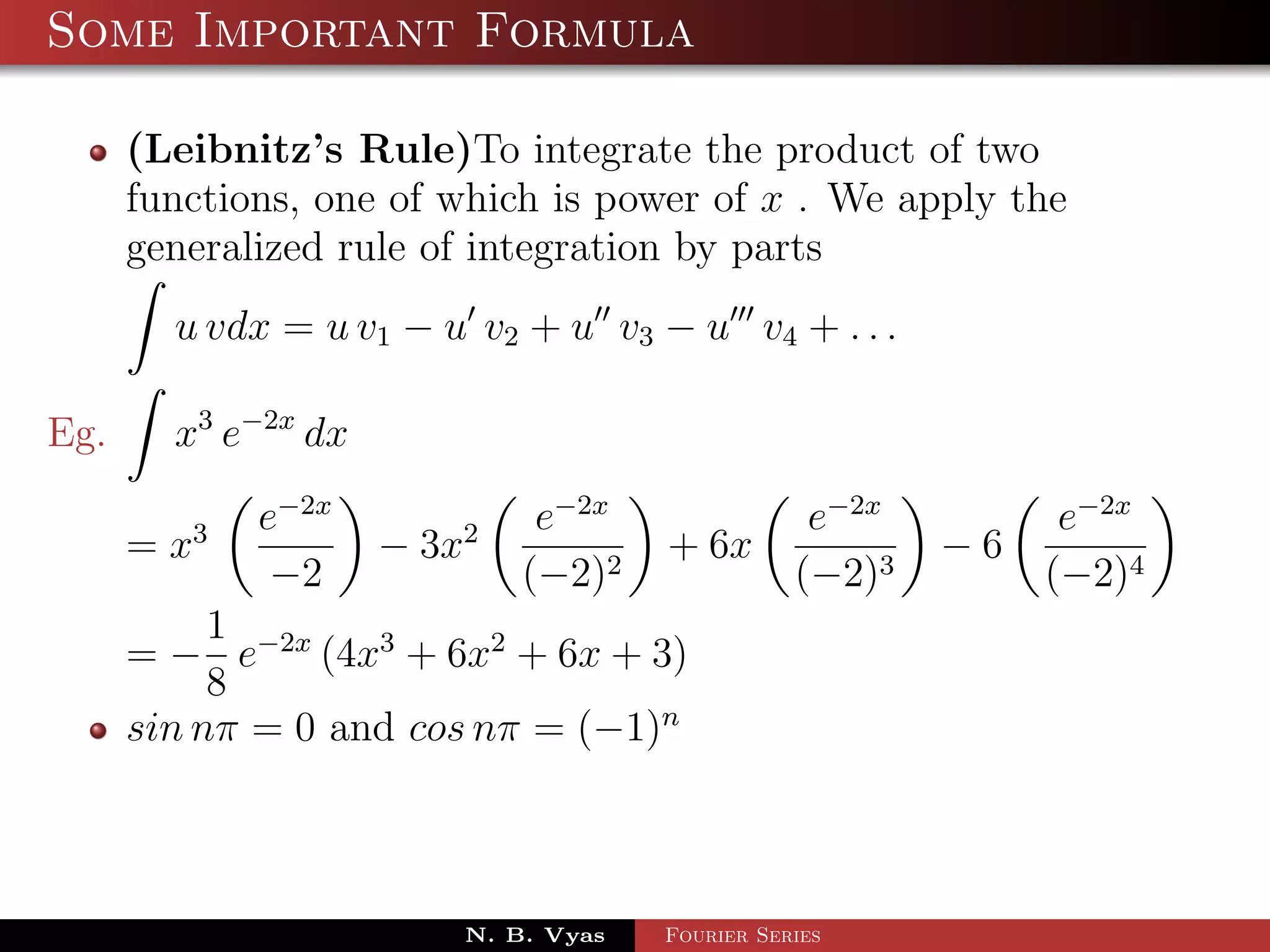
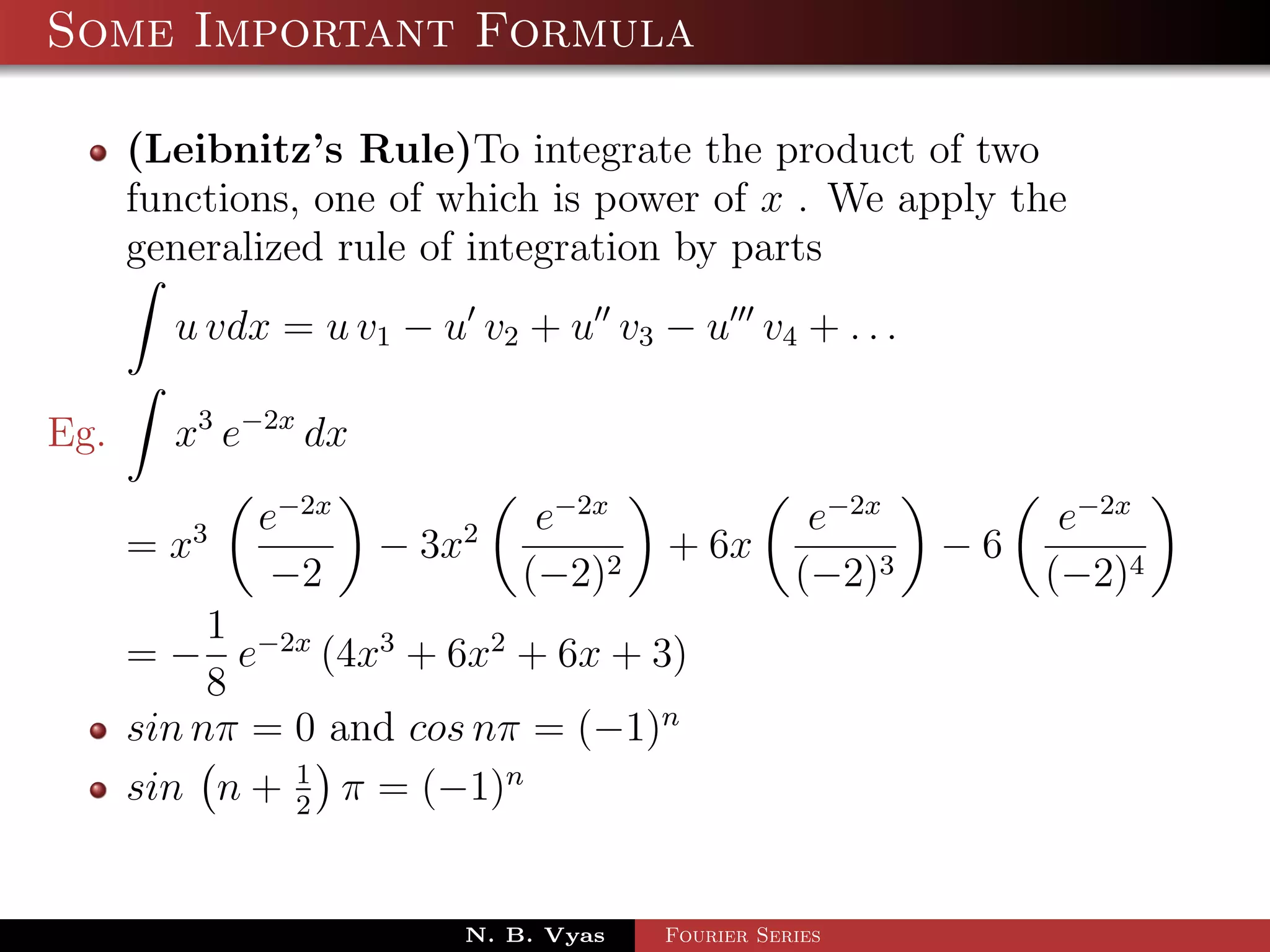
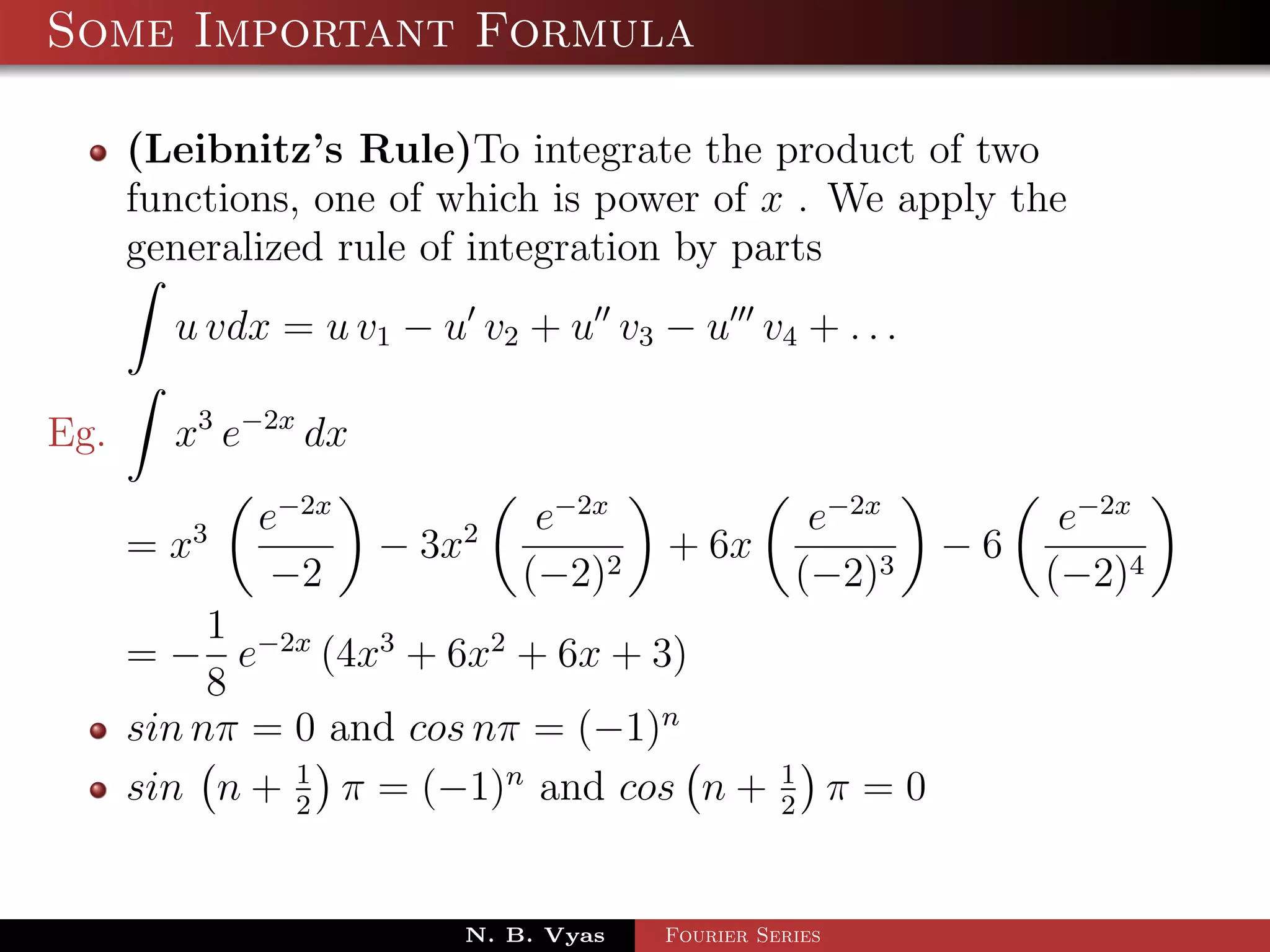
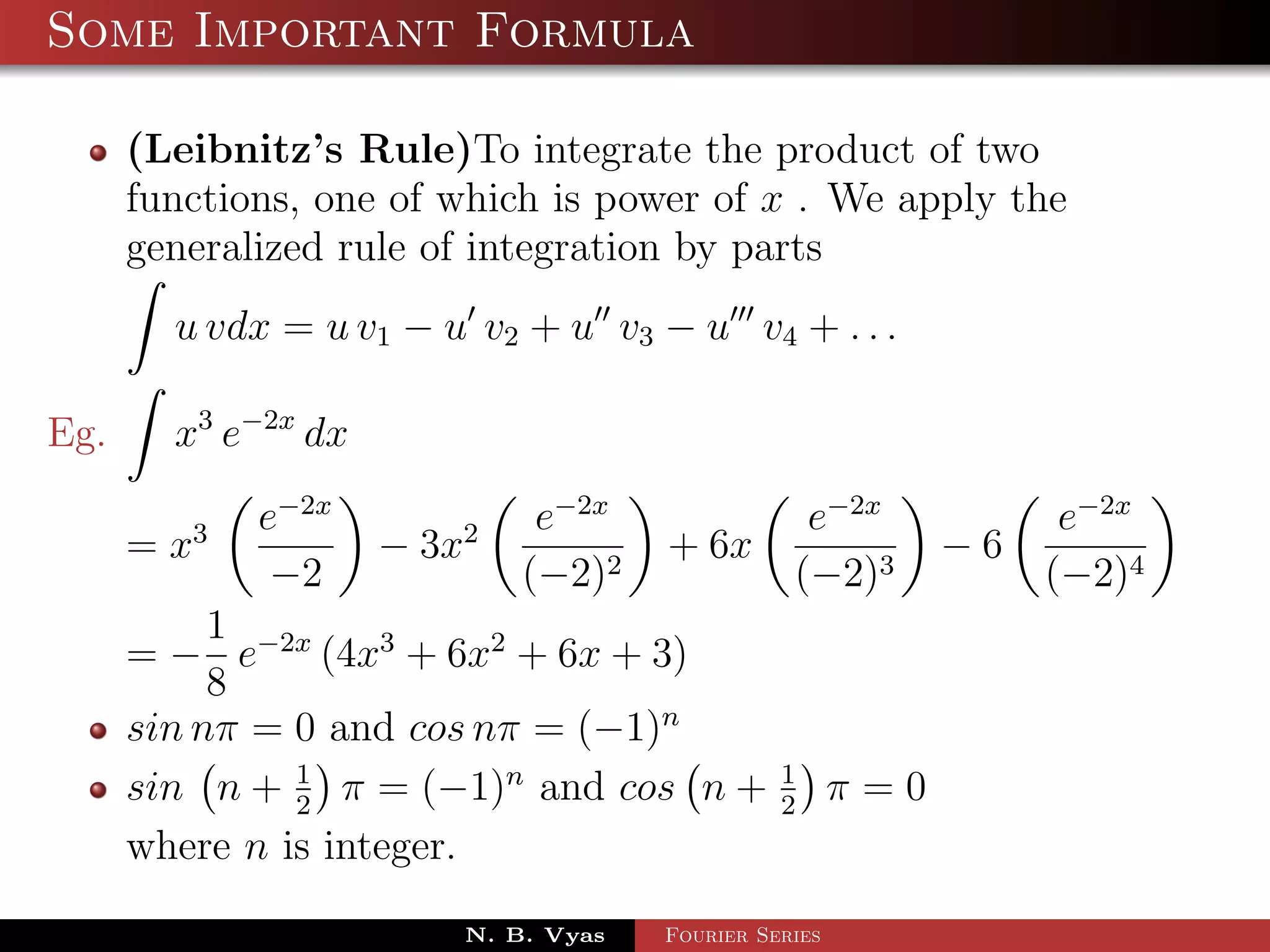
- Several important formulas are provided for integrating exponential and trigonometric functions.


















