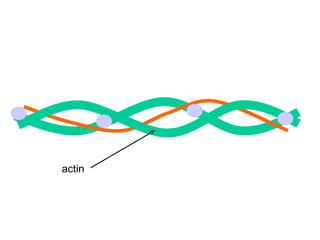
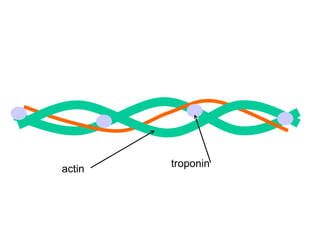
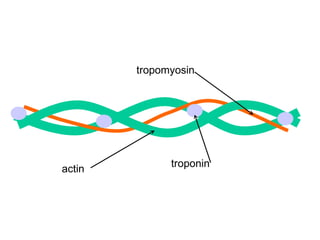
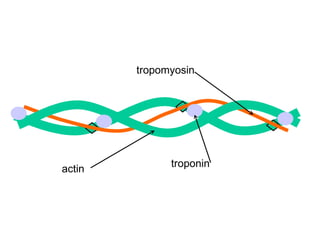
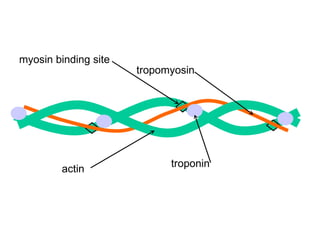
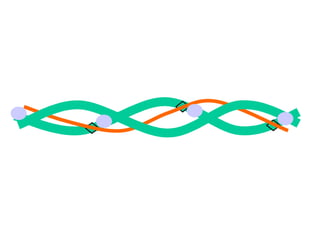
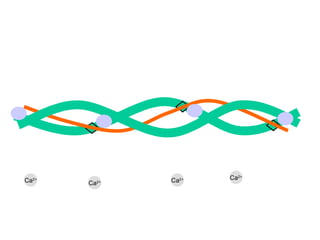
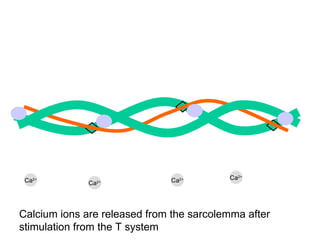
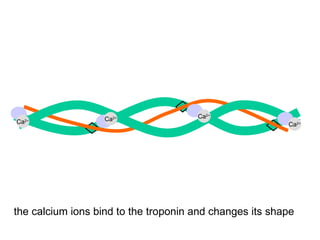
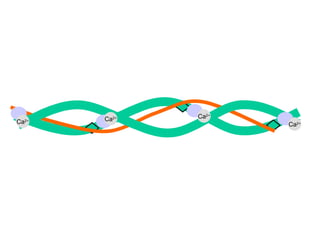
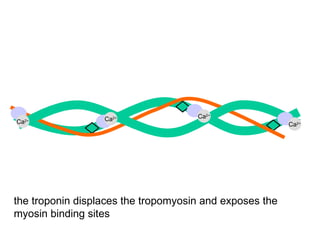
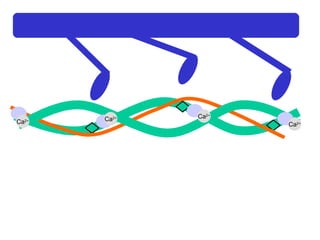
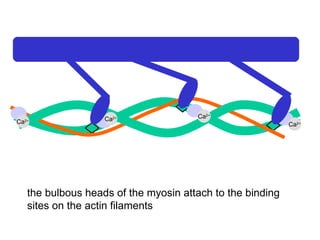
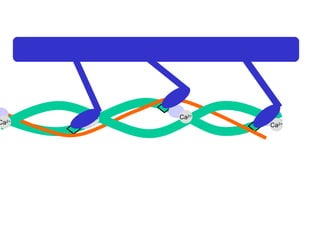
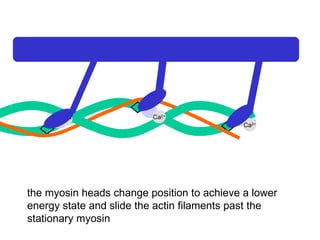
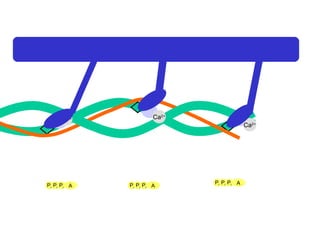
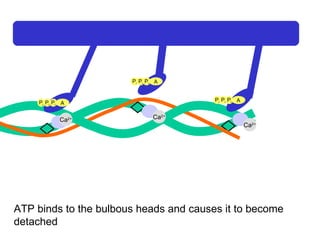
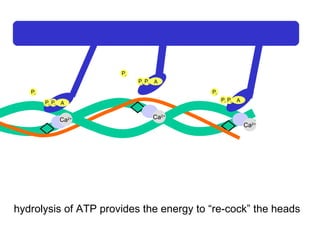
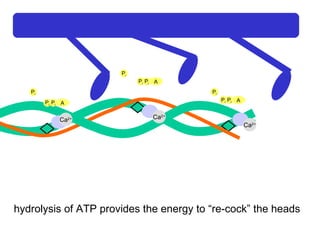
