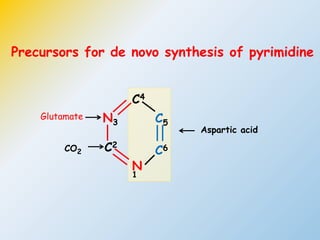
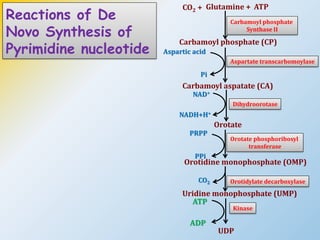
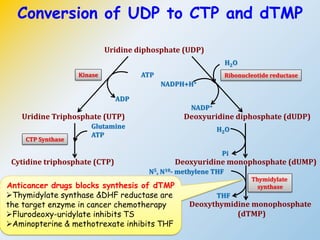
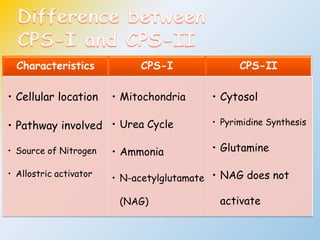
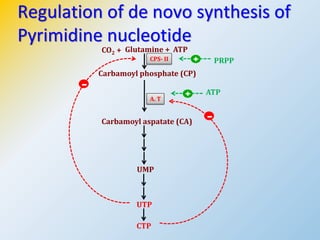
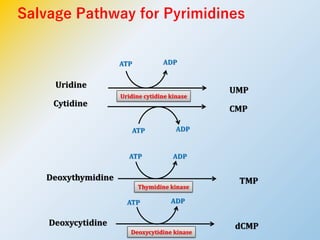
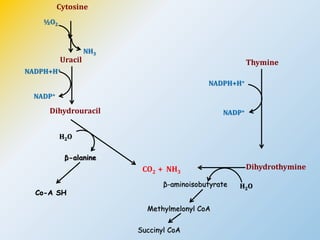
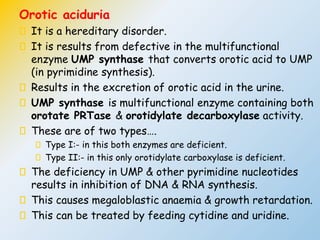
This document summarizes the de novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides. It describes the precursors and reactions involved in synthesizing the pyrimidine ring and then attaching it to ribose phosphate to form the pyrimidine nucleotides CMP, UMP and TMP. It also discusses the conversion of UDP to CTP and dTMP, the regulation of pyrimidine synthesis, salvage pathways, catabolism of pyrimidines, and the genetic disorder orotic aciduria caused by a defect in the enzyme UMP synthase.