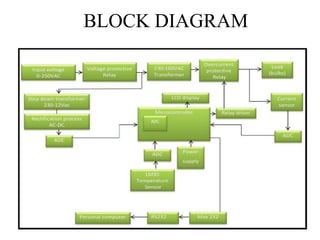
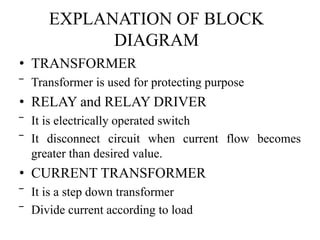
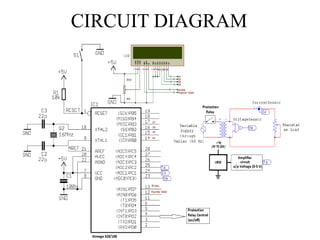
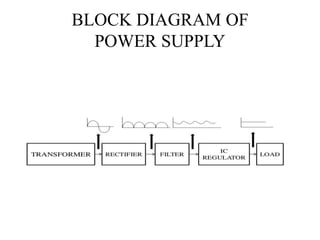
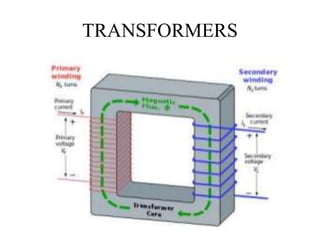
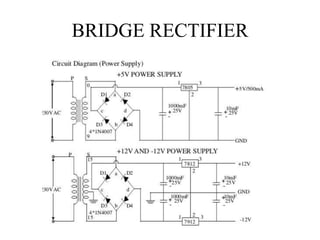
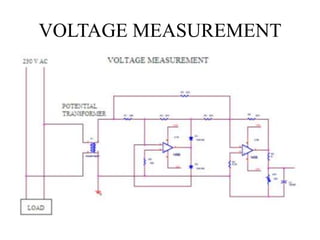
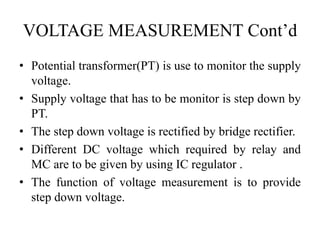
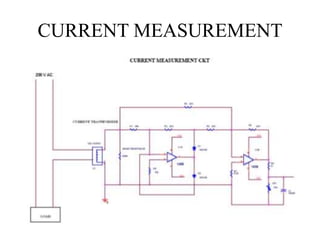
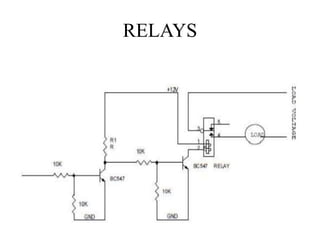
