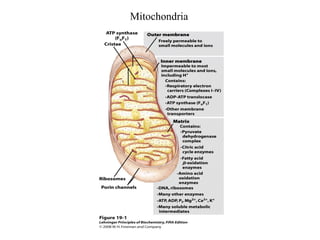
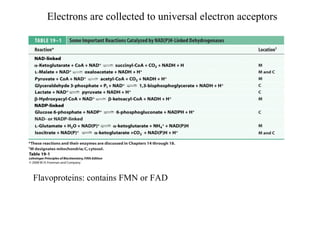
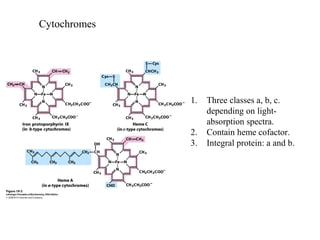
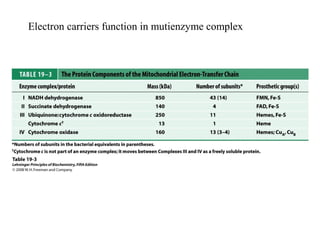
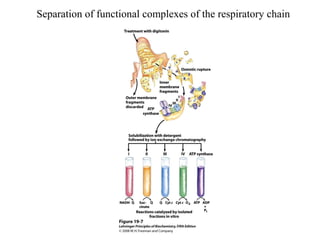
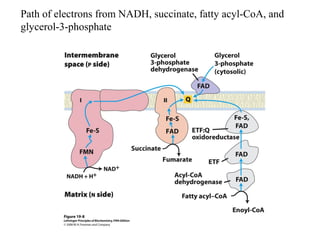
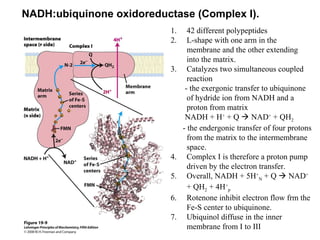
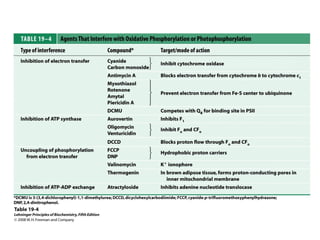
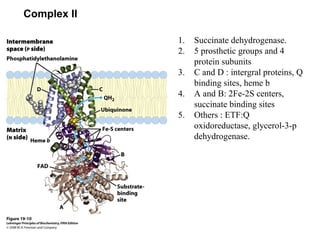
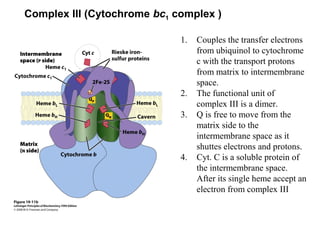
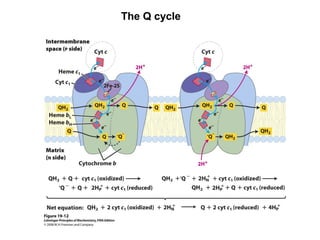
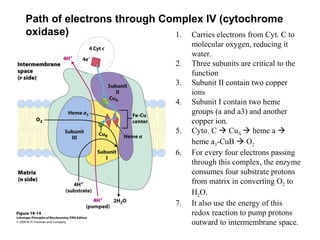
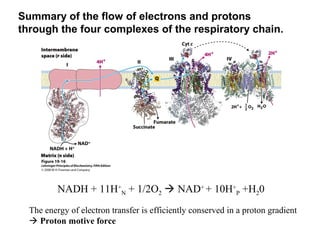
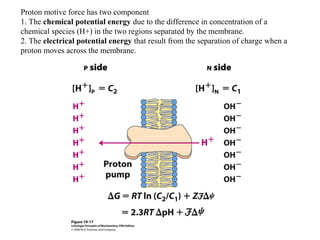
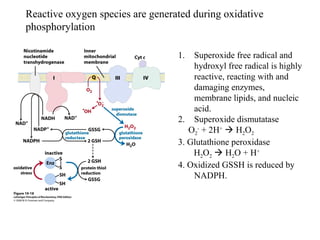
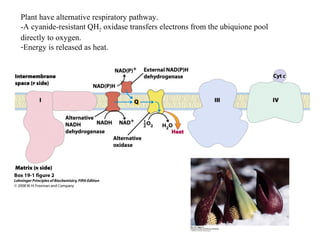
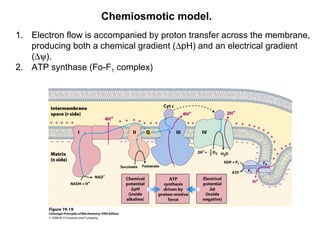
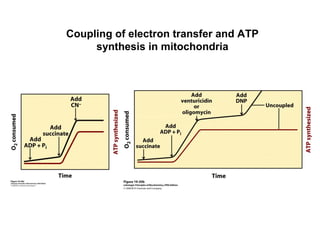
