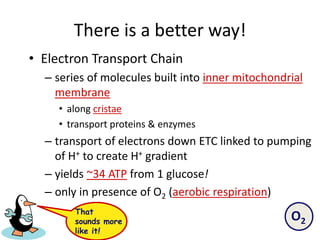
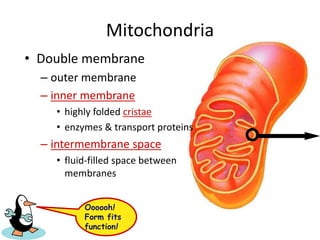
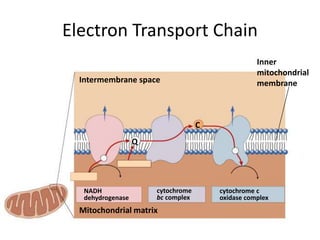
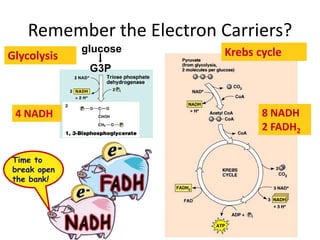
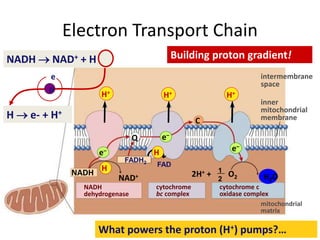
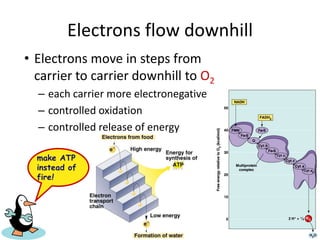
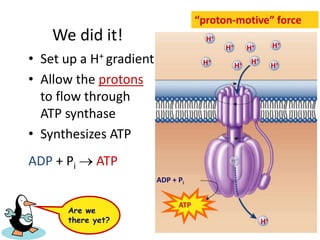
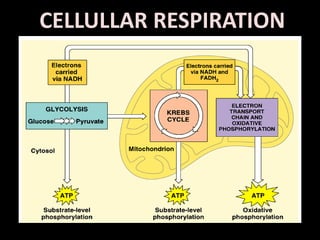
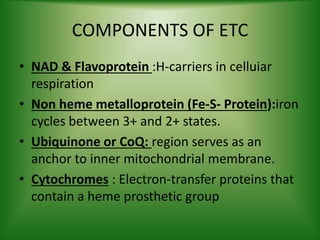
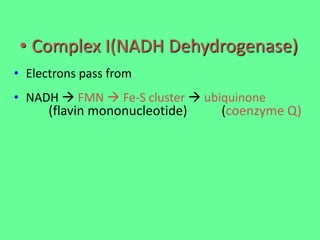
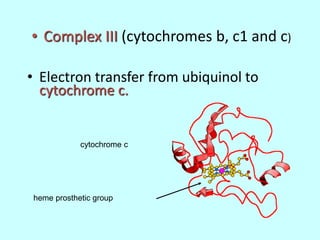
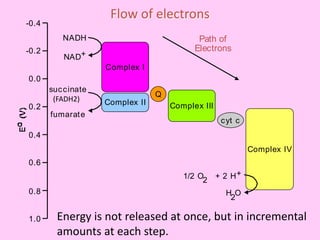
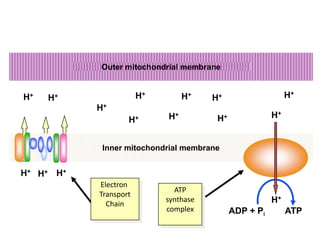
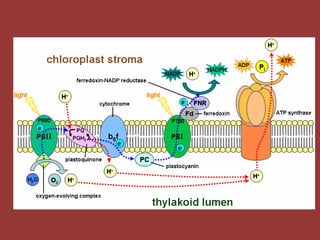
The electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and carriers in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transport electrons from electron donors like NADH to final acceptors like oxygen. This transports protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, building up a proton gradient. ATP synthase uses this proton gradient to phosphorylate ADP, producing approximately 34 ATP per glucose. The ETC is crucial for aerobic respiration as it extracts much more energy than glycolysis and the Krebs cycle alone.