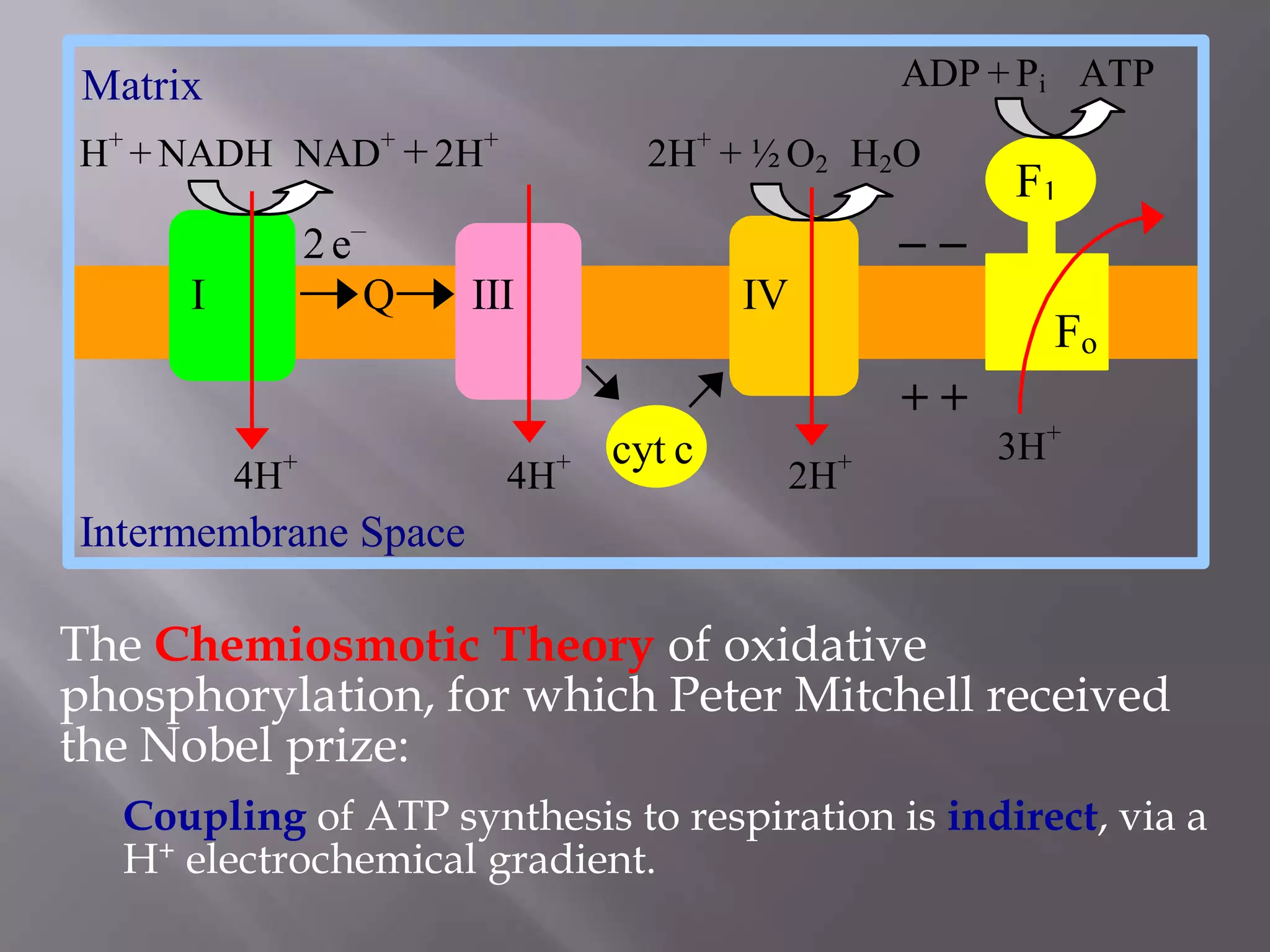
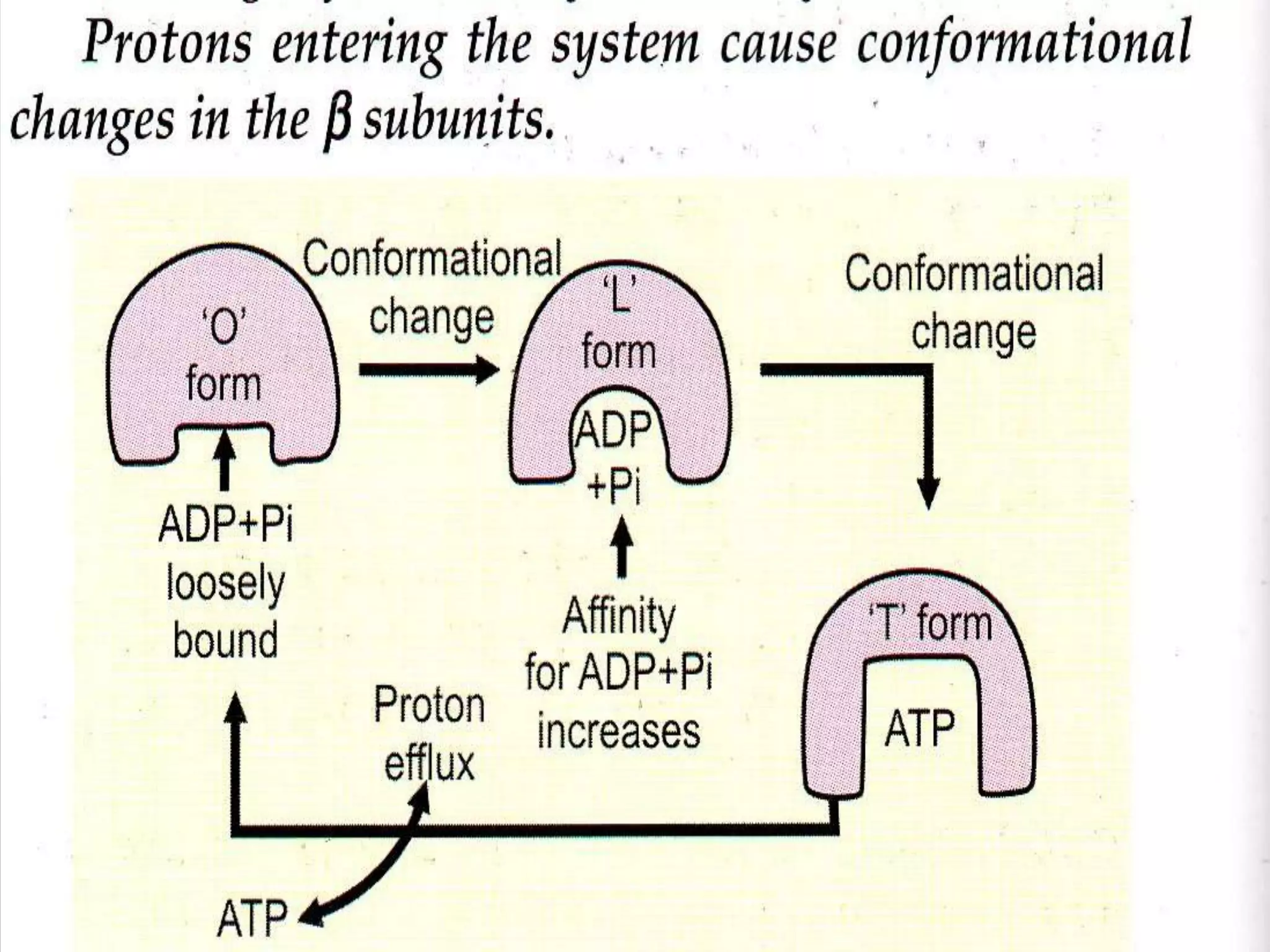
The document summarizes key theories and mechanisms of oxidative phosphorylation:
1) Chemiosmotic theory proposed by Peter Mitchell describes how ATP synthesis is coupled to respiration via an electrochemical proton gradient generated by electron transport complexes pumping protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
2) Boyer's binding change mechanism describes how ATP synthase uses the proton gradient to drive the sequential binding and conformational changes of its beta subunits to synthesize ATP.
3) Factors that regulate oxidative phosphorylation include inhibitors that block electron transport complexes or uncouple the proton gradient from ATP synthesis.