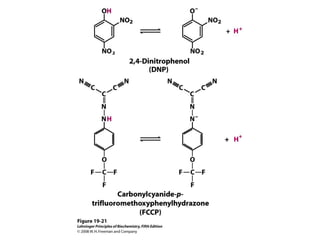
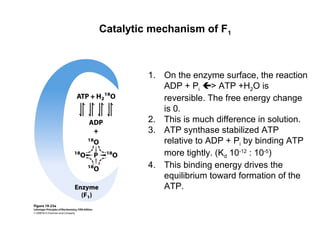
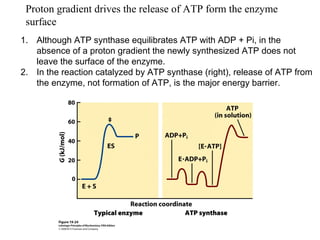
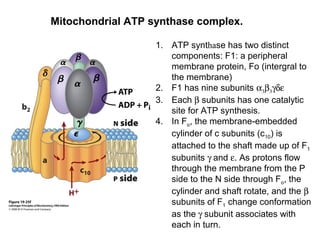
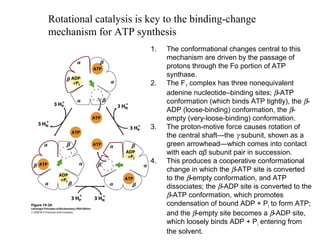
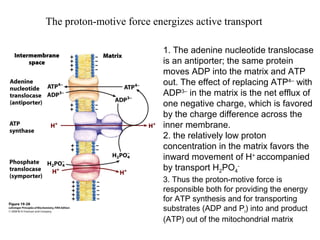
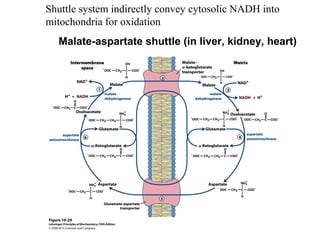
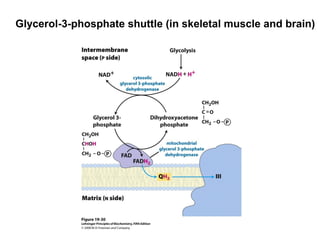
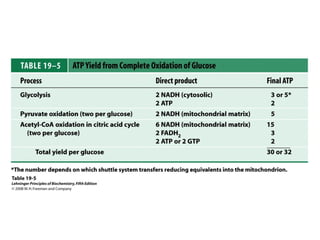
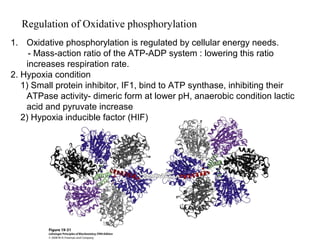
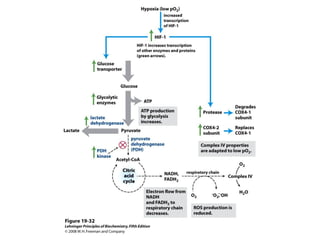
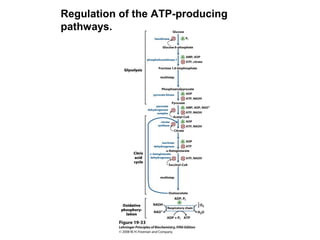
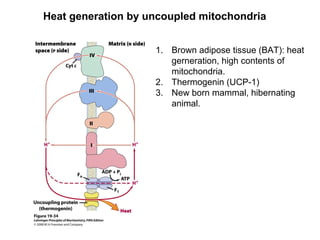
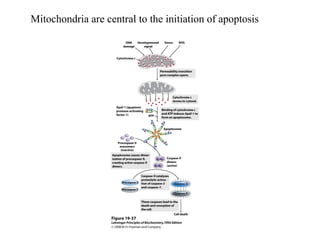
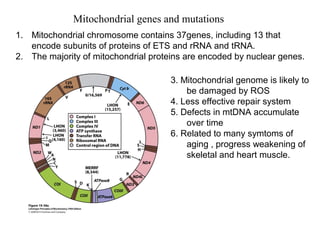
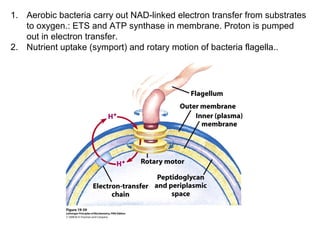
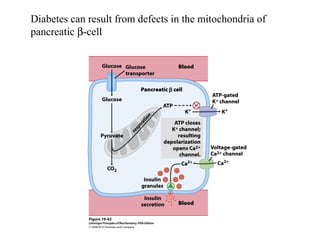
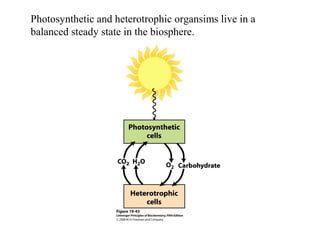
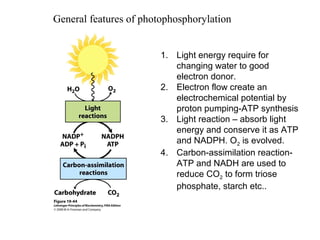
