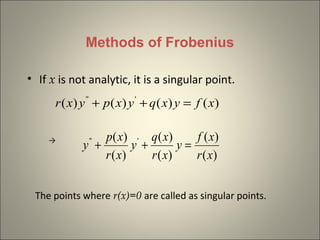
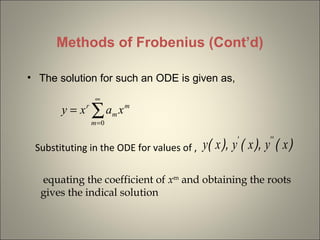
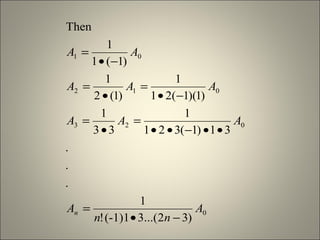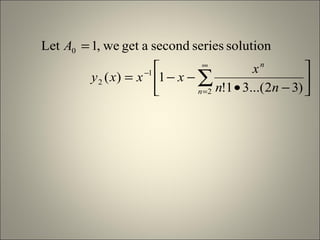The document discusses the Method of Frobenius for solving ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with singular points. It states that the solution for such an ODE is given as an infinite series involving powers of x. To determine the coefficients in the series, one substitutes the series solution into the original ODE, equates coefficients of like powers of x, and obtains the indical equation. Solving this indical equation gives the indicial solution and recurrence relations for the coefficients.


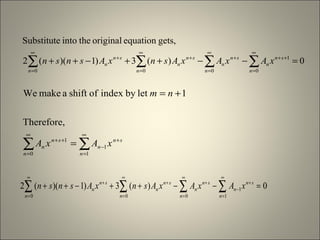
![∑
∞
=
+
− =−−++−+++−+−
1
10 0}]1)(3)1)((2{[]13)1(2[
n
sn
nn
s
xAAsnsnsnxAsss
1or
0)1)(12(
or
013)1(2
then,0Since
22
1
1
0
−==
=+−
=−+−
≠
ss
ss
sss
A
1,]1)(3)1)((2[ 1 ≥=−++−++ − nAAsnsnsn nn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themethodoffrobenius-130719130101-phpapp02/85/The-method-of-frobenius-6-320.jpg)