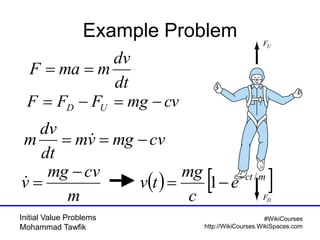
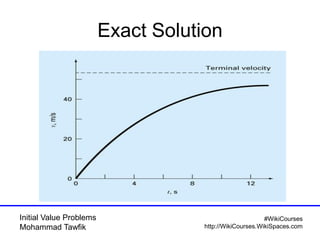
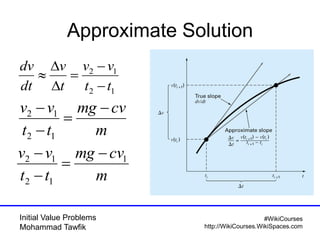
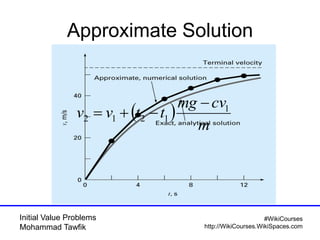
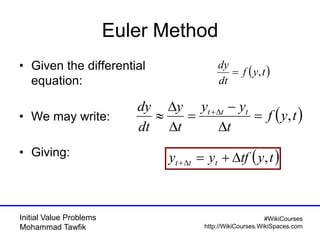
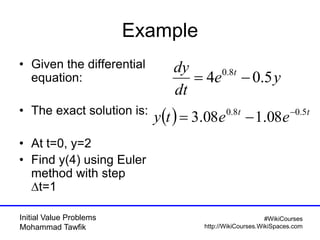
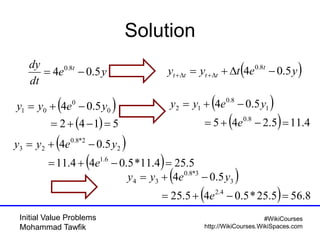
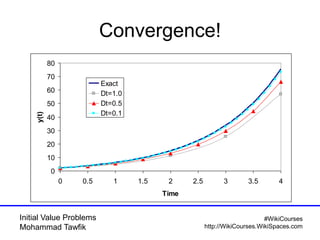
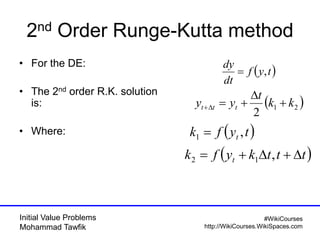
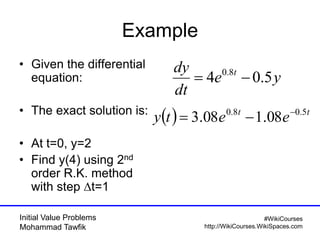
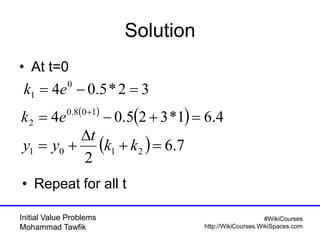
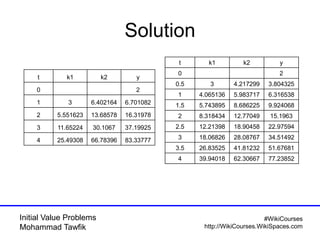
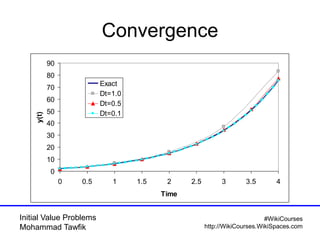
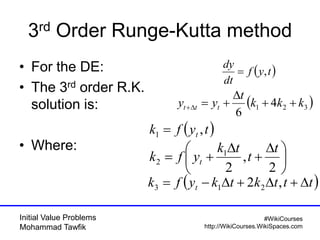
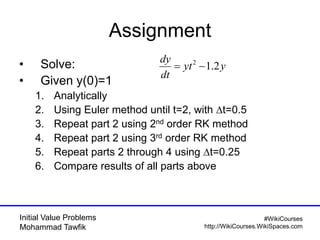
The document covers initial value problems and methods for solving them, particularly focusing on the Euler method and the Runge-Kutta methods. It provides examples and mathematical formulations for applying these methods to specific differential equations, along with convergence analysis. Additionally, it includes assignments for further practice on the discussed methods.