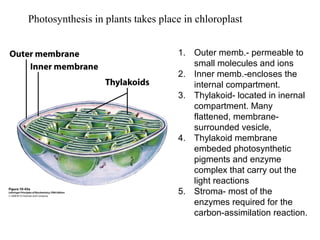
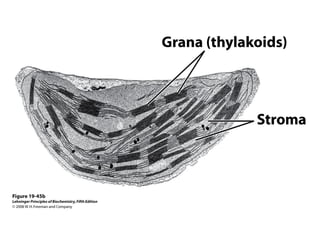
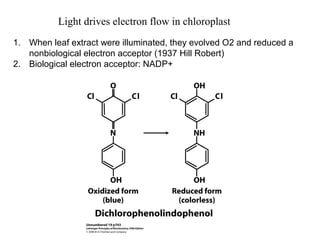
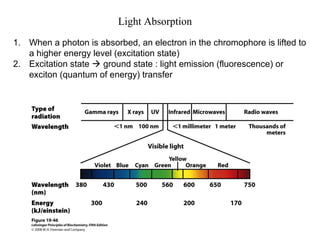
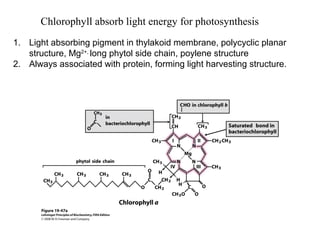
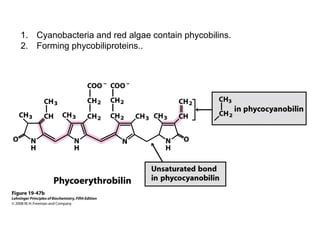
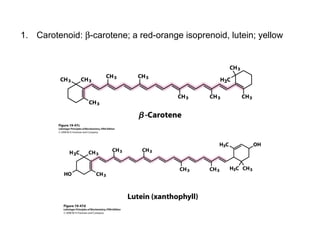
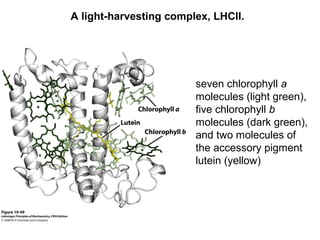
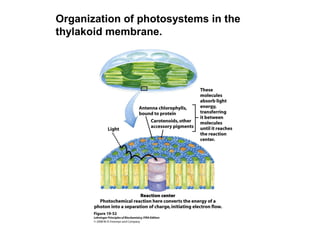
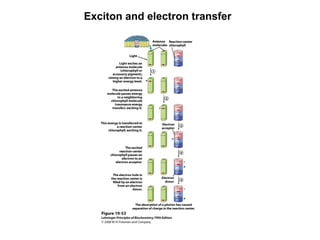
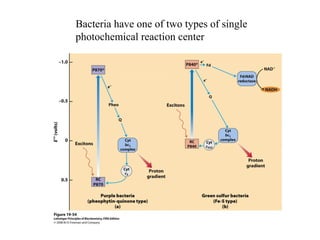
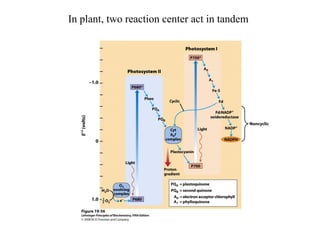
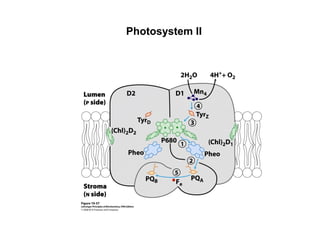
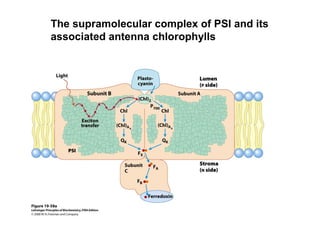
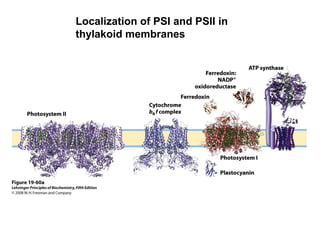
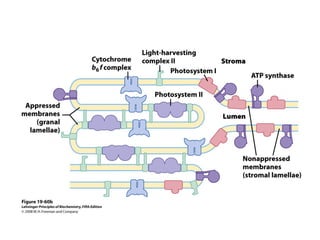
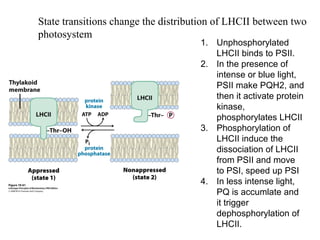
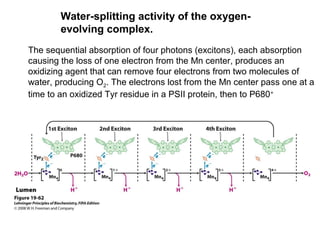
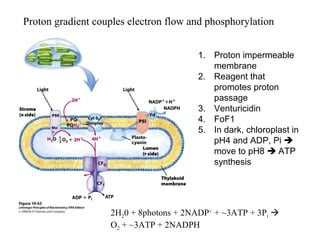
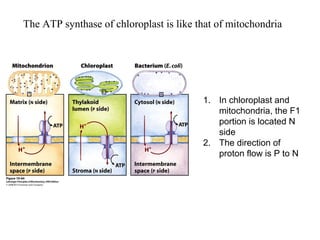
Oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation are two pathways that generate ATP through electron transport chains located in mitochondria and chloroplasts respectively. Both pathways use proton gradients generated by electron transport to power ATP synthase and produce ATP. In mitochondria, electrons from NADH and FADH2 enter the electron transport chain at Complex I and II and are passed through a series of carriers including ubiquinone, cytochromes, and Complexes III and IV until they reduce oxygen to water. This electron flow is coupled to the pumping of protons out of the mitochondrial matrix, generating a proton gradient used by ATP synthase to produce ATP.