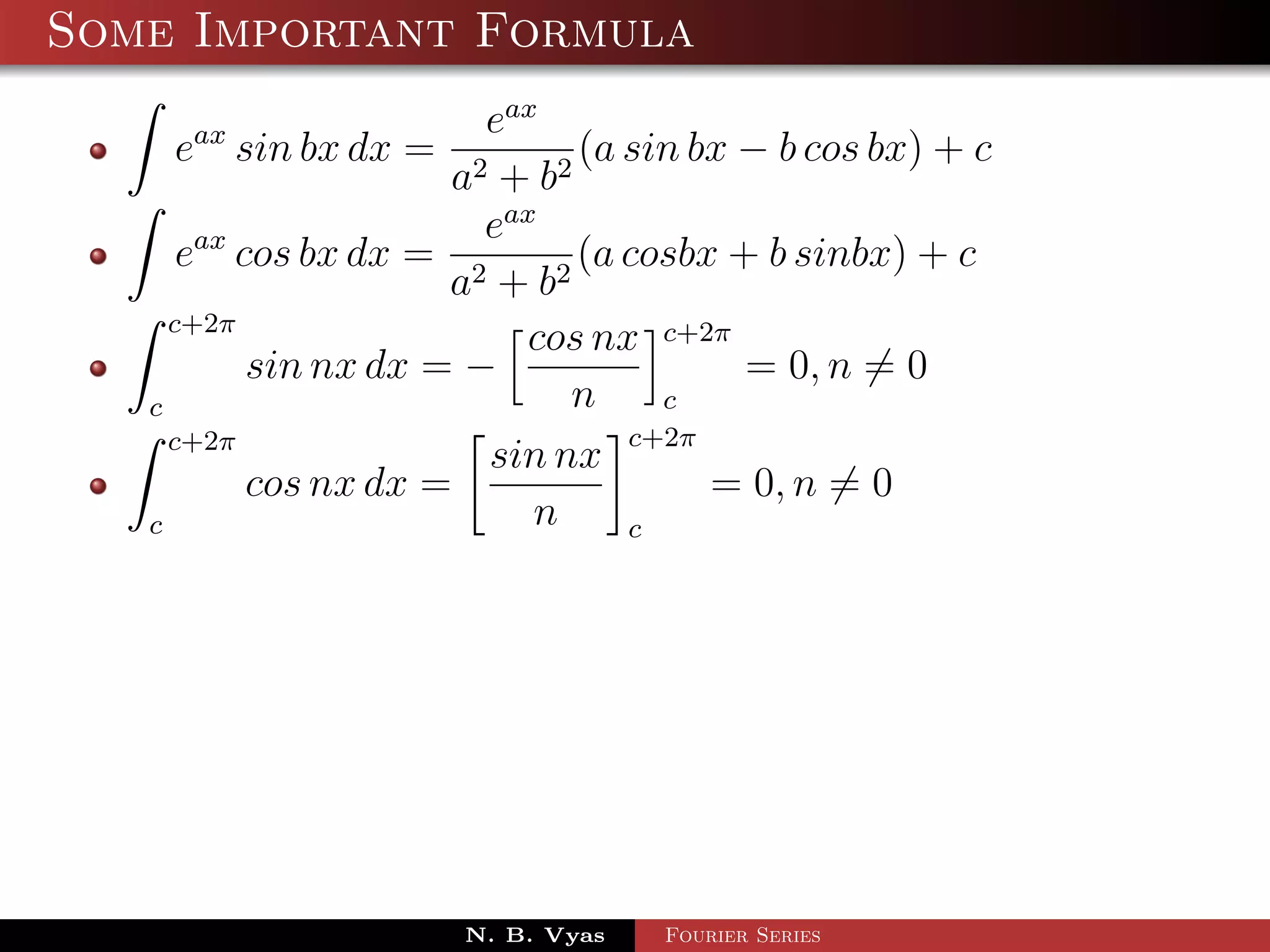

![Some Important Formula
eax
eax sin bx dx = (a sin bx − b cos bx) + c
a2 + b 2
eax
eax cos bx dx = 2 (a cosbx + b sinbx) + c
a + b2
c+2π
cos nx c+2π
sin nx dx = − = 0, n = 0
c n c
c+2π c+2π
sin nx
cos nx dx = = 0, n = 0
c n c
c+2π
1 c+2π
sin mx cos nx dx = 2sin mx cos nx dx
c 2 c
1 c+2π
= [sin (m + n)x + sin (m − n)x] dx
2 c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-21-2048.jpg)
![Some Important Formula
eax
eax sin bx dx = (a sin bx − b cos bx) + c
a2 + b 2
eax
eax cos bx dx = 2 (a cosbx + b sinbx) + c
a + b2
c+2π
cos nx c+2π
sin nx dx = − = 0, n = 0
c n c
c+2π c+2π
sin nx
cos nx dx = = 0, n = 0
c n c
c+2π
1 c+2π
sin mx cos nx dx = 2sin mx cos nx dx
c 2 c
1 c+2π
= [sin (m + n)x + sin (m − n)x] dx
2 c
c+2π
1 cos (m + n)x cos (m − n)x
=− + = 0, n = 0
2 m+n m−n c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-22-2048.jpg)

![Some Important Formula
c+2π c+2π
1
cos mx cos nx dx = 2
2cos mx cos nx dx
c c
c+2π
1
= 2
[cos (m + n)x + cos (m − n)x] dx
c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-24-2048.jpg)
![Some Important Formula
c+2π c+2π
1
cos mx cos nx dx = 2
2cos mx cos nx dx
c c
c+2π
1
= 2
[cos (m + n)x + cos (m − n)x] dx
c
c+2π
1 sin (m + n)x sin (m − n)x
= 2
+ = 0, m = n
m+n m−n c
c+2π
sin mx sin nx dx
c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-25-2048.jpg)
![Some Important Formula
c+2π c+2π
1
cos mx cos nx dx = 2
2cos mx cos nx dx
c c
c+2π
1
= 2
[cos (m + n)x + cos (m − n)x] dx
c
c+2π
1 sin (m + n)x sin (m − n)x
= 2
+ = 0, m = n
m+n m−n c
c+2π
sin mx sin nx dx = 0
c
c+2π
sin nx cos nx dx
c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-26-2048.jpg)
![Some Important Formula
c+2π c+2π
1
