1. Biological oxidation is the cellular process by which organic substances like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins release energy through redox reactions, producing CO2, H2O, and ATP.
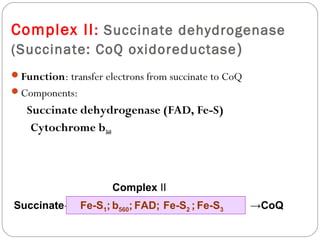
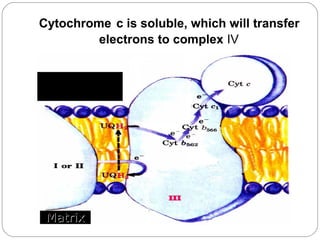
2. In the mitochondria, electrons are transferred through redox carriers in the electron transport chain from NADH or FADH2 to oxygen, driving the pumping of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane and building an electrochemical gradient.
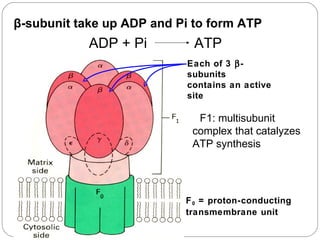
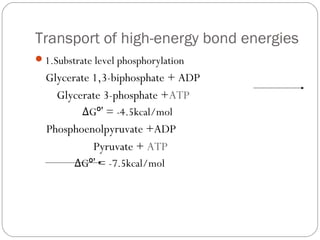
3. The potential energy of this proton gradient is harnessed by ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP, coupling electron transport to oxidative phosphorylation and the production of ATP through chemiosmosis.




























![Electrochemical H+ gradient (Protonmotive force)
2 components involved
1. Chemical potential energy due to
difference in [H+]
in two regions separated by a
membrane
2. Electrical potential energy that results
from the separation of charge when a
proton moves across the membrane
without a electron.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicaloxidation-3-131214071556-phpapp01/85/Biological-oxidation-3-32-320.jpg)