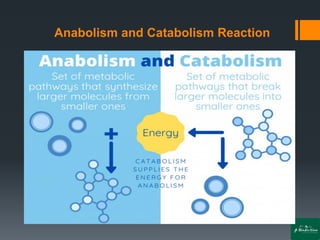
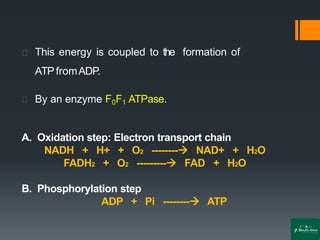
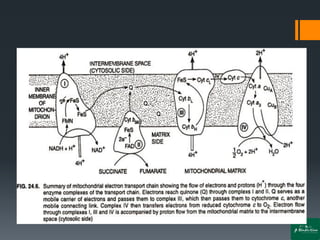
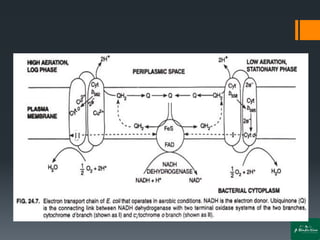
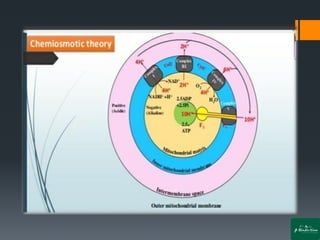
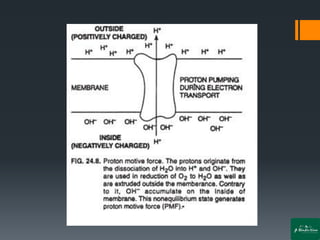
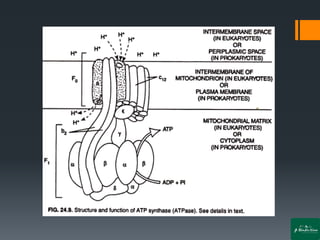
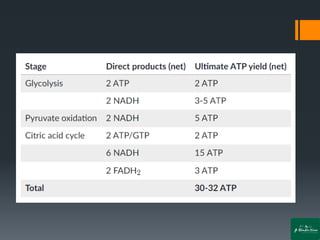
Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that generates ATP through the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to oxygen, occurring in the mitochondria of eukaryotes. The process involves an electron transport chain and the chemiosmotic theory, where proton movement creates an electrochemical gradient that drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase. This mechanism is responsible for about 90% of ATP production in cells during aerobic respiration.