cos mx cos nx dx = 2
2cos mx cos nx dx
c c
c+2π
1
= 2
[cos (m + n)x + cos (m − n)x] dx
c
c+2π
1 sin (m + n)x sin (m − n)x
= 2
+ = 0, m = n
m+n m−n c
c+2π
sin mx sin nx dx = 0
c
c+2π
sin nx cos nx dx = 0, n = 0
c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-27-2048.jpg)
![Some Important Formula
c+2π c+2π
1
cos mx cos nx dx = 2
2cos mx cos nx dx
c c
c+2π
1
= 2
[cos (m + n)x + cos (m − n)x] dx
c
c+2π
1 sin (m + n)x sin (m − n)x
= 2
+ = 0, m = n
m+n m−n c
c+2π
sin mx sin nx dx = 0
c
c+2π
sin nx cos nx dx = 0, n = 0
c
c+2π
cos2 nx dx
c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-28-2048.jpg)
![Some Important Formula
c+2π c+2π
1
cos mx cos nx dx = 2
2cos mx cos nx dx
c c
c+2π
1
= 2
[cos (m + n)x + cos (m − n)x] dx
c
c+2π
1 sin (m + n)x sin (m − n)x
= 2
+ = 0, m = n
m+n m−n c
c+2π
sin mx sin nx dx = 0
c
c+2π
sin nx cos nx dx = 0, n = 0
c
c+2π
cos2 nx dx = π
c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-29-2048.jpg)
![Some Important Formula
c+2π c+2π
1
cos mx cos nx dx = 2
2cos mx cos nx dx
c c
c+2π
1
= 2
[cos (m + n)x + cos (m − n)x] dx
c
c+2π
1 sin (m + n)x sin (m − n)x
= 2
+ = 0, m = n
m+n m−n c
c+2π
sin mx sin nx dx = 0
c
c+2π
sin nx cos nx dx = 0, n = 0
c
c+2π
cos2 nx dx = π
c
c+2π
sin2 nx dx
c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-30-2048.jpg)
![Some Important Formula
c+2π c+2π
1
cos mx cos nx dx = 2
2cos mx cos nx dx
c c
c+2π
1
= 2
[cos (m + n)x + cos (m − n)x] dx
c
c+2π
1 sin (m + n)x sin (m − n)x
= 2
+ = 0, m = n
m+n m−n c
c+2π
sin mx sin nx dx = 0
c
c+2π
sin nx cos nx dx = 0, n = 0
c
c+2π
cos2 nx dx = π
c
c+2π
sin2 nx dx = π
c
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-31-2048.jpg)











































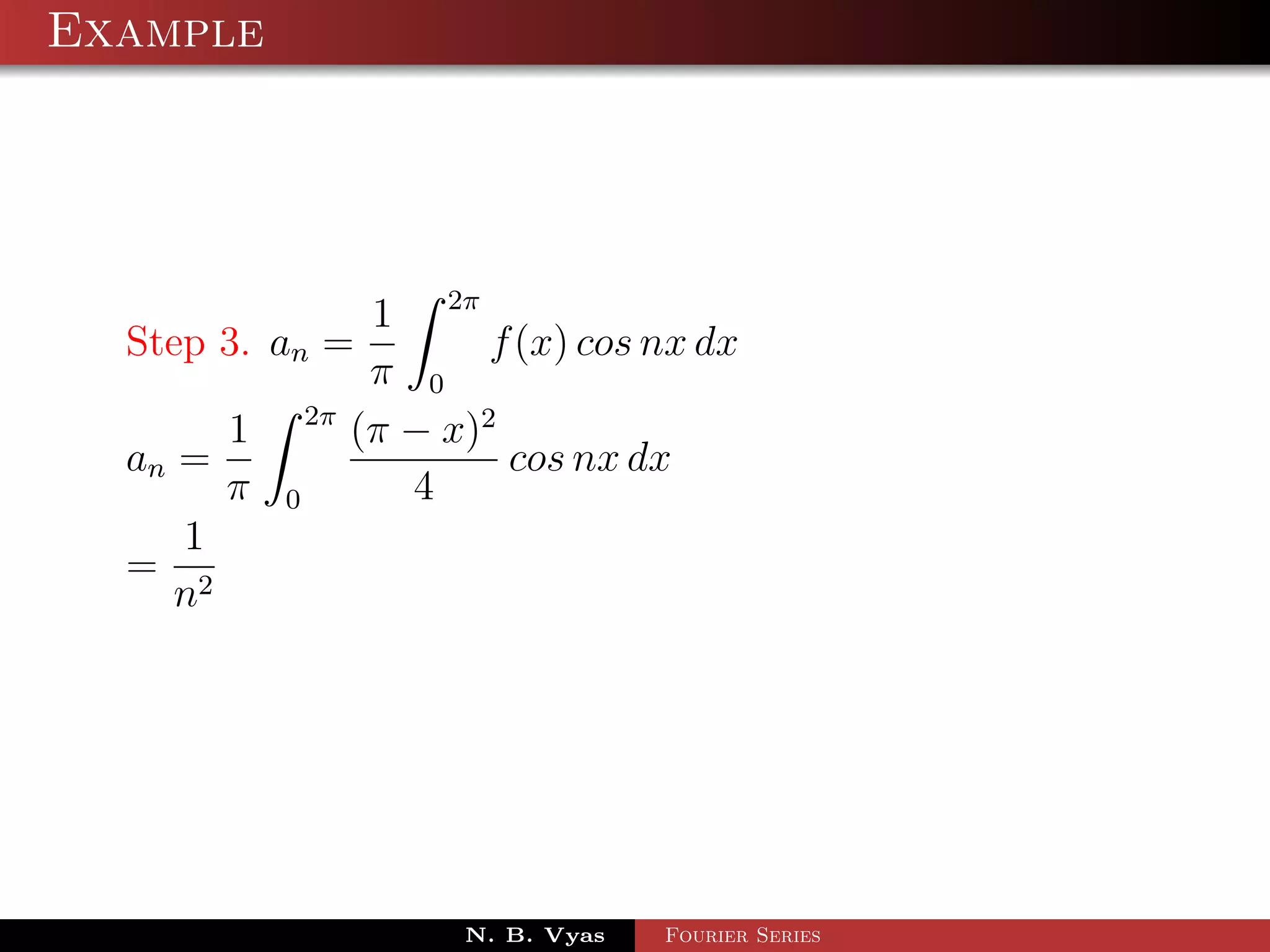



