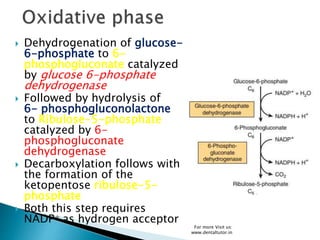
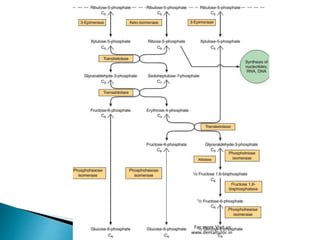
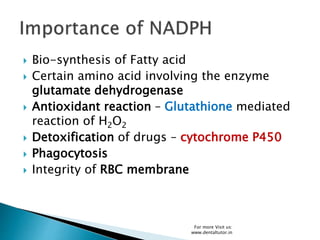
The pentose phosphate pathway, also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt, is an alternative metabolic pathway to glycolysis that occurs in the cytosol. It is a complex pathway that helps generate NADPH for fatty acid synthesis and glutathione for antioxidant activity, as well as synthesizing ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide and nucleic acid formation. Glucose-6-phosphate enters the pathway and is oxidized through a two-phase process involving dehydrogenation using NADP+ instead of NAD+. Several intermediates are formed and rearranged before regenerating glucose-6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to complete the nonoxidative phase. Genetic defects in glucose-6