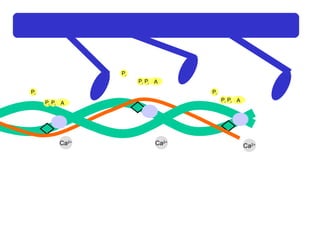
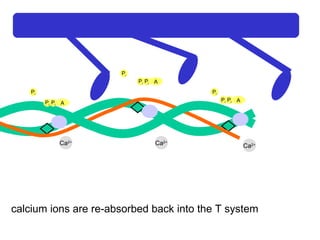
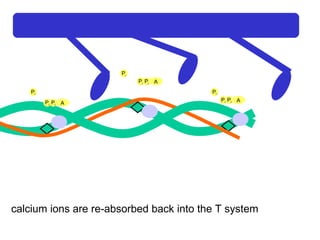
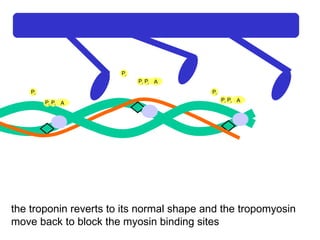
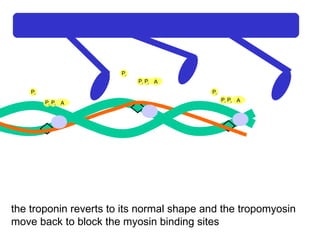
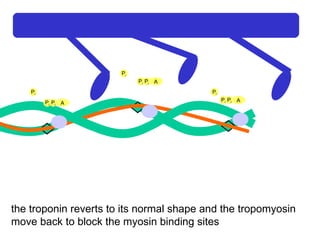
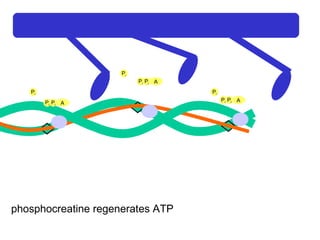
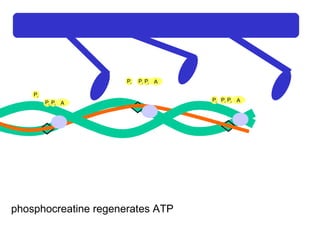
The document summarizes the process of muscle contraction via actin and myosin. Calcium ions are released which bind to troponin, displacing tropomyosin and exposing myosin binding sites on actin filaments. Myosin heads attach and change position to slide actin filaments, then detach when ATP binds. Hydrolysis of ATP provides energy to detach myosin heads, and calcium is reabsorbed allowing tropomyosin to reblock binding sites.