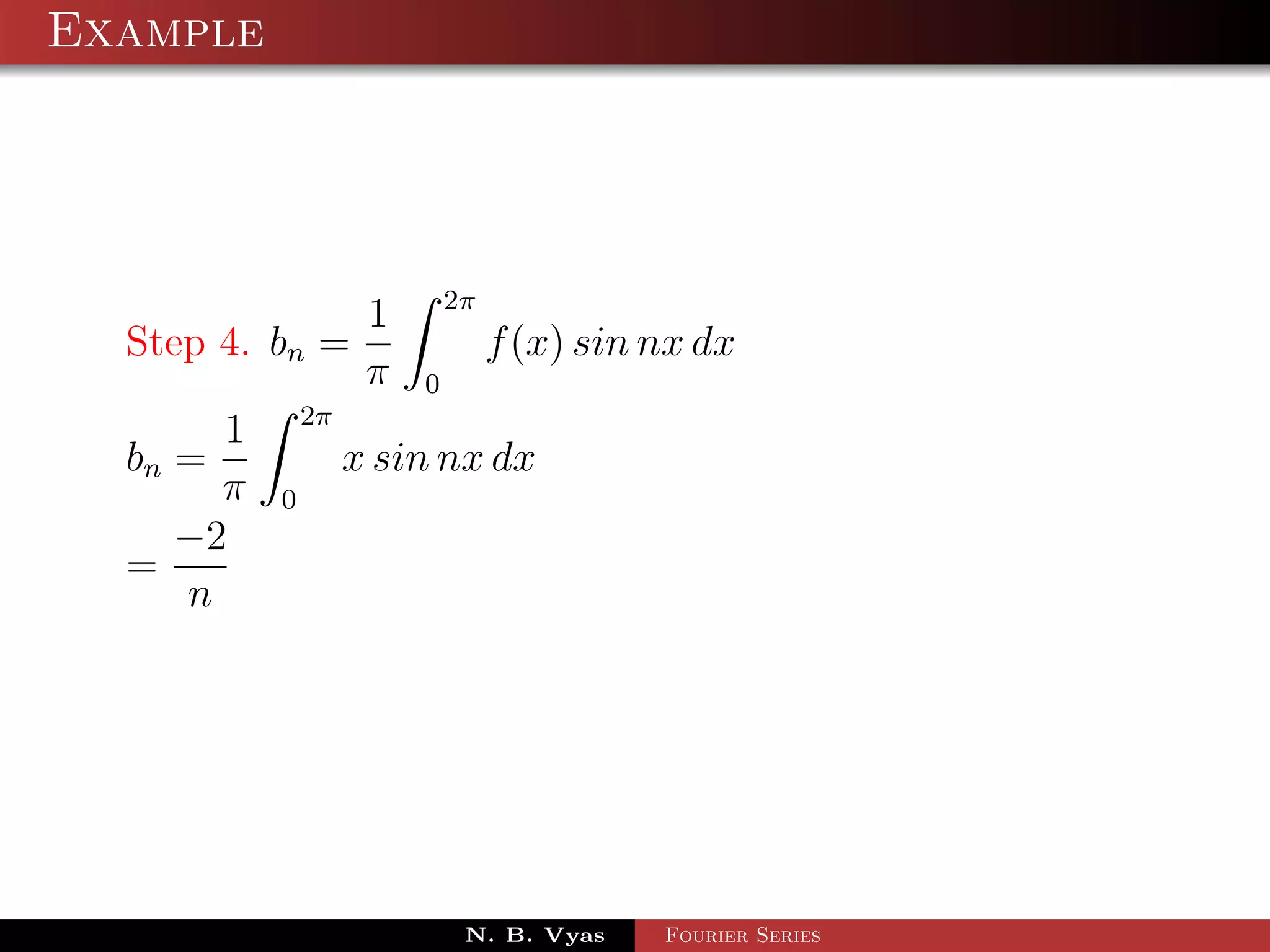
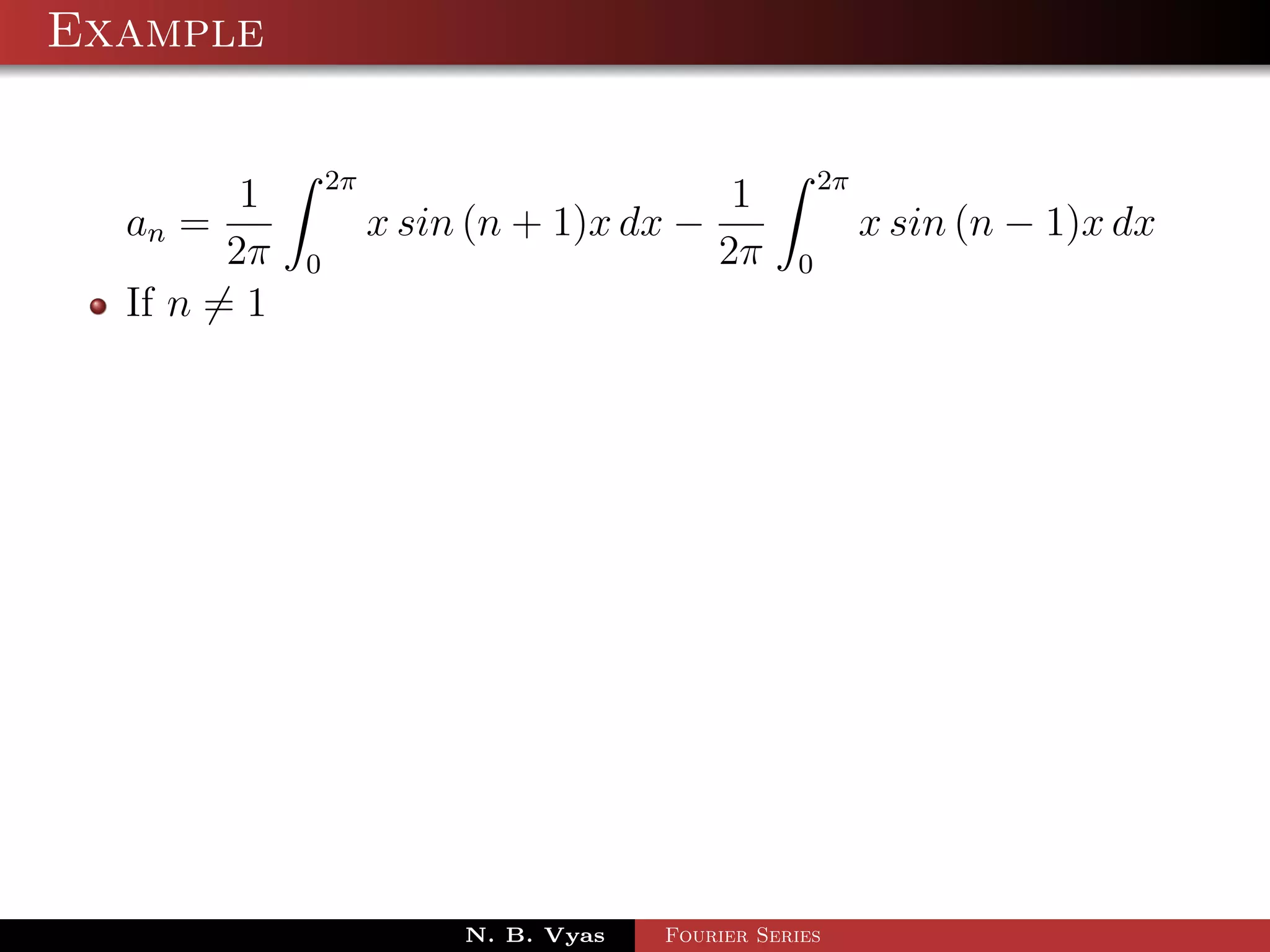
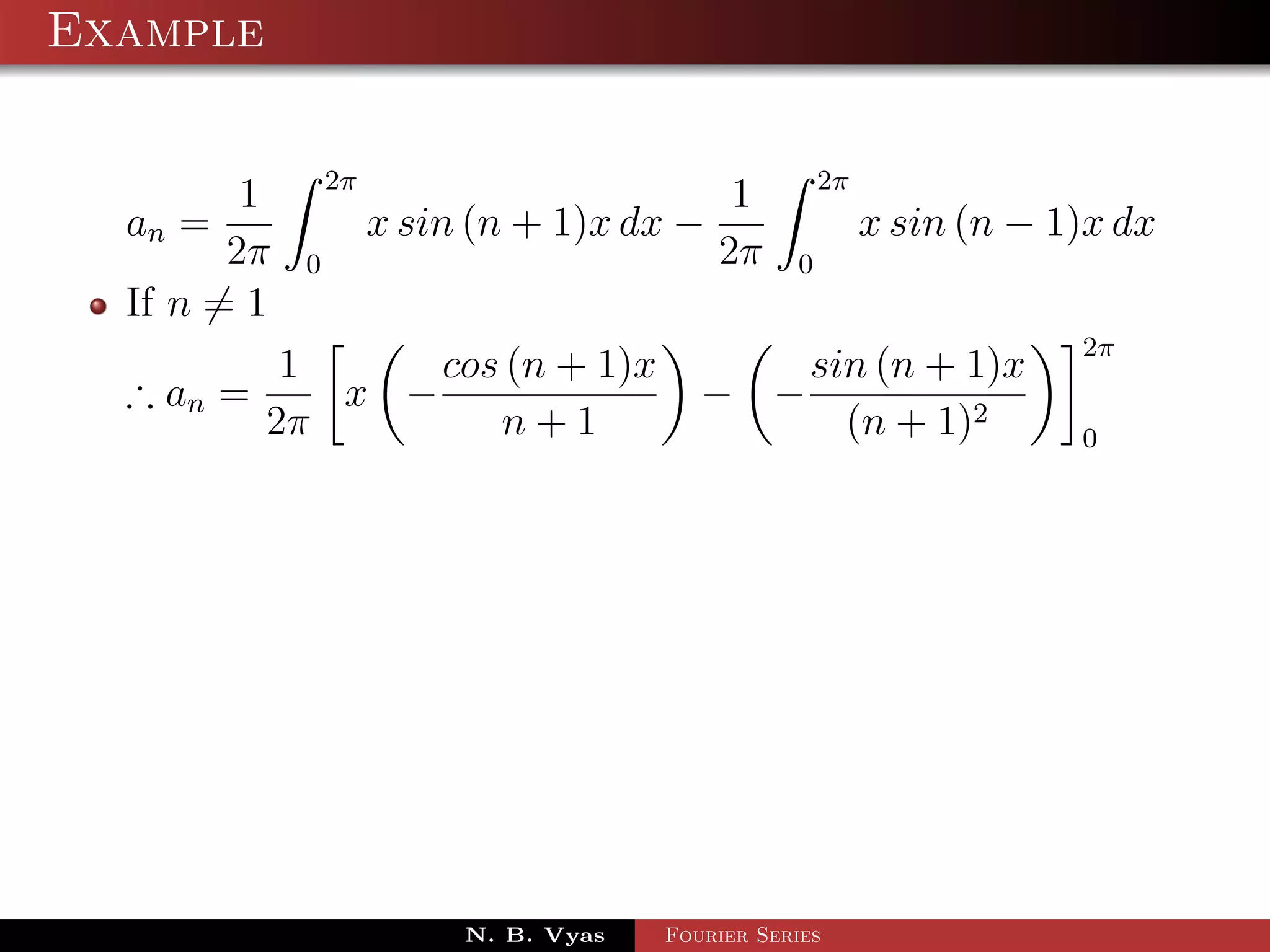
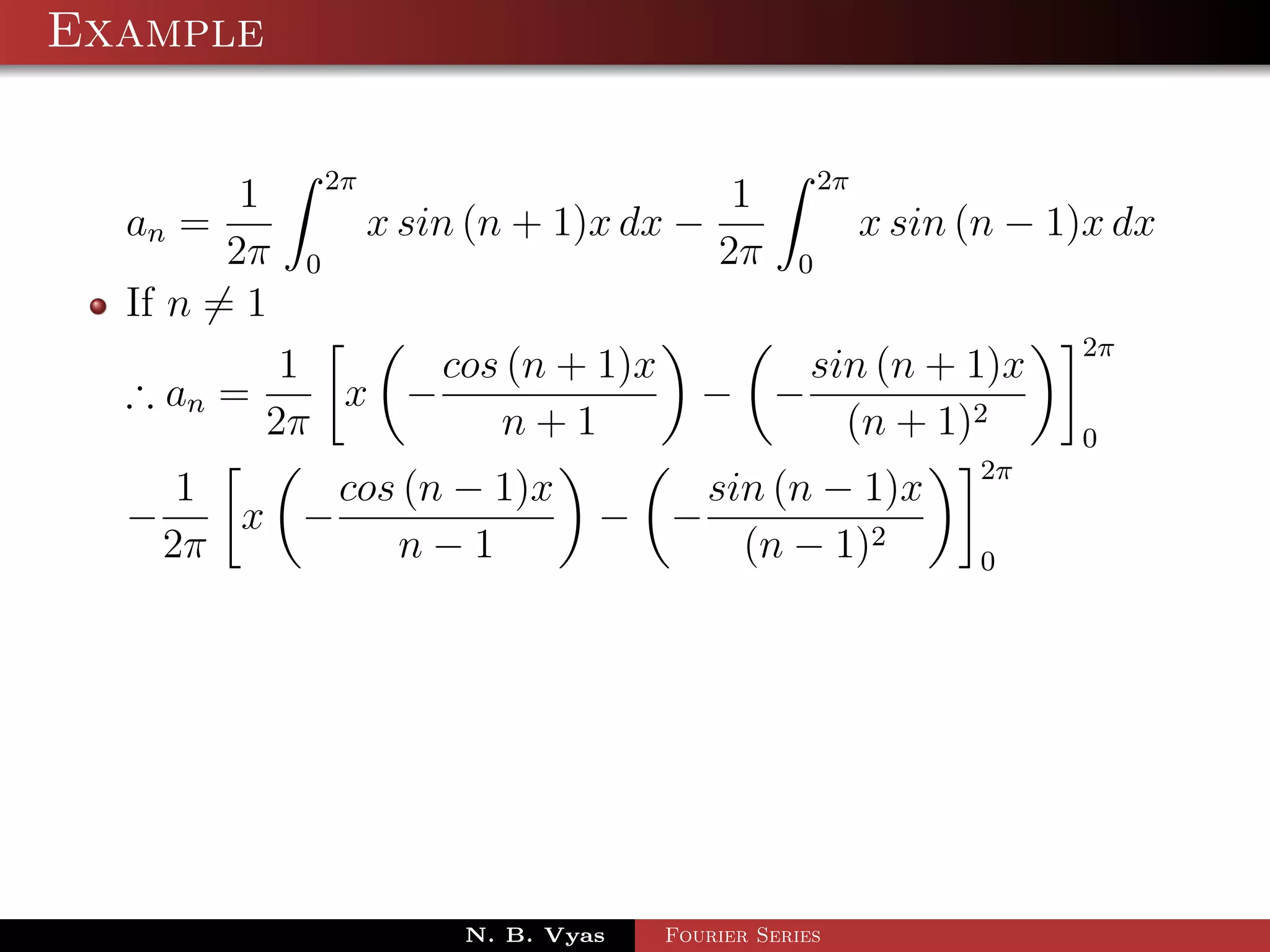
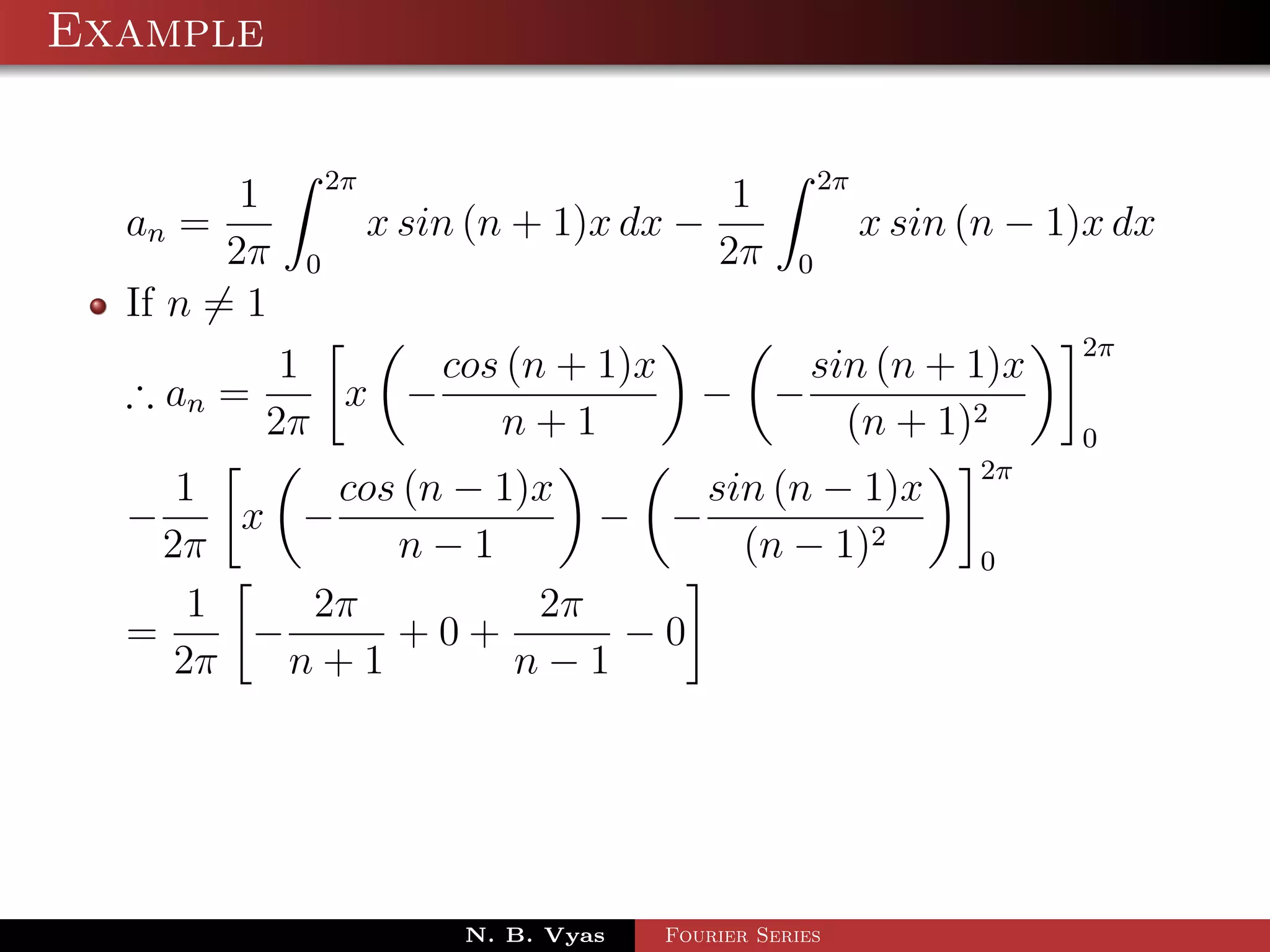
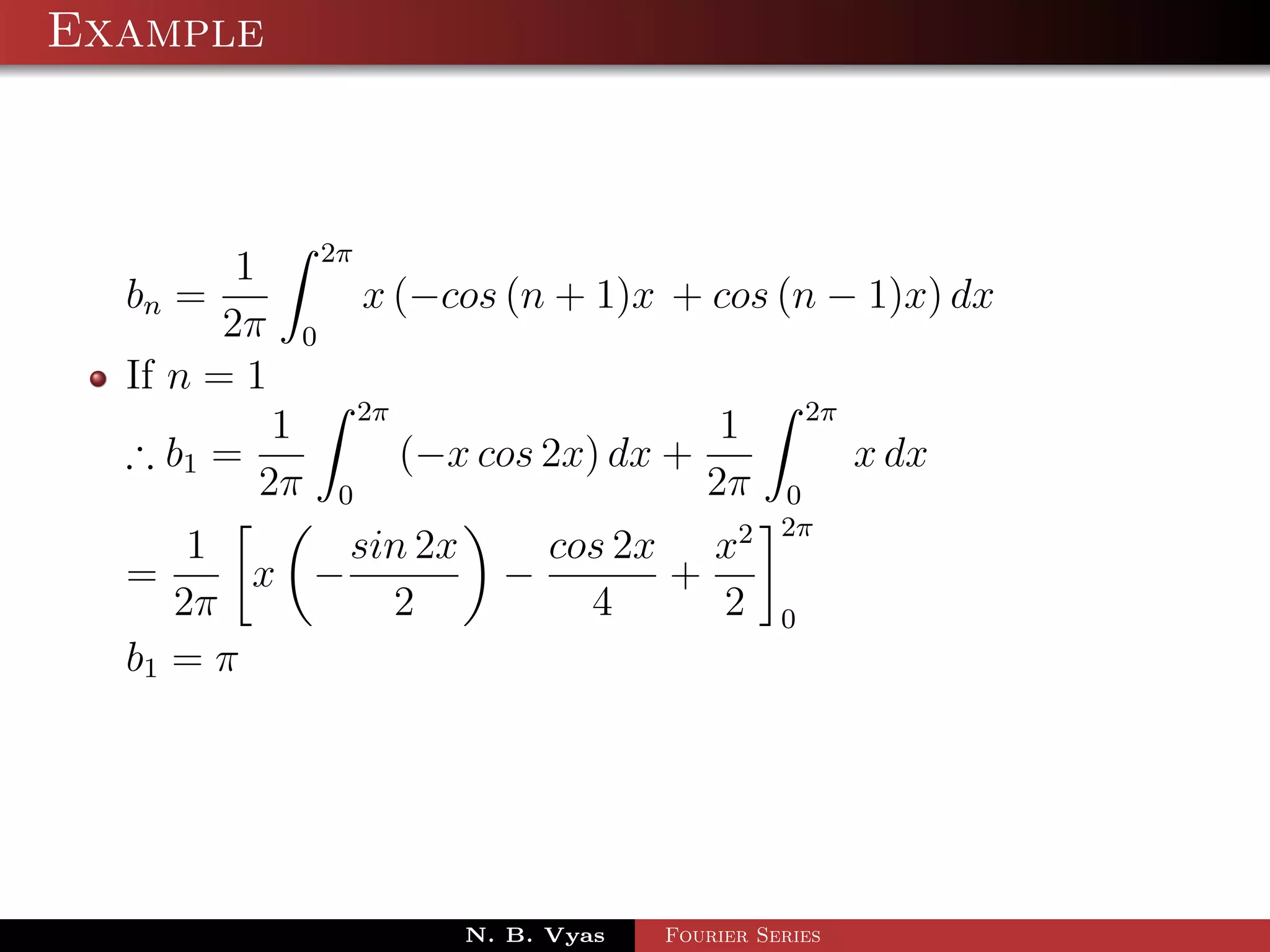
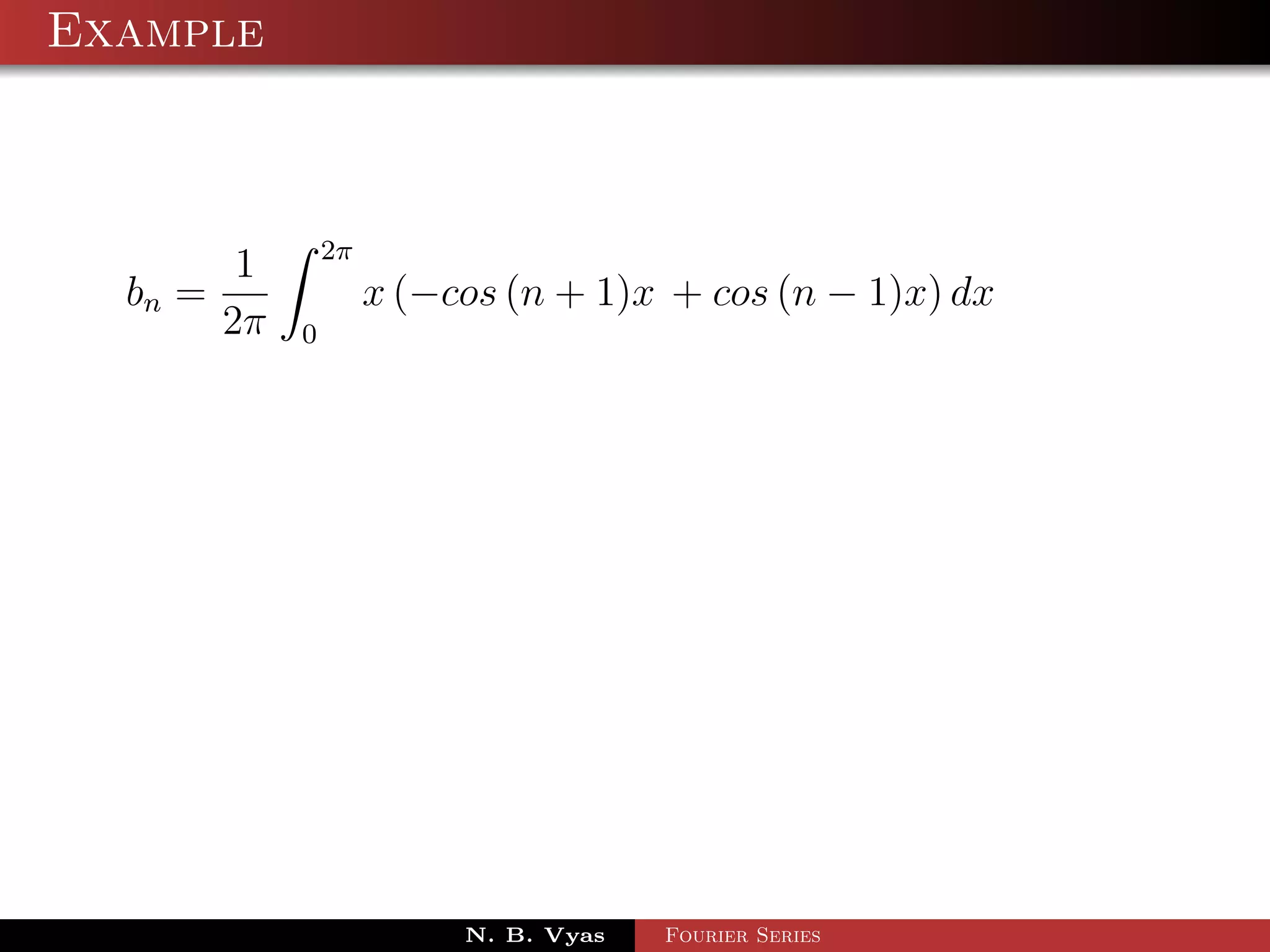
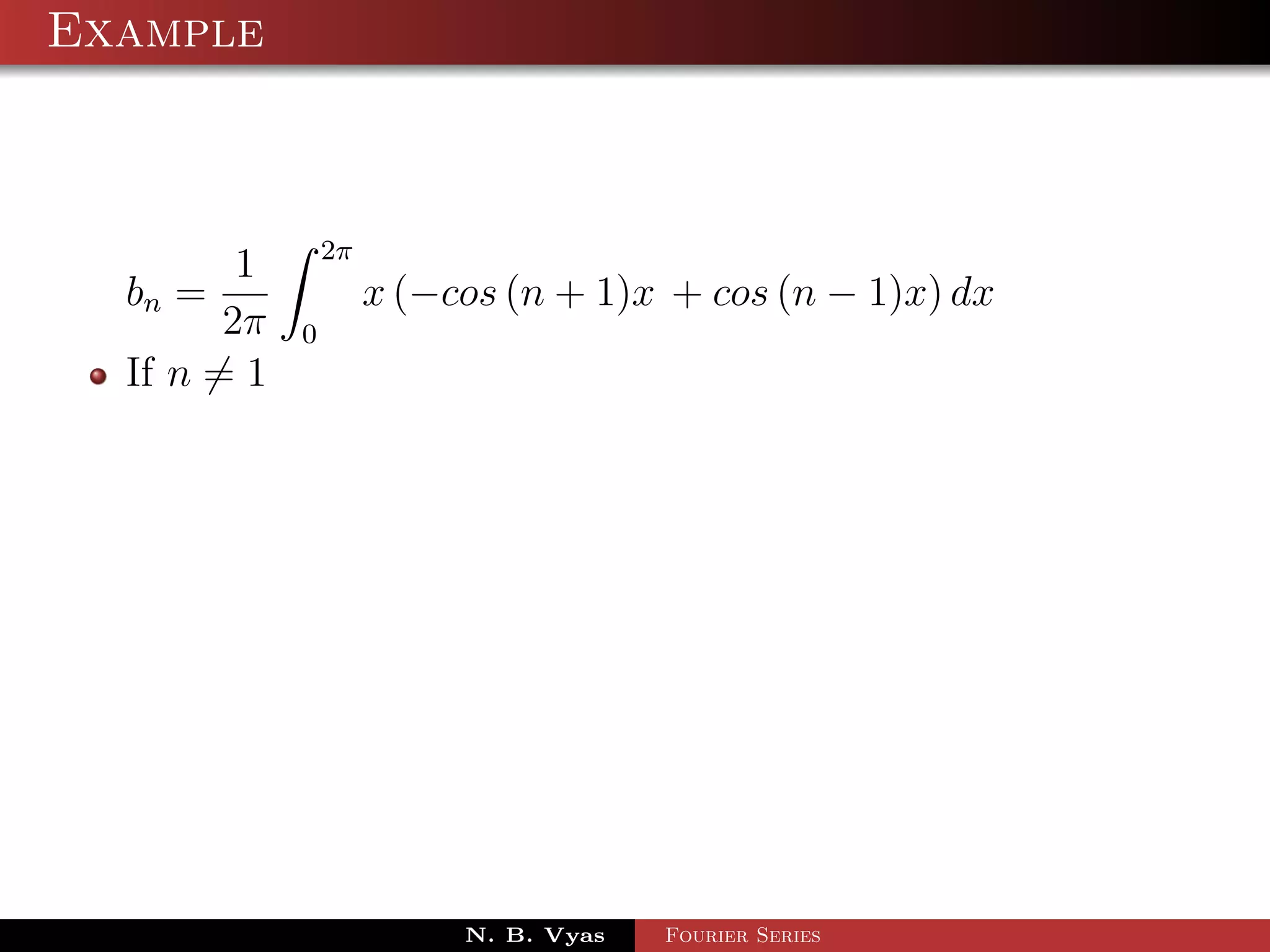
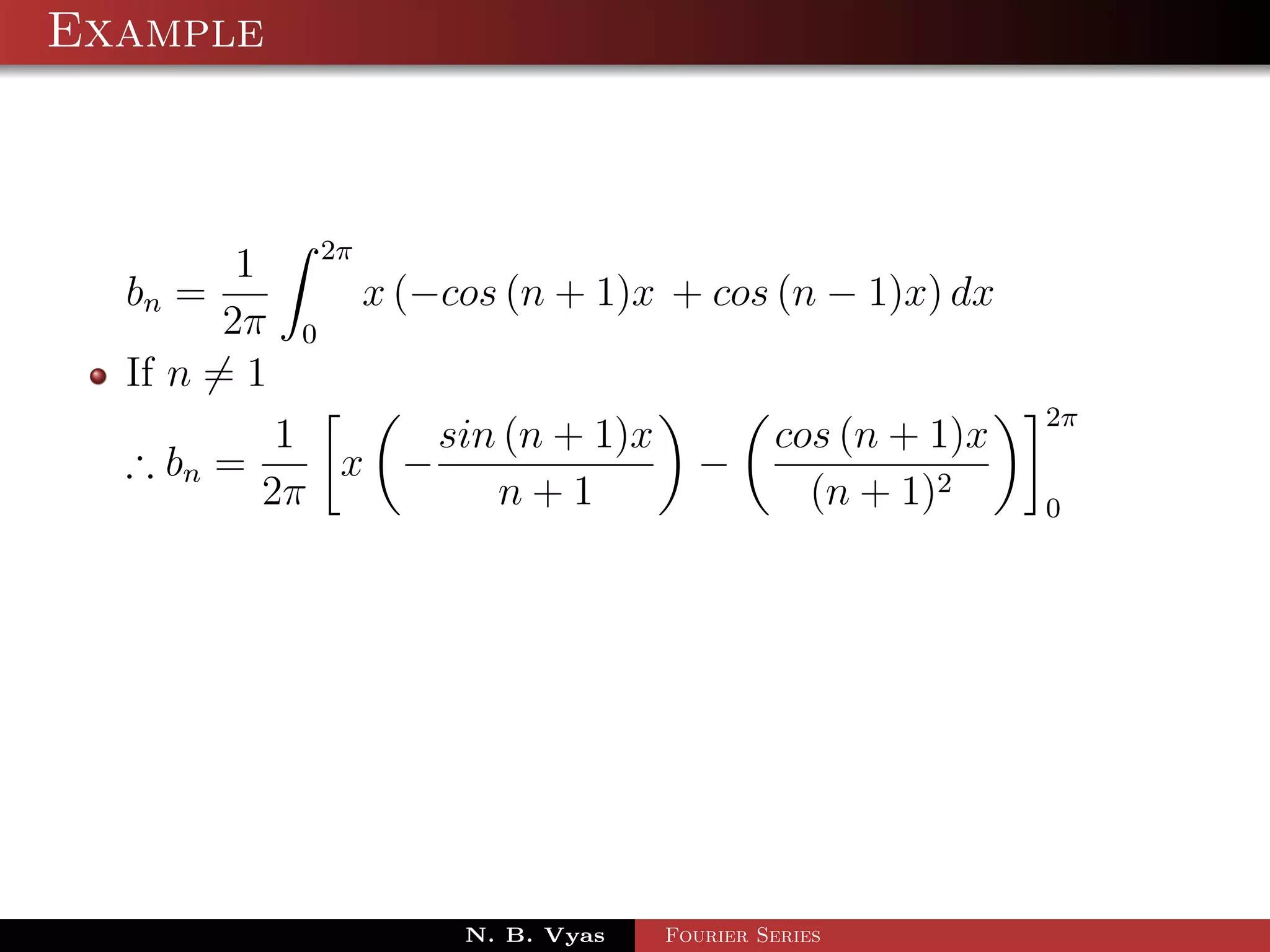
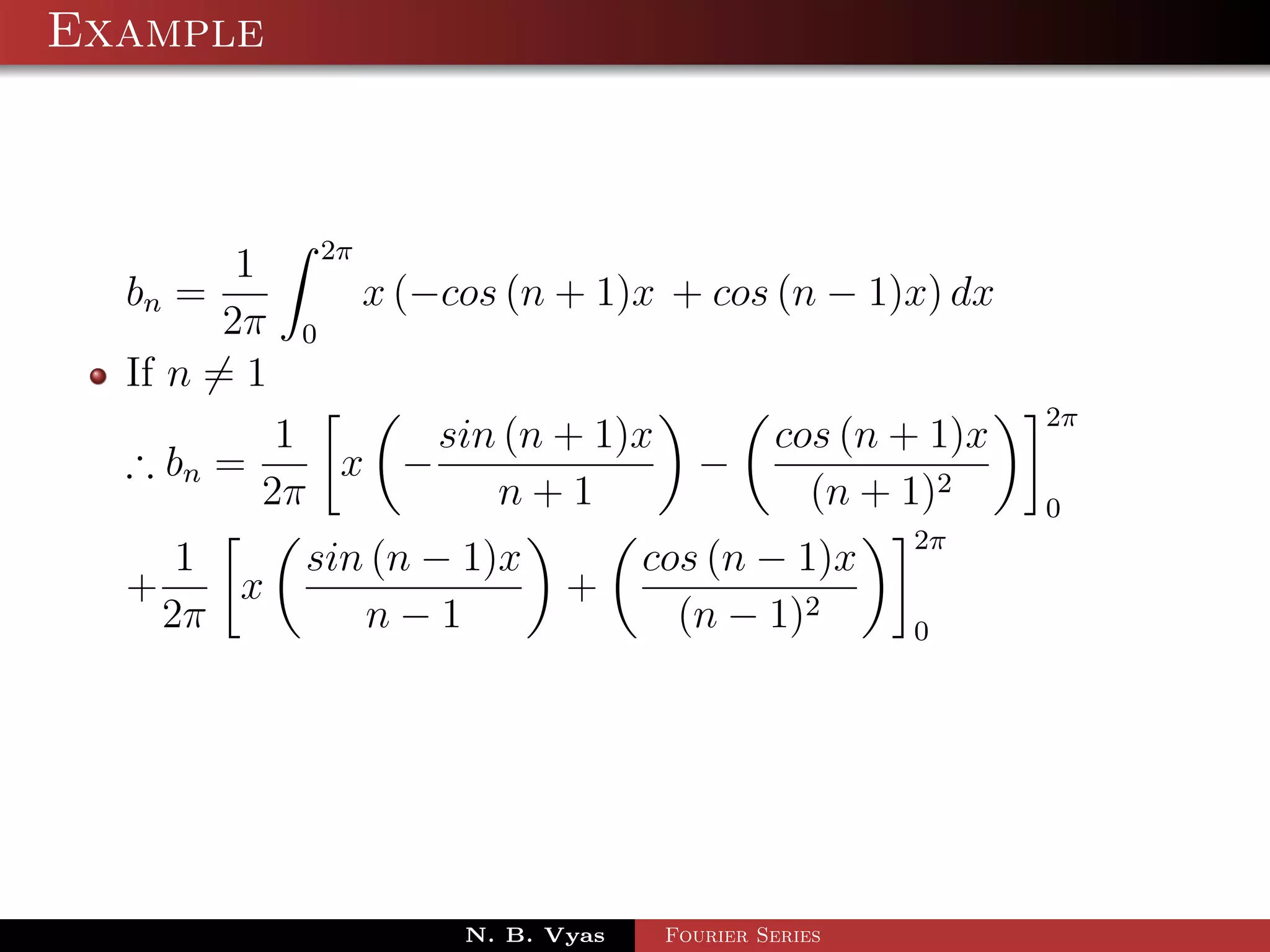
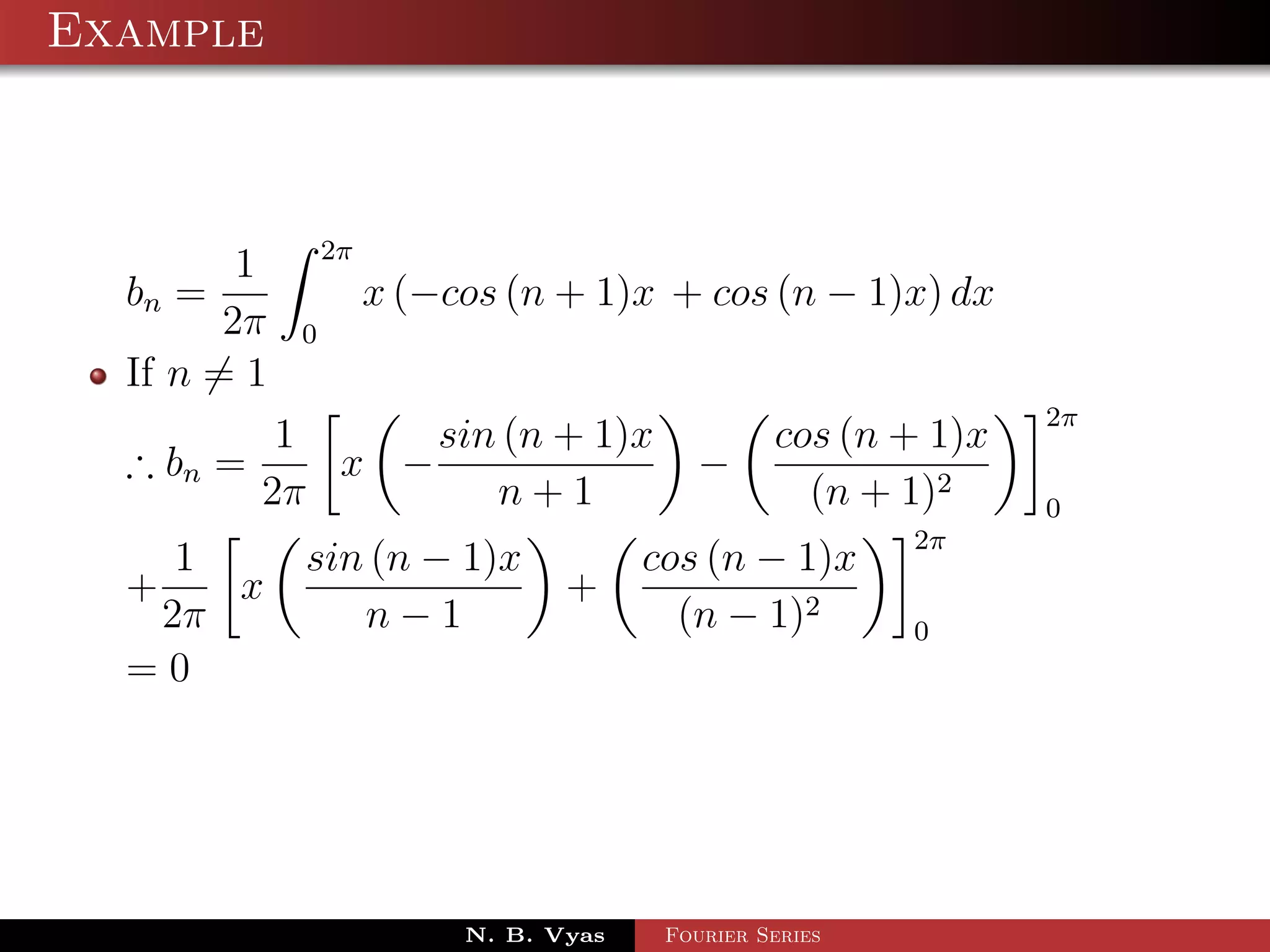
![Example
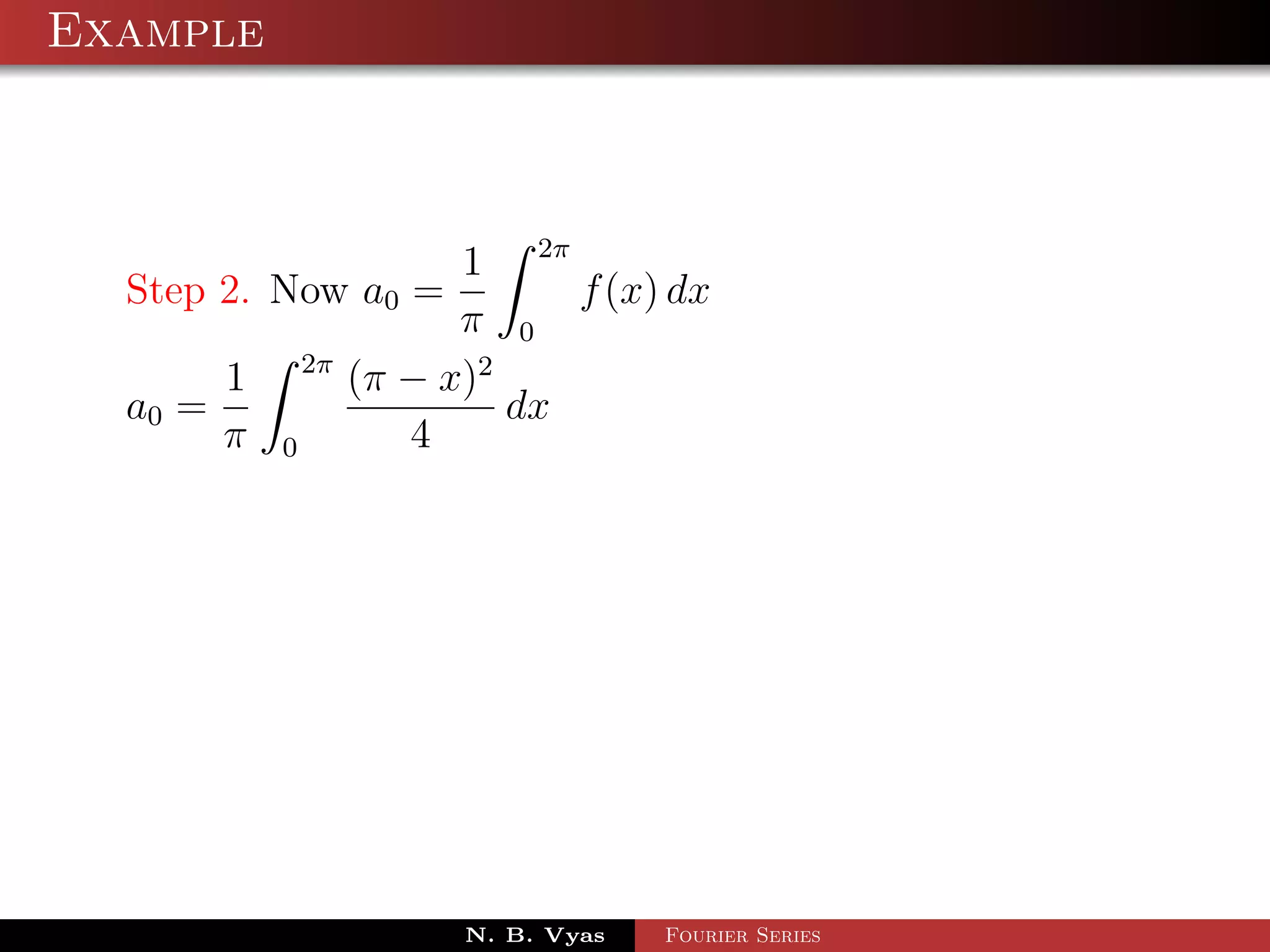
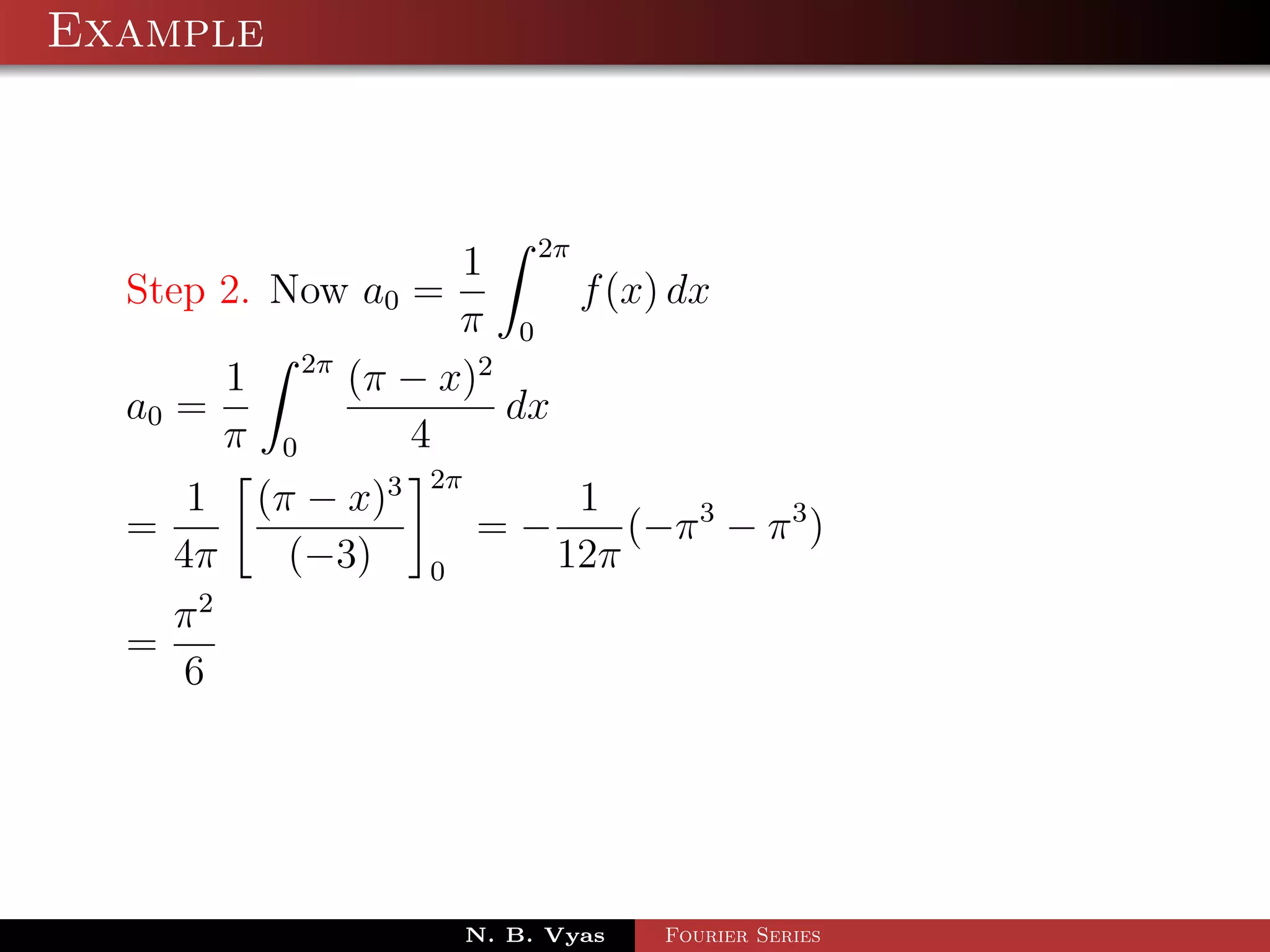
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-88-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
2 ∞
π−x π2 1
= + cos nx
2 12 n=1 n2
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-89-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
2 ∞
π−x π2 1
= + cos nx
2 12 n=1 n2
π2 1 1 1
= + 2 cos x + 2 cos 2x + 2 cos 3x + . . .
12 1 2 3
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-90-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
2 ∞
π−x π2 1
= + cos nx
2 12 n=1 n2
π2 1 1 1
= + 2 cos x + 2 cos 2x + 2 cos 3x + . . .
12 1 2 3
Putting x = π, we get
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-91-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
2 ∞
π−x π2 1
= + cos nx
2 12 n=1 n2
π2 1 1 1
= + 2 cos x + 2 cos 2x + 2 cos 3x + . . .
12 1 2 3
Putting x = π, we get
π2 1 1 1 1
0= − 2 + 2 − 2 + 2 − ...
12 1 2 3 4
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-92-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
2 ∞
π−x π2 1
= + cos nx
2 12 n=1 n2
π2 1 1 1
= + 2 cos x + 2 cos 2x + 2 cos 3x + . . .
12 1 2 3
Putting x = π, we get
π2 1 1 1 1
0= − 2 + 2 − 2 + 2 − ...
12 1 2 3 4
π2 1 1 1 1
= 2 − 2 + 2 − 2 + ...
12 1 2 3 4
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-93-2048.jpg)








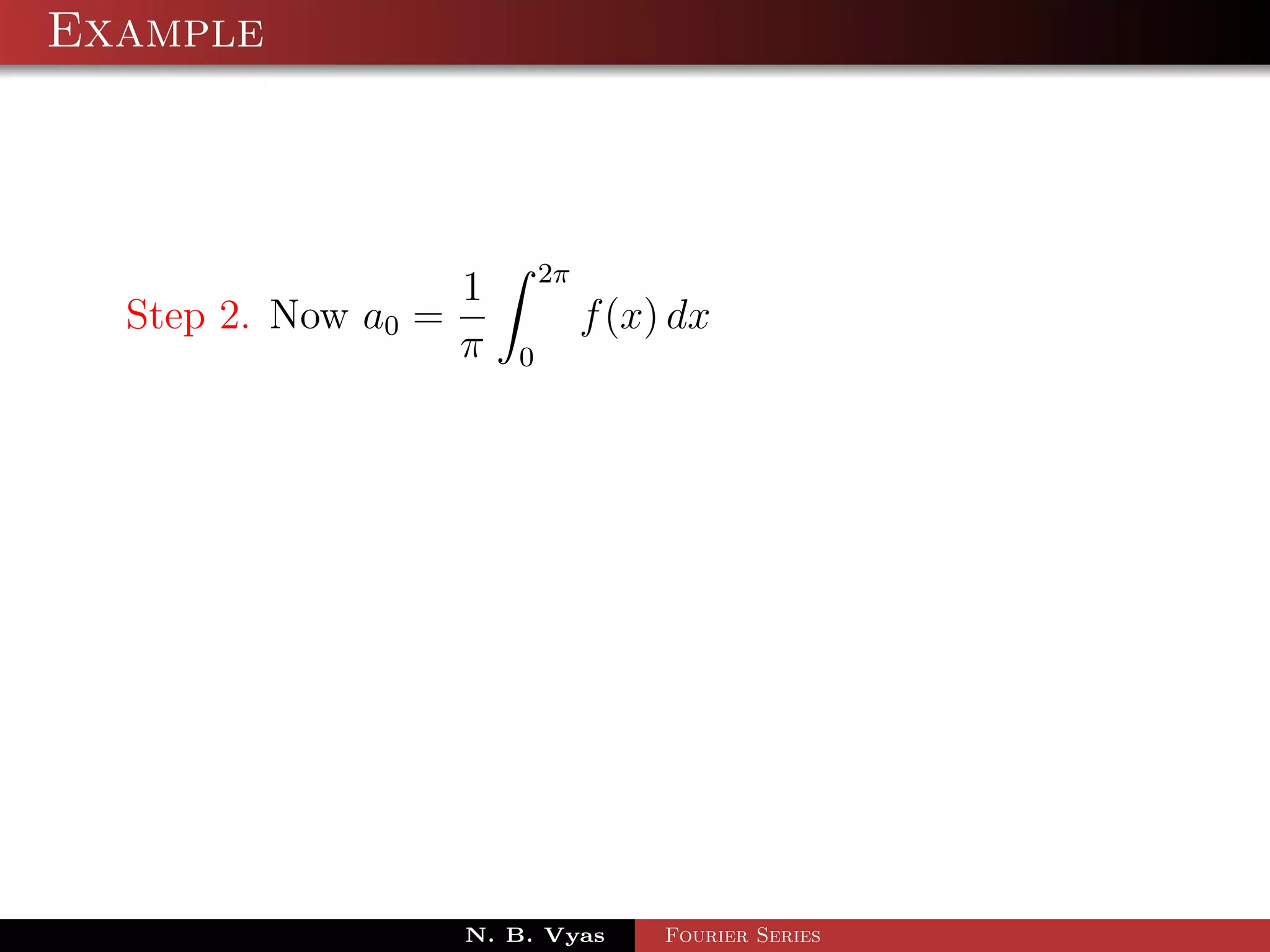

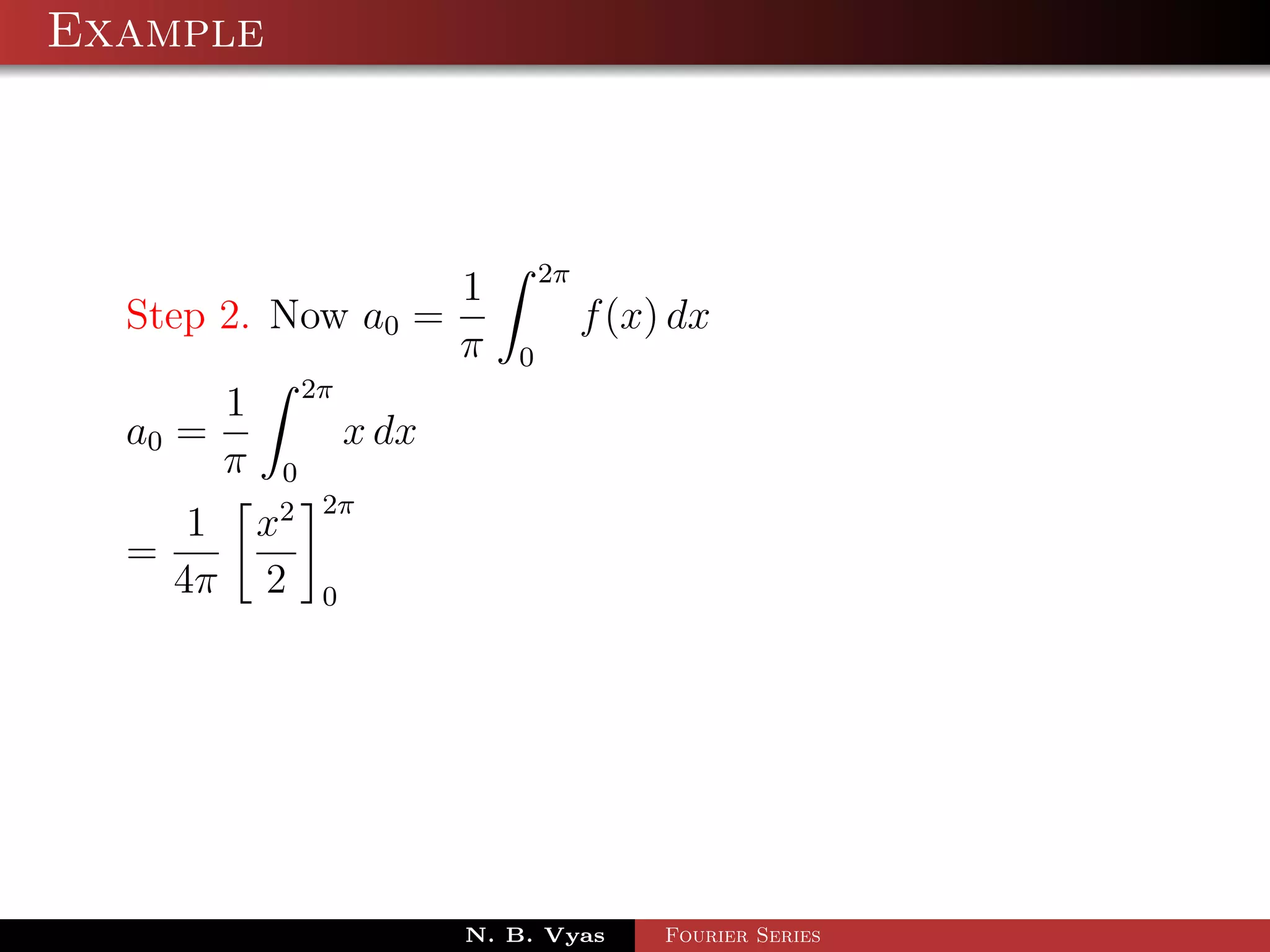
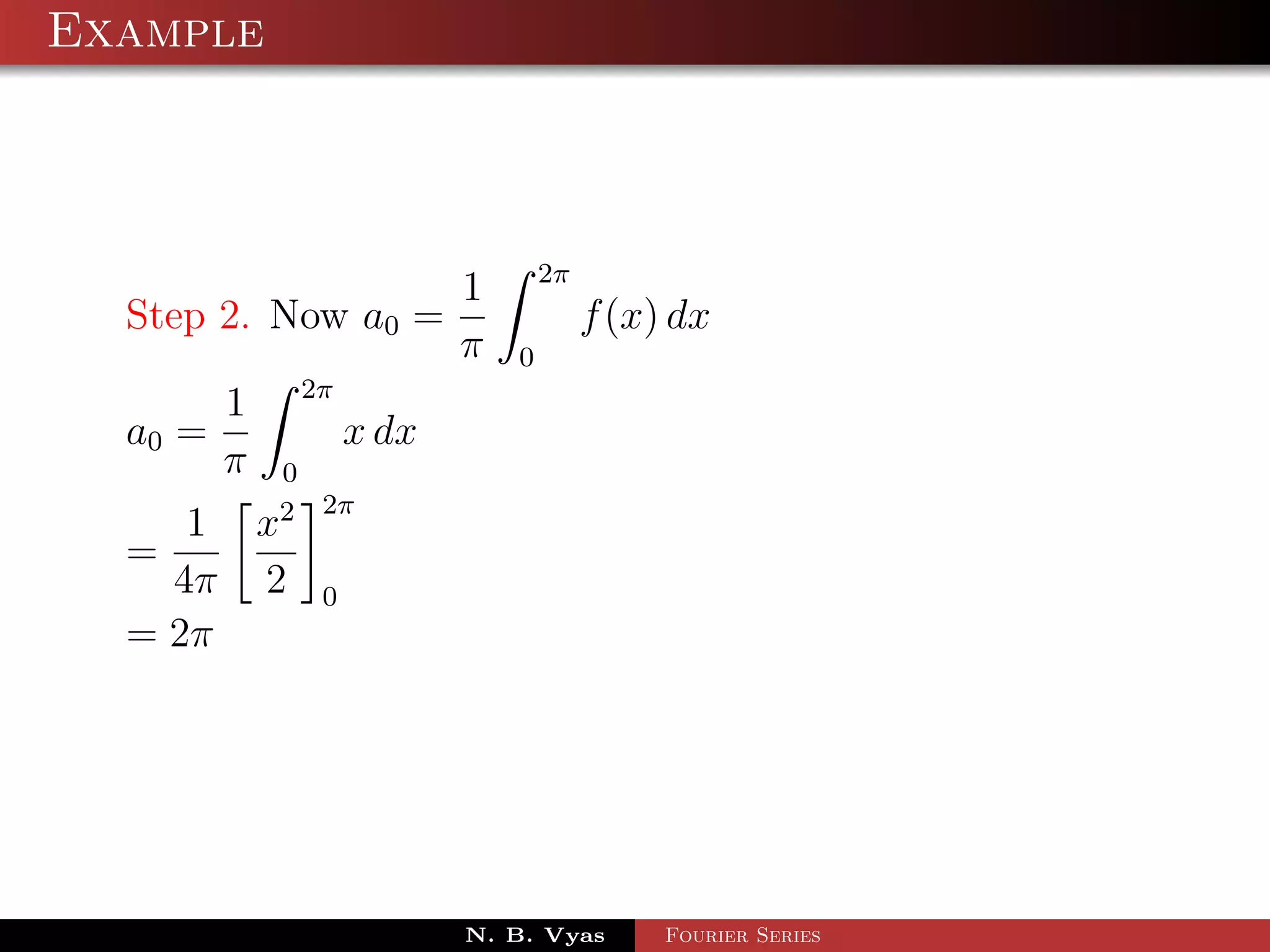






![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-113-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
∞
2π −2
f (x) = +0+ sin nx
2 n=1
n
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-114-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
∞
2π −2
f (x) = +0+ sin nx
2 n=1
n
∞
sin nx
=π−
n=1
n
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-115-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , an and bn in (1), we get the
required Fourier series of f (x) in the interval [0, 2π]
∞
2π −2
f (x) = +0+ sin nx
2 n=1
n
∞
sin nx
=π−
n=1
n
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-116-2048.jpg)








