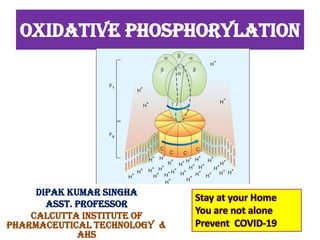
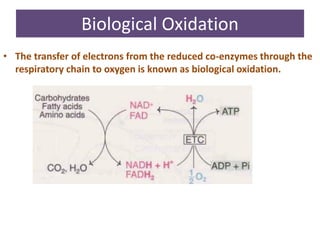
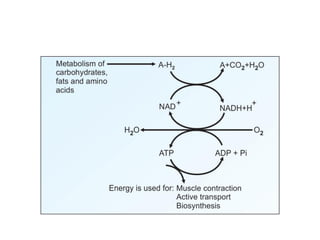
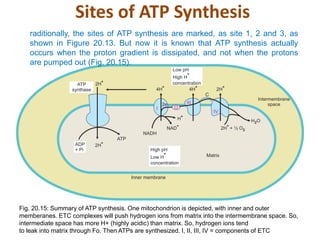
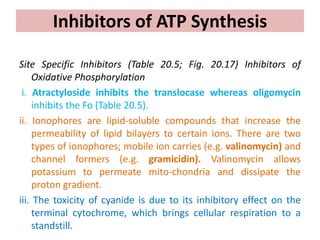
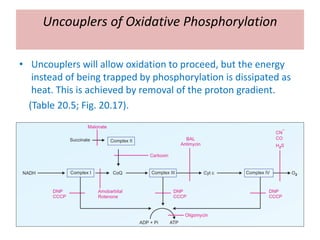
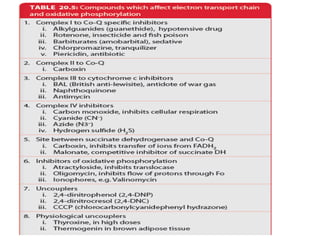
1. Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which cells generate ATP by coupling the electron transport chain to phosphorylation. During this process, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, generating a proton gradient.
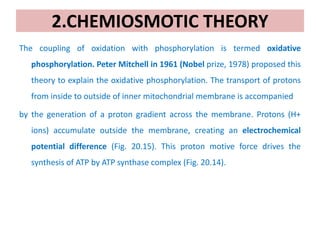
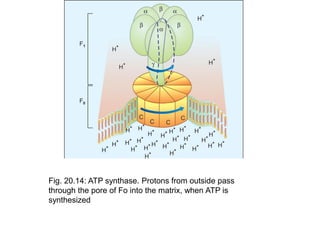
2. Peter Mitchell proposed the chemiosmotic theory to explain how this proton gradient is used to drive ATP synthesis. As protons flow back into the matrix through ATP synthase, the energy from their downhill movement is used to phosphorylate ADP into ATP.
3. The chemiosmotic theory states that the electron transport chain pumps protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating an electrochemical proton gradient. This proton motive force drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase.