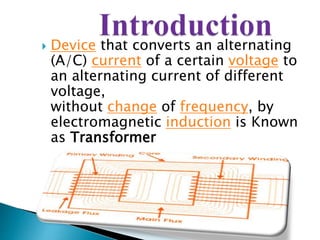
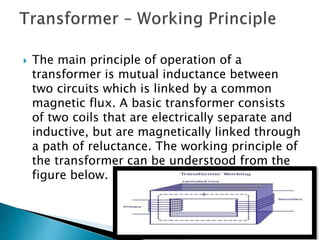
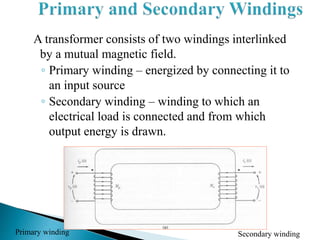
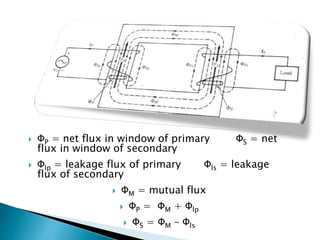
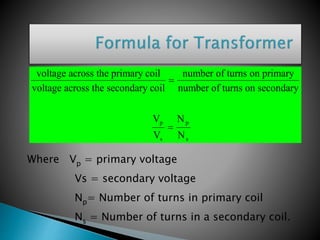
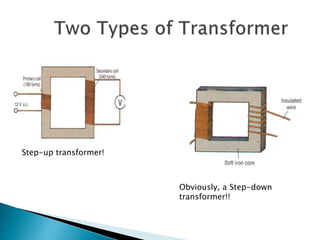
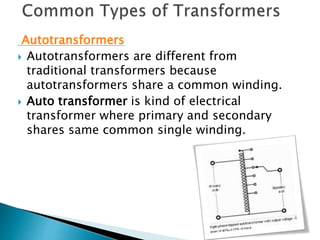
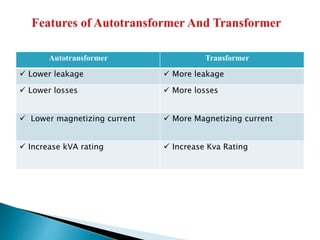
A transformer consists of two coils with a mutual magnetic field that allows it to convert alternating current of one voltage to another without changing frequency. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction between the primary and secondary windings. There are several types of losses that occur in transformers like copper, eddy current, and hysteresis losses. The ratio of voltages out to voltages in depends on the turns ratio of the number of windings in the primary coil to the secondary coil. Transformers can either step up or step down voltages and are used widely in power transmission and applications requiring different voltages.