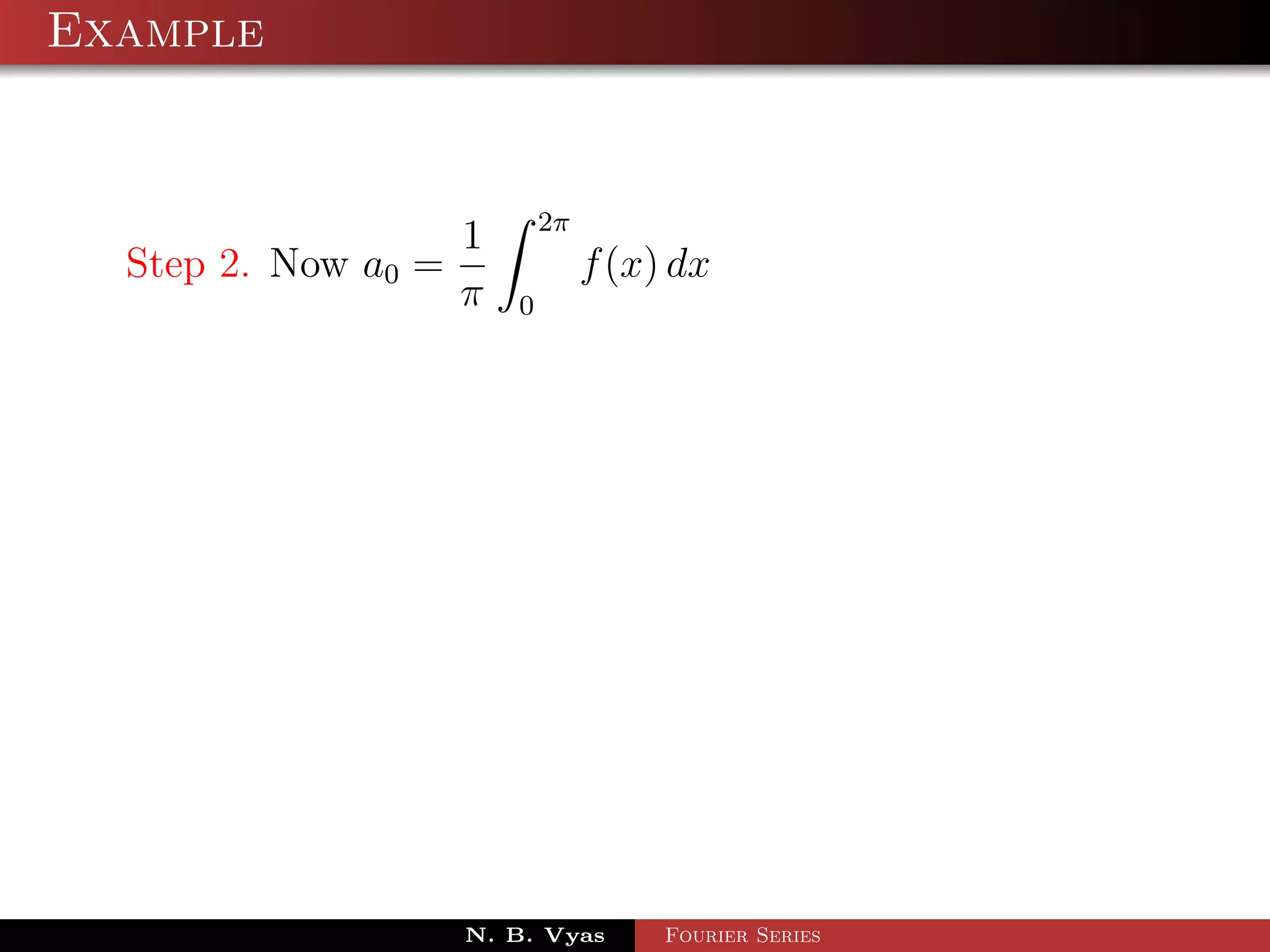

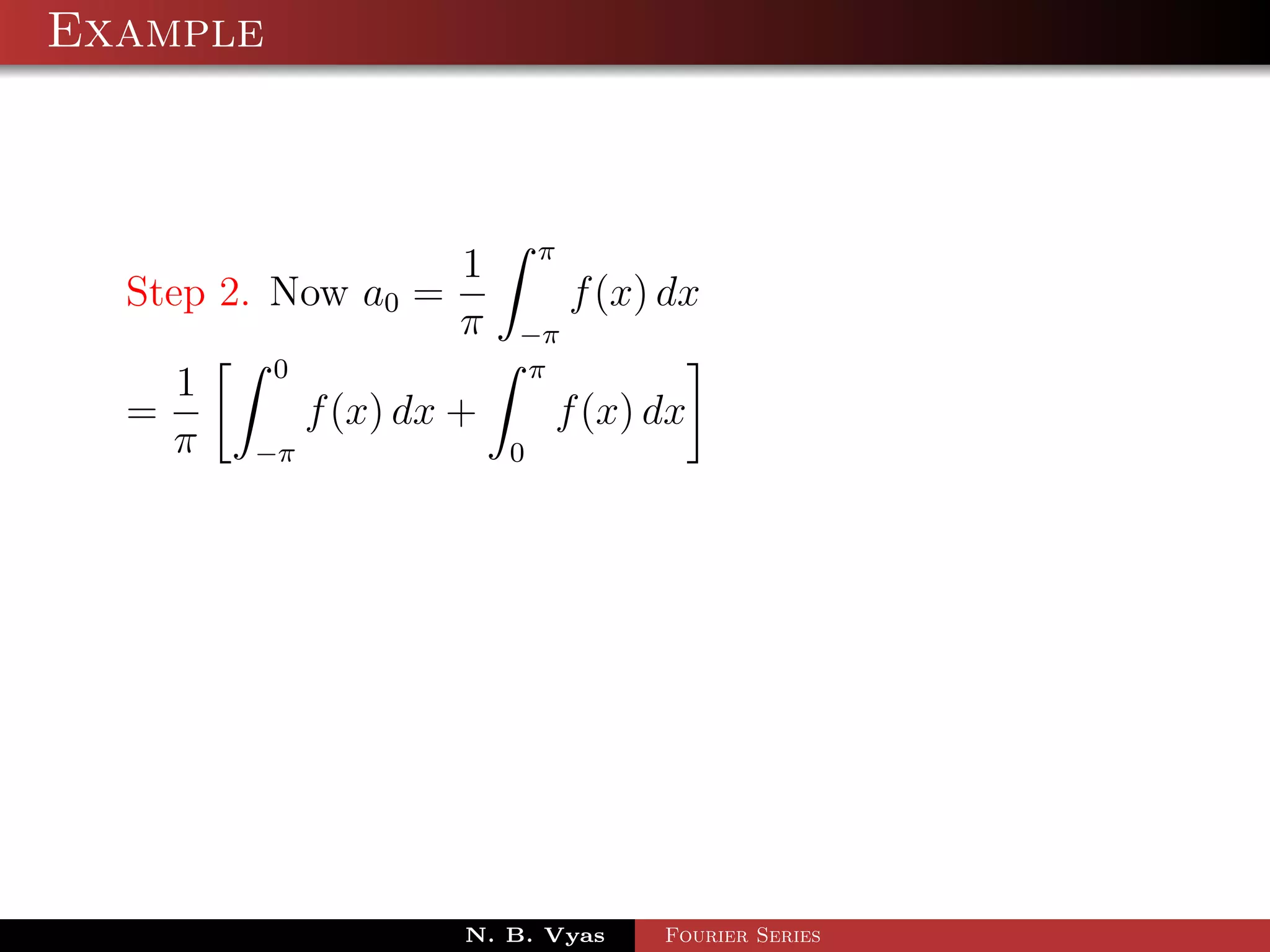
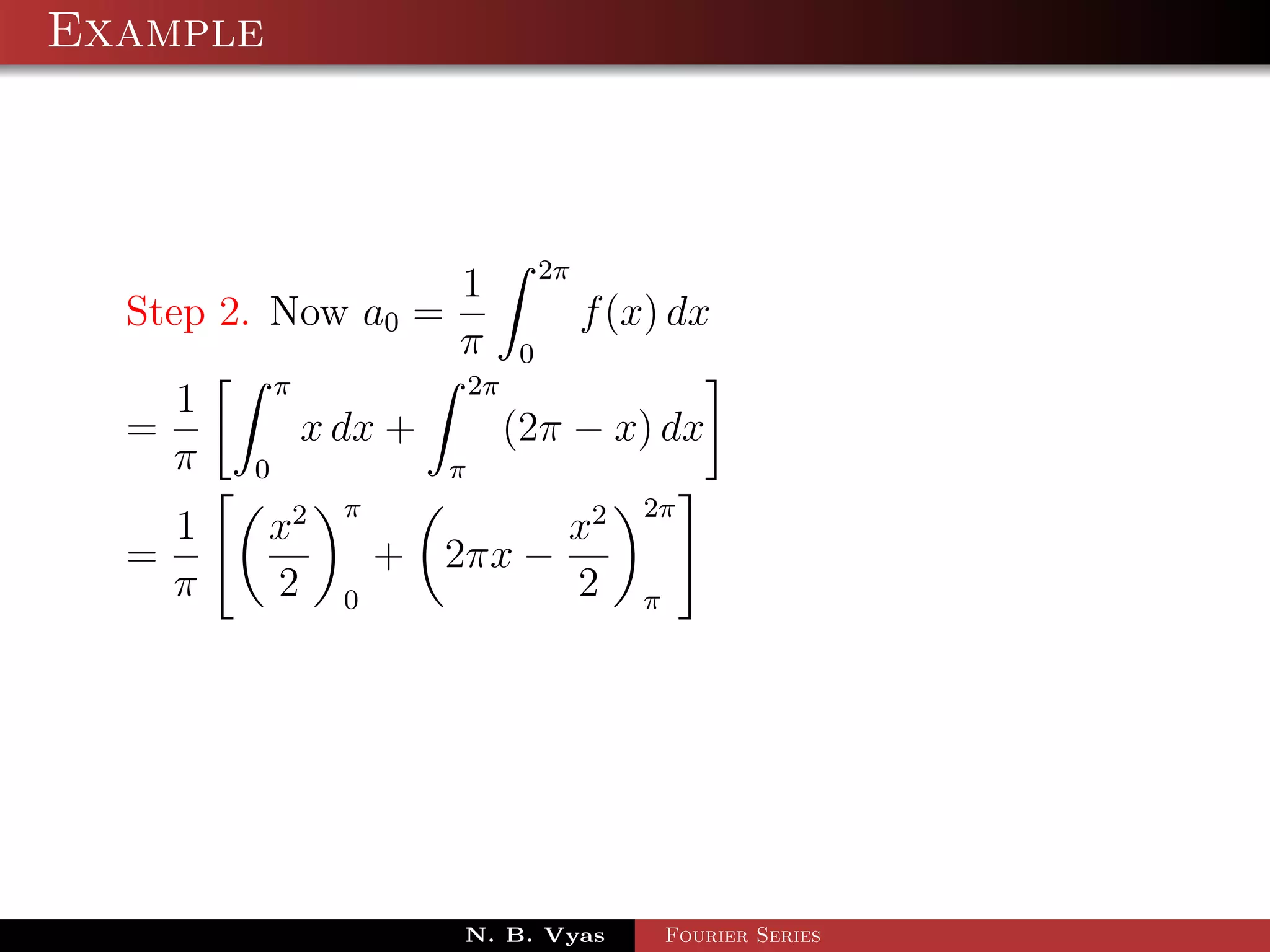
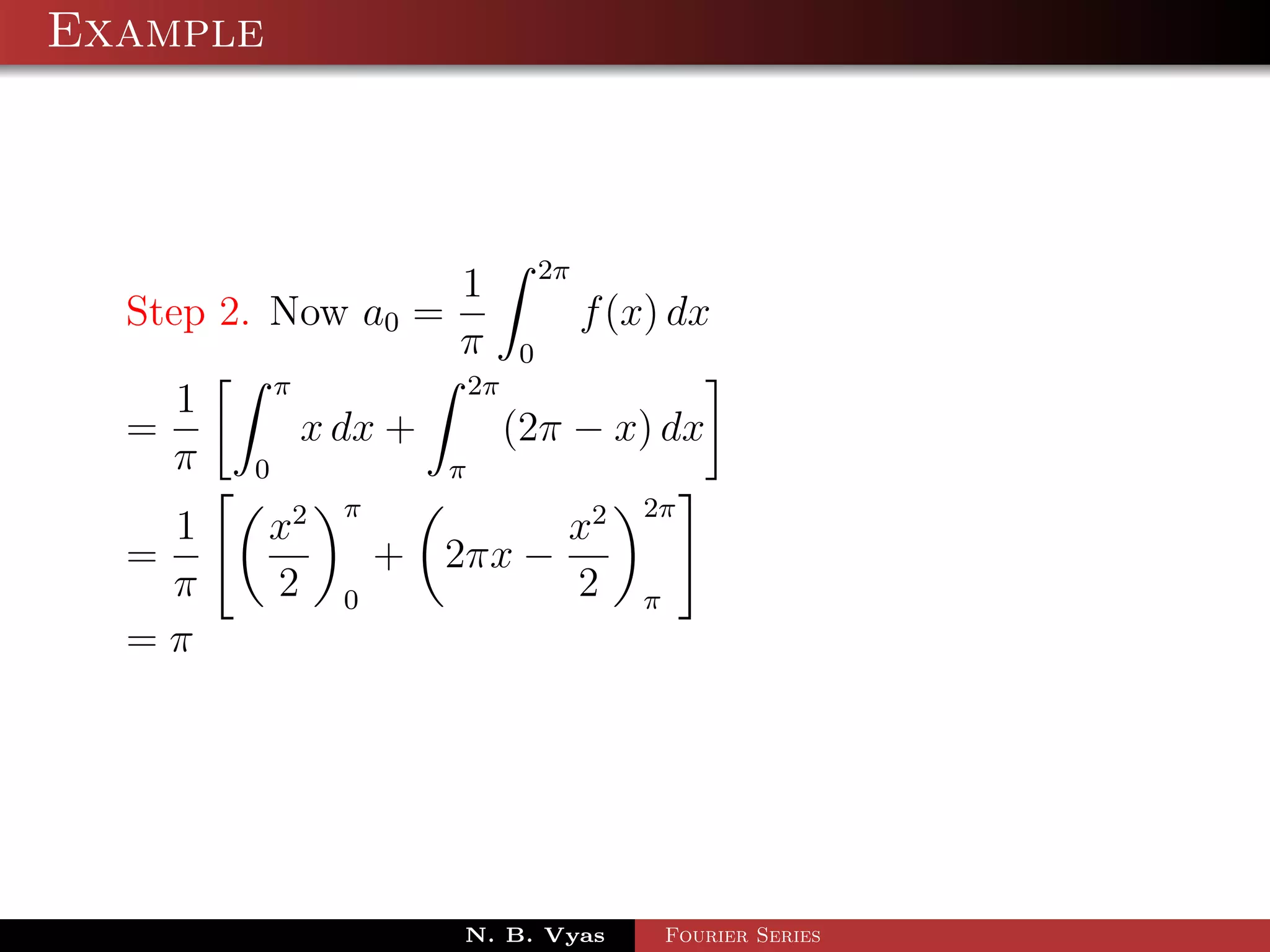
![Example
2π
1
Step 2. Now a0 = f (x) dx
π 0
1 2π
a0 = x sin x dx
π 0
1
= [−x cos x + sin x]2π
0
π
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-127-2048.jpg)
![Example
2π
1
Step 2. Now a0 = f (x) dx
π 0
1 2π
a0 = x sin x dx
π 0
1
= [−x cos x + sin x]2π
0
π
1
= (−2 π cos 2π + sin 2π − 0 + sin 0)
π
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-128-2048.jpg)
![Example
2π
1
Step 2. Now a0 = f (x) dx
π 0
1 2π
a0 = x sin x dx
π 0
1
= [−x cos x + sin x]2π
0
π
1
= (−2 π cos 2π + sin 2π − 0 + sin 0)
π
−2π
a0 = = −2
π
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-129-2048.jpg)





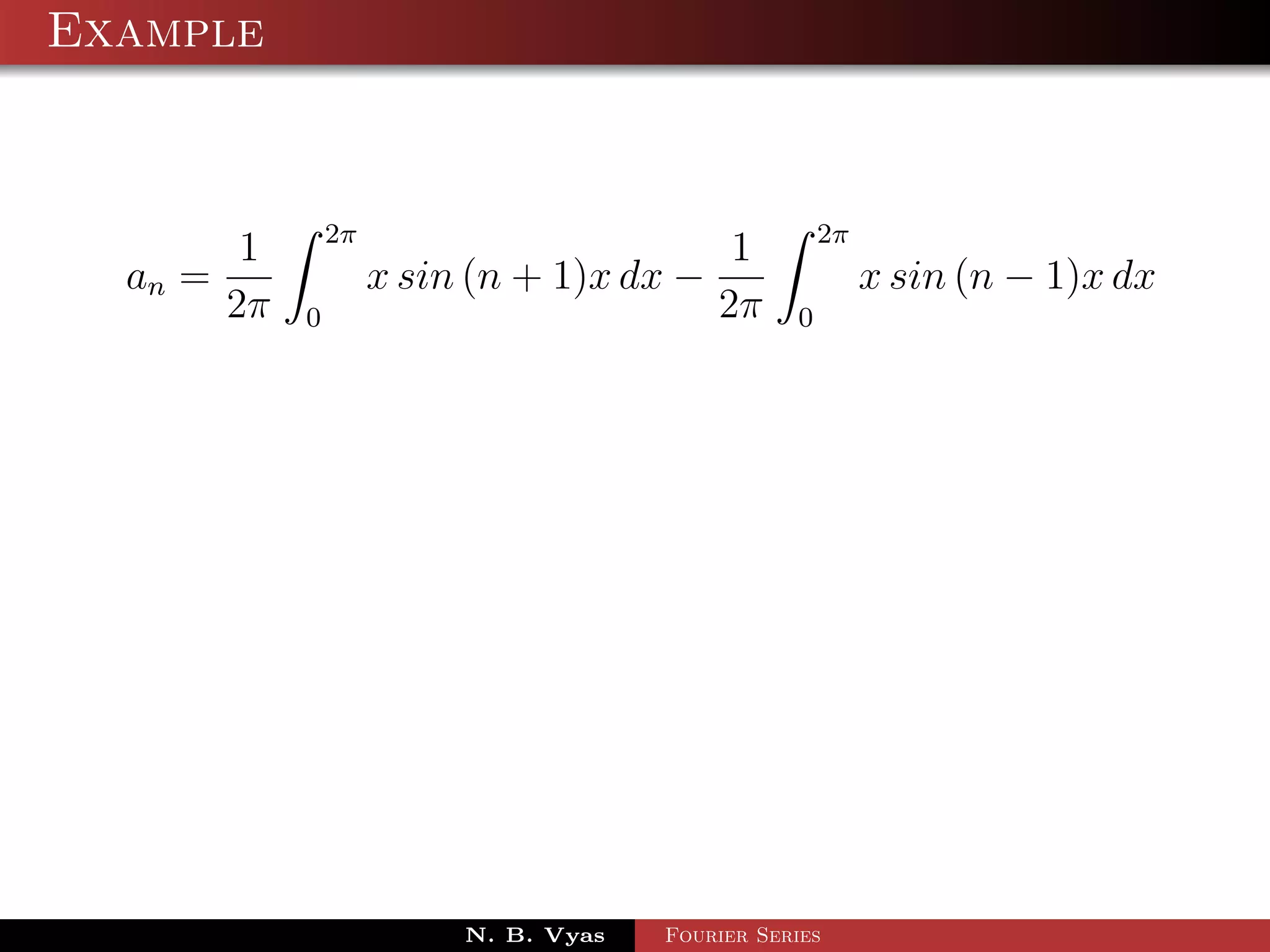
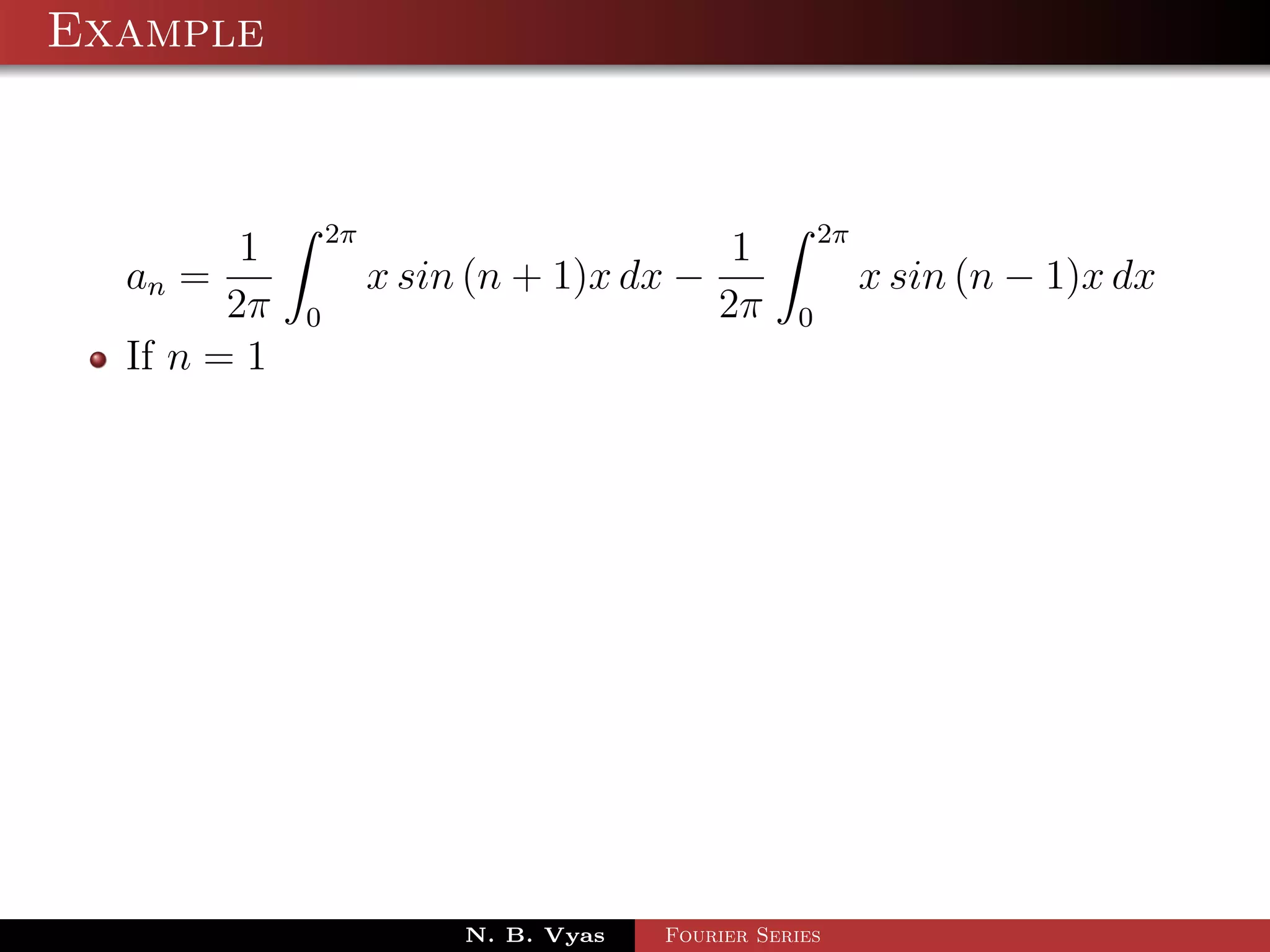
