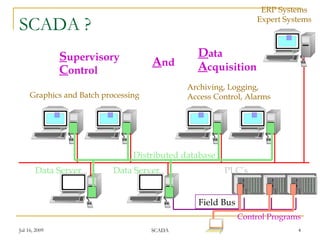
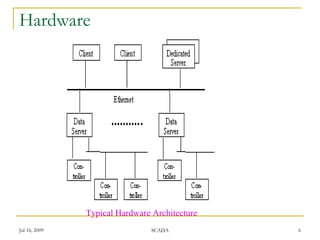
This document discusses supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. It describes the typical hardware and software architectures of SCADA, including distributed databases, data servers, programmable logic controllers, and field buses. The document outlines common SCADA functions such as access control, human-machine interface, trending, alarm handling, logging, archiving, report generation, and automation. It also mentions SCADA development tools and data access mechanisms. In conclusion, the document states that SCADA systems offer more front-end functionality, efficient storage, and device-oriented configuration than distributed control systems.