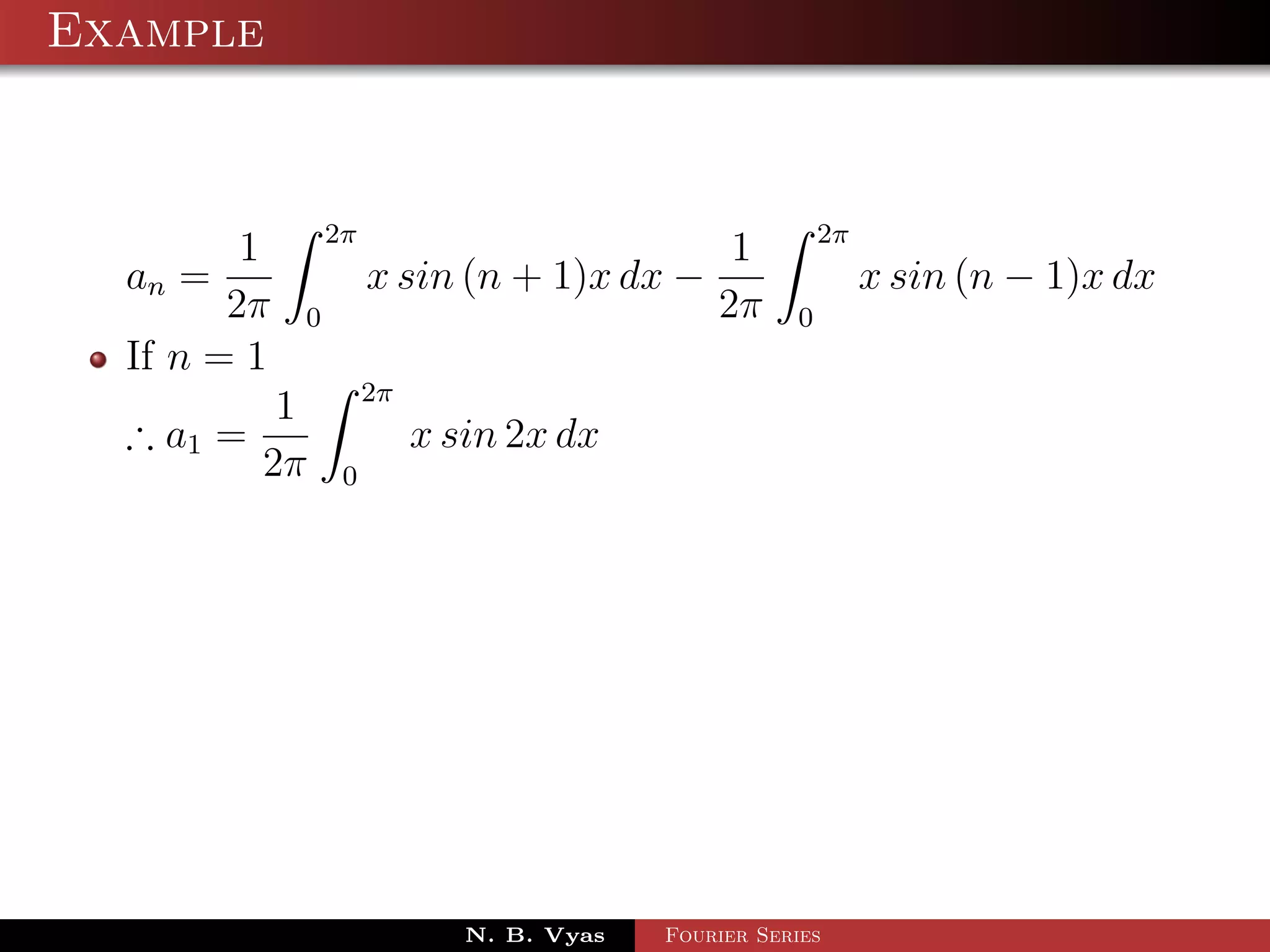
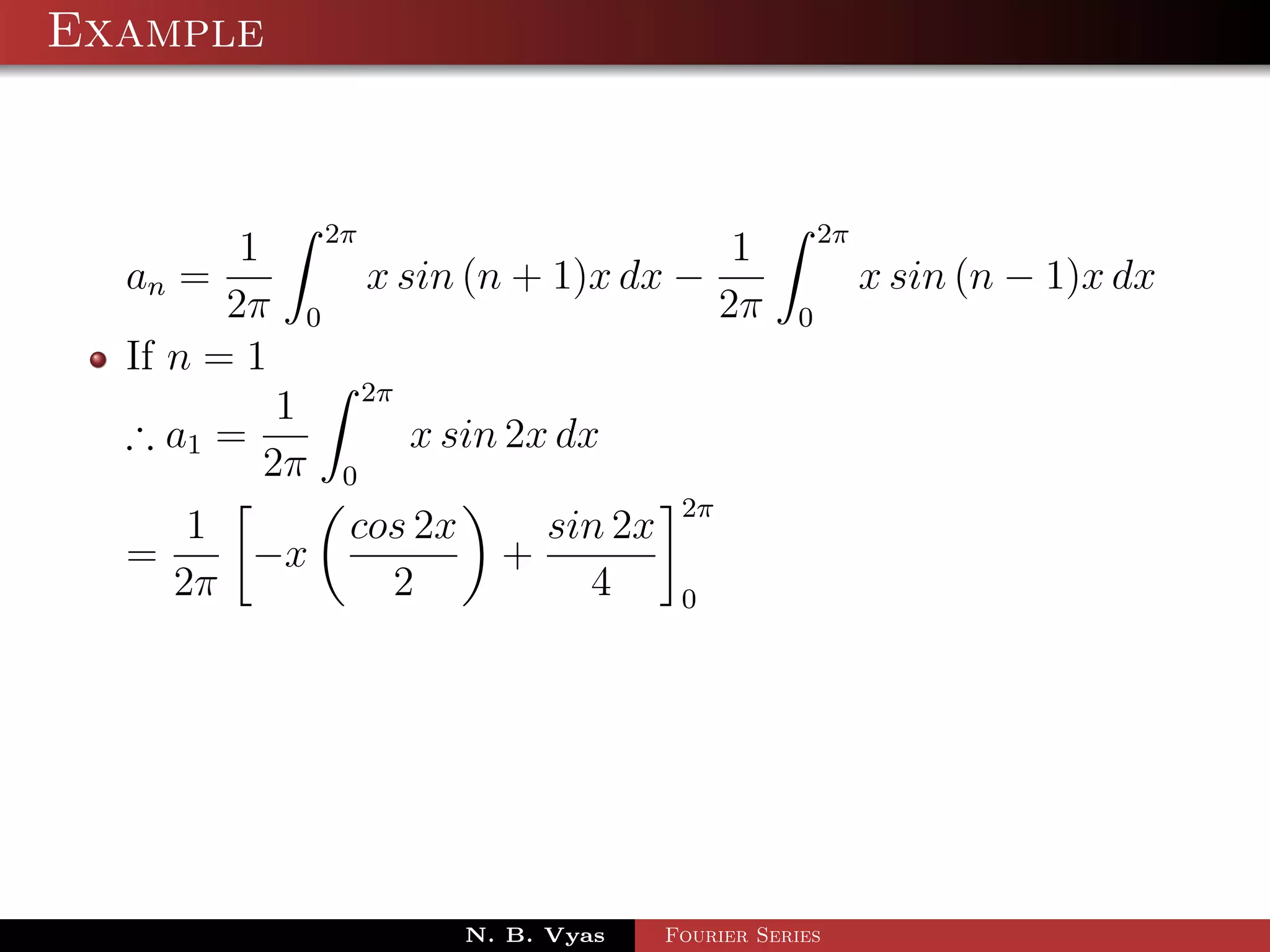
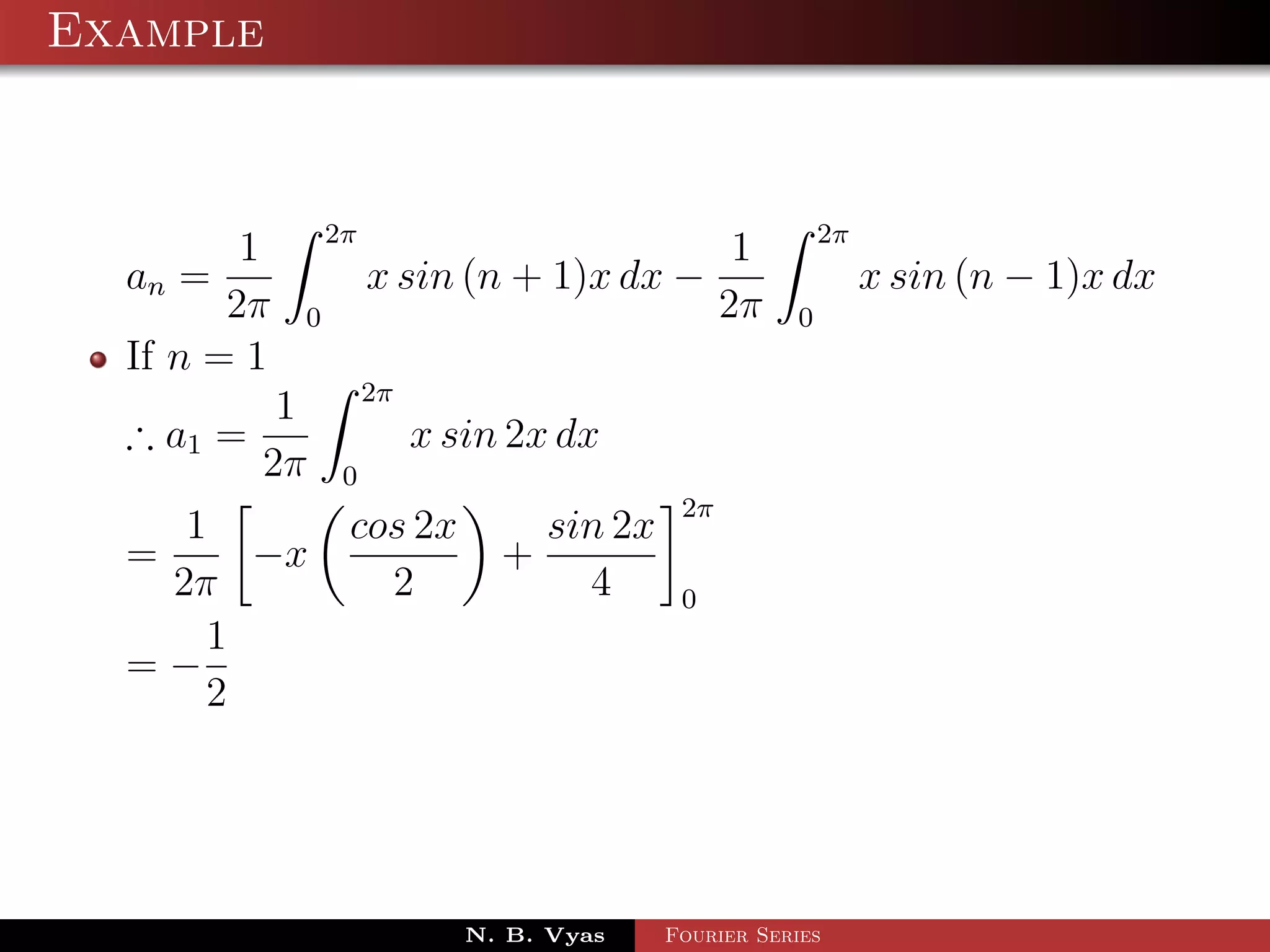
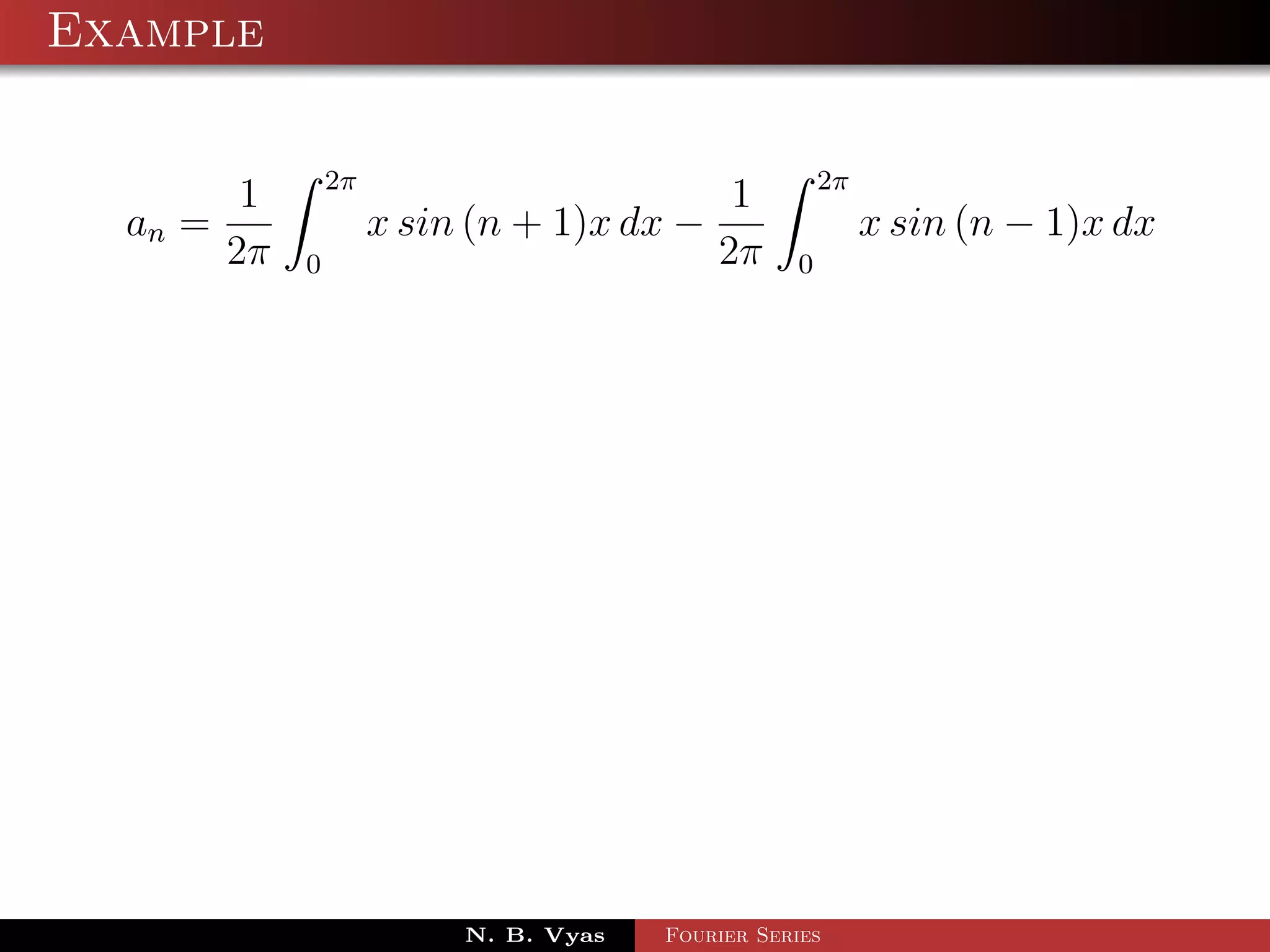





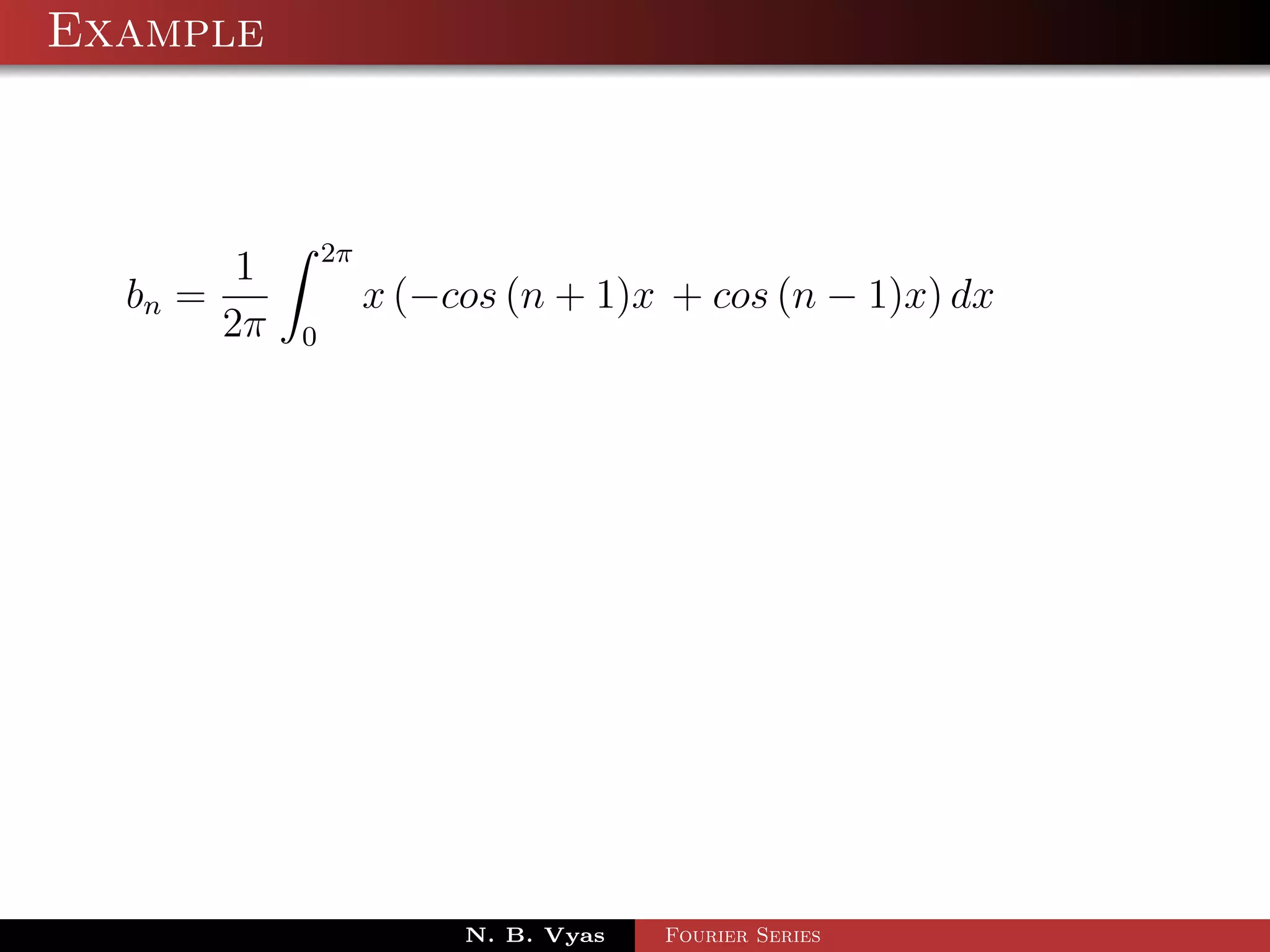
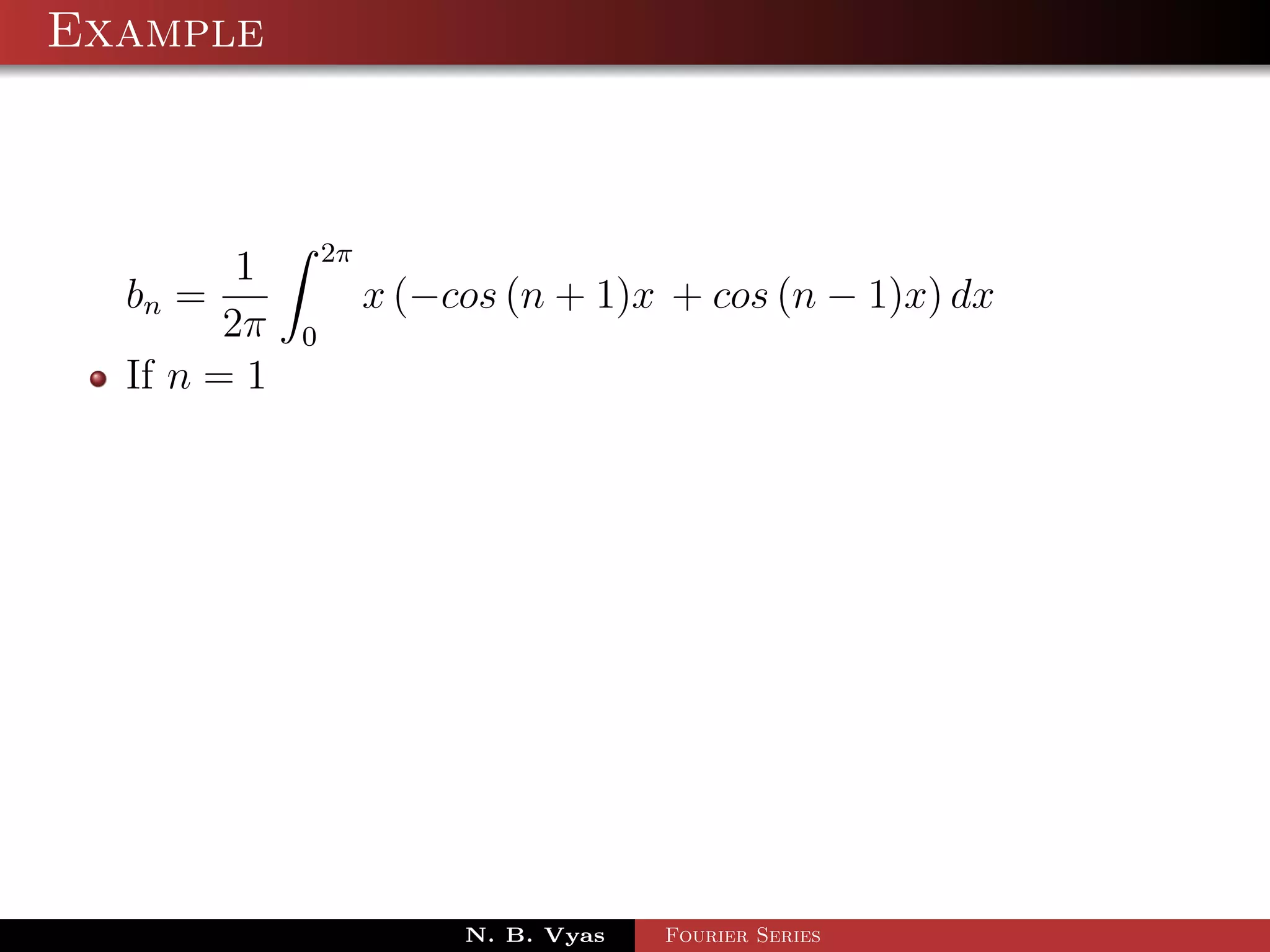
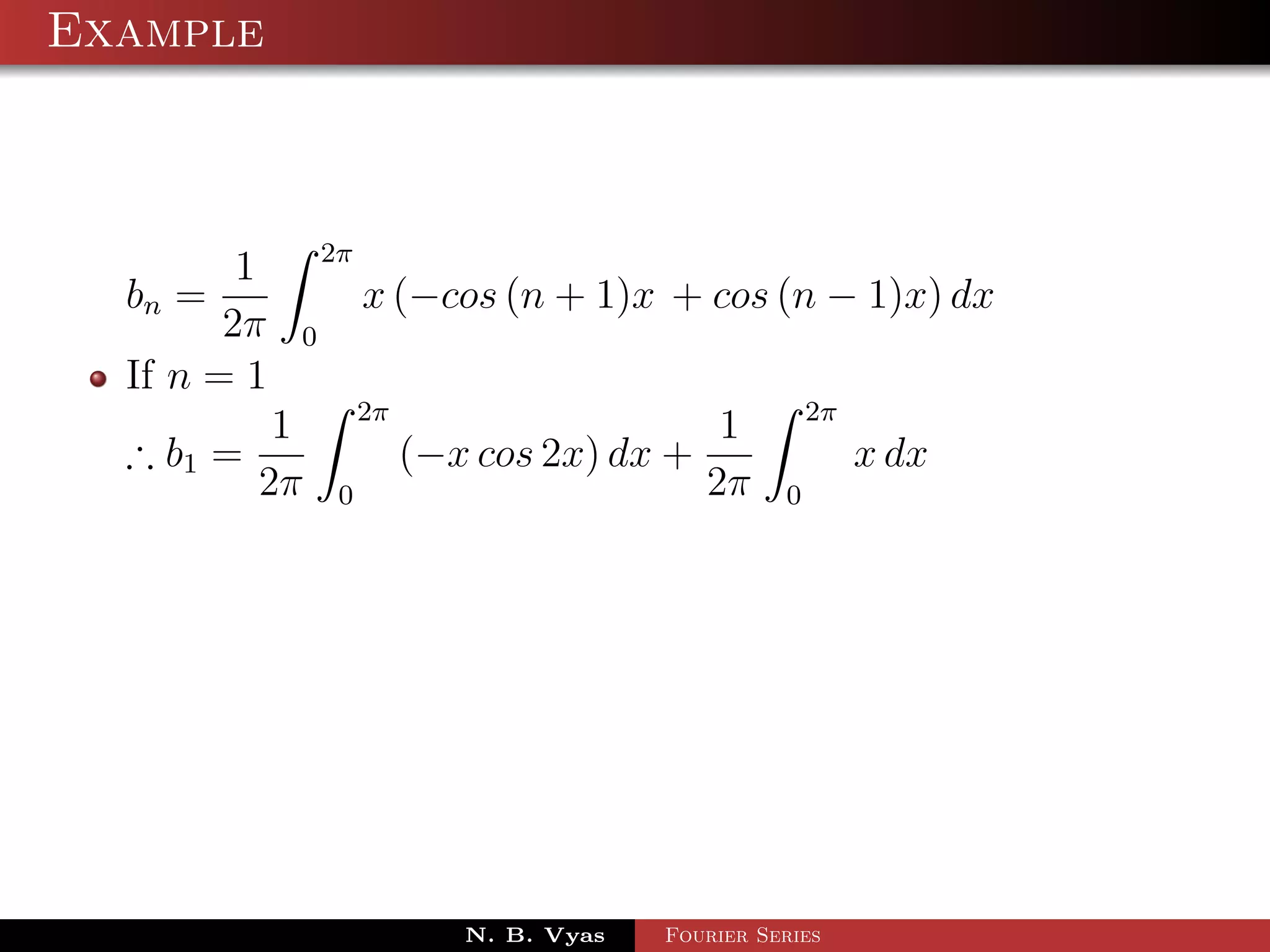
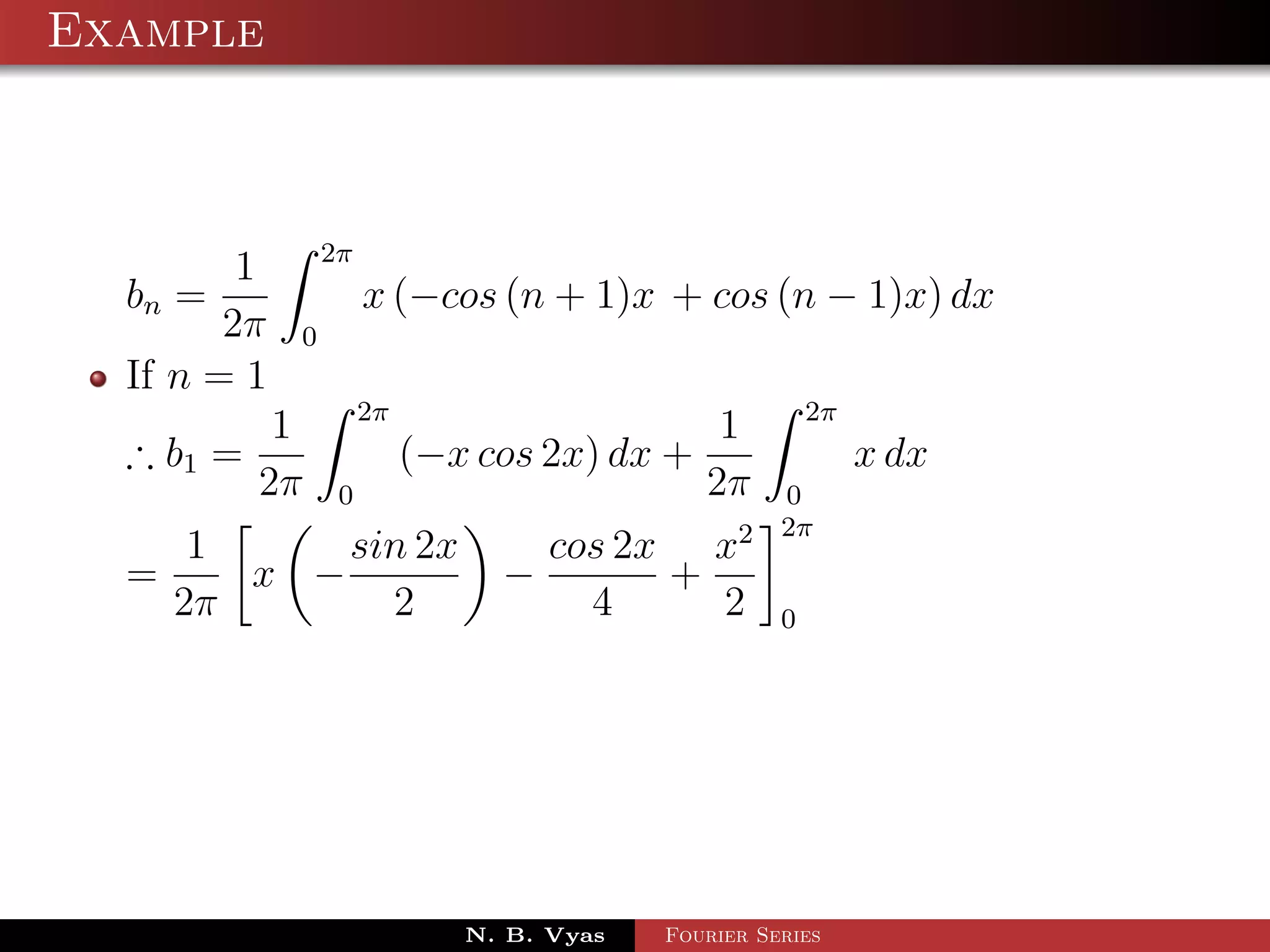
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , a1 , an (n > 1), b1 and
bn (n > 1) in (1), we get the required Fourier series of f (x) in
the interval [0, 2π]
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-160-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , a1 , an (n > 1), b1 and
bn (n > 1) in (1), we get the required Fourier series of f (x) in
the interval [0, 2π]
∞
−2
f (x) = + (an cos nx + bn sin nx)
2 n=1
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-161-2048.jpg)
![Example
Step 5. Substituting values of a0 , a1 , an (n > 1), b1 and
bn (n > 1) in (1), we get the required Fourier series of f (x) in
the interval [0, 2π]
∞
−2
f (x) = + (an cos nx + bn sin nx)
2 n=1
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-162-2048.jpg)








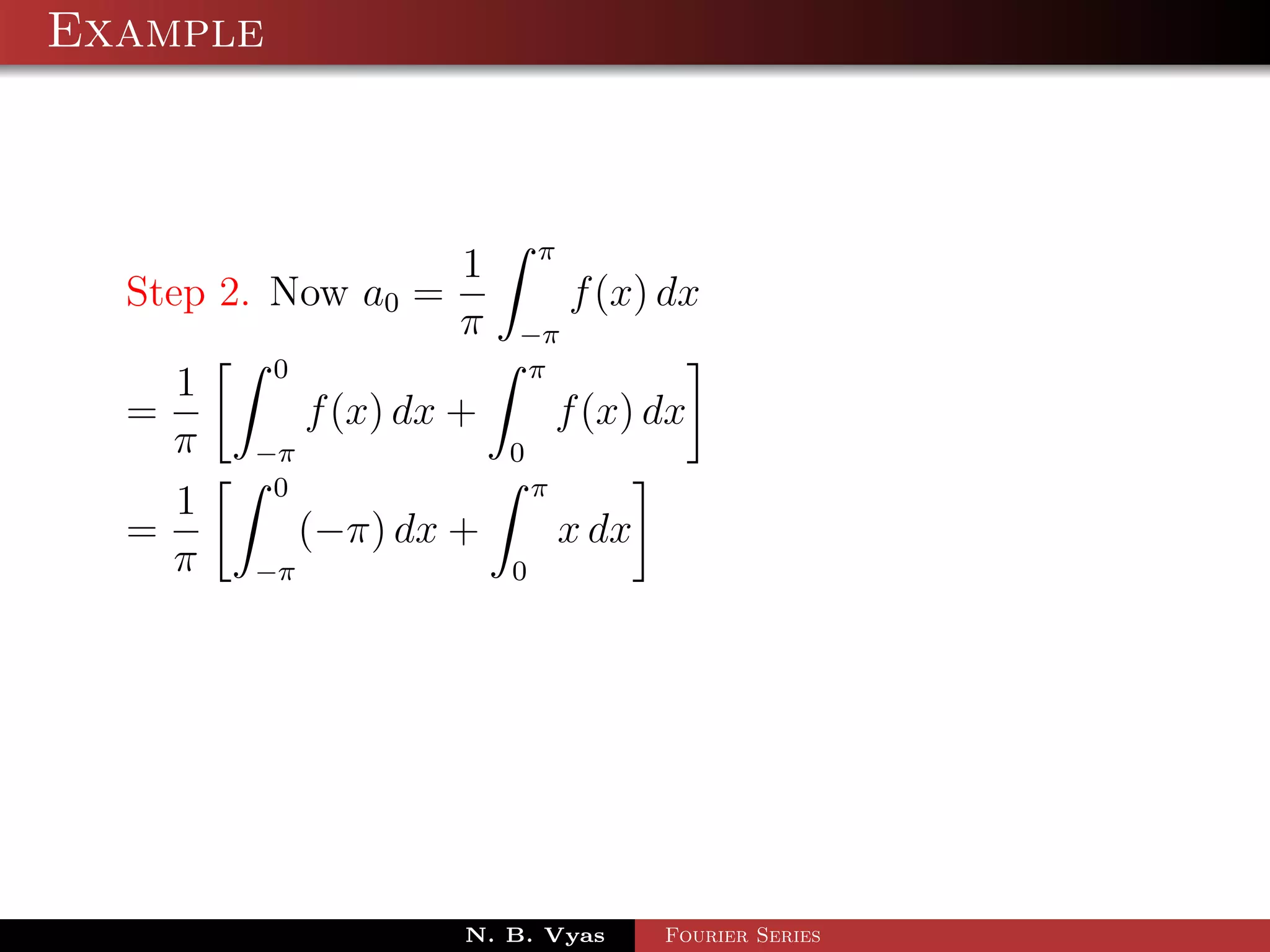
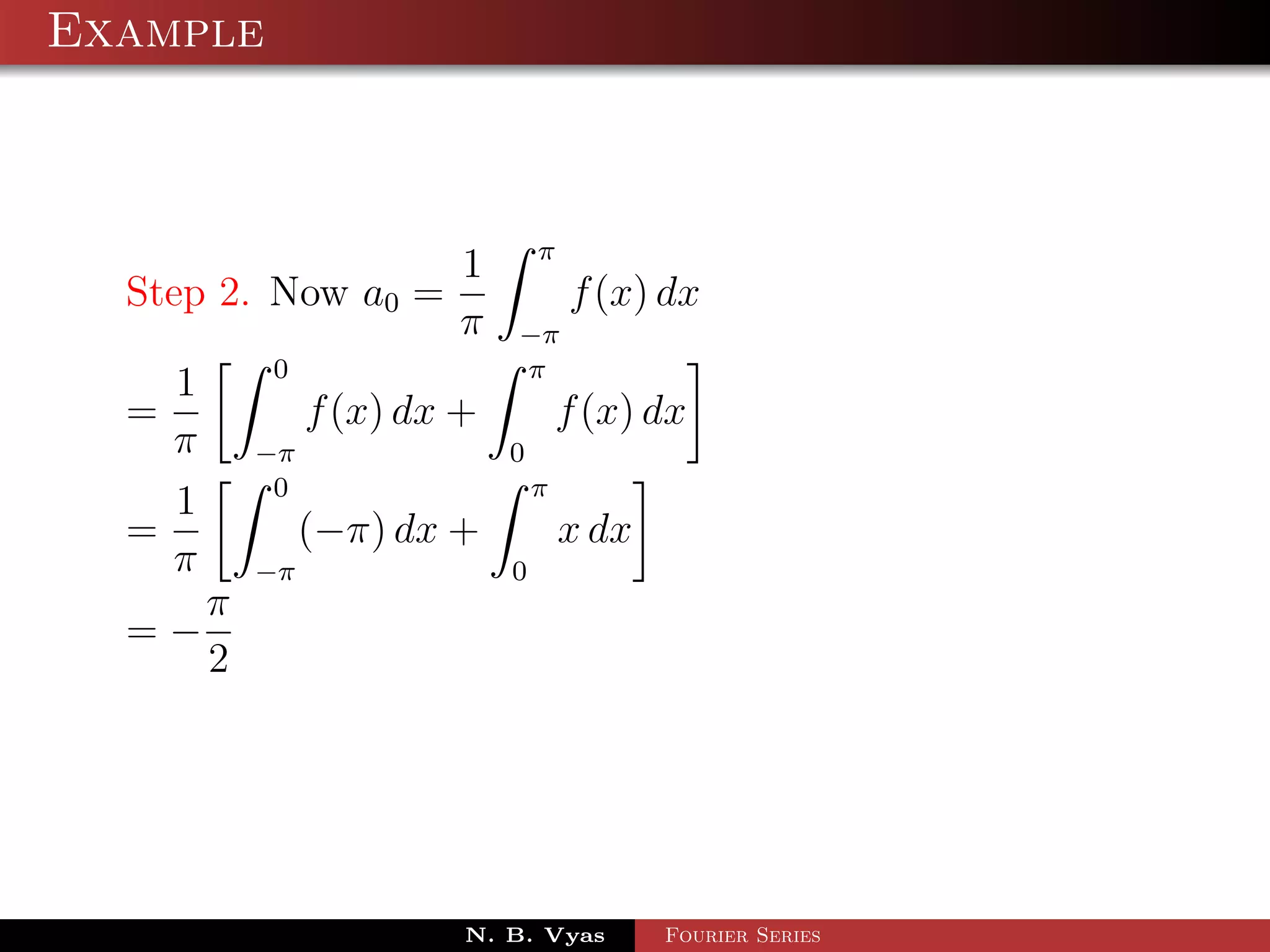
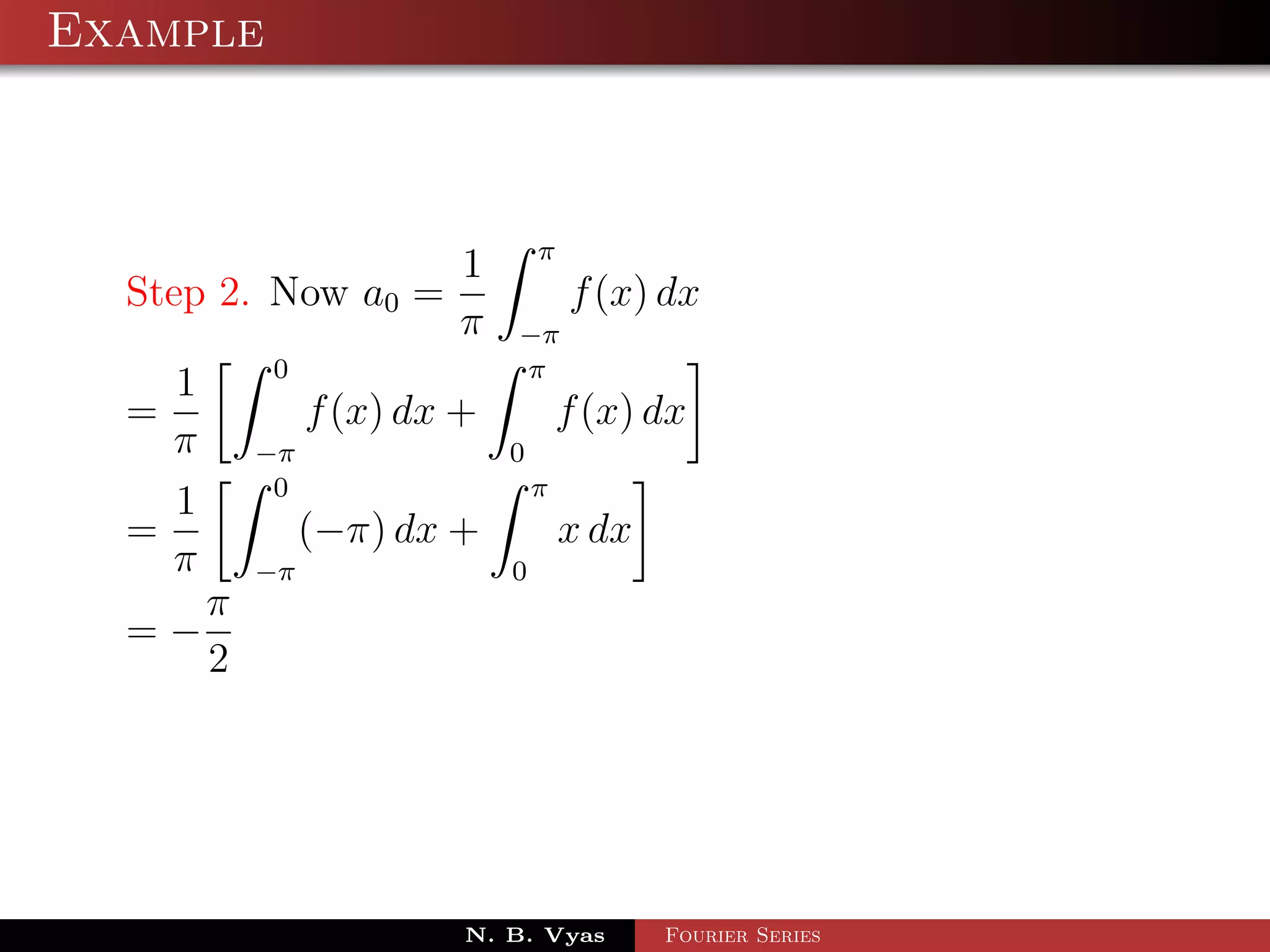






























![Example
π 2π
1
Step 3. an = f (x) cos nx dx + f (x) cos nx dx
π 0 π
π 2π
1
= x cos nx dx + (2π − x) cos nx dx
π 0 π
π
1 sin nx cos nx
= x − (1) −
π n n2 0
2π
1 sin nx cos nx
+ (2π − x) − (−1) −
π n n2 π
1 cos nπ 1
= 0+ 2
− 0+ 2
π n n
1 cos 2nπ cos nπ
+ 0− 2
− 0−
π n n2
2 [(−1)n − 1]
=
πn2
N. B. Vyas Fourier Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseries-130124053615-phpapp02/75/Fourier-series-1-209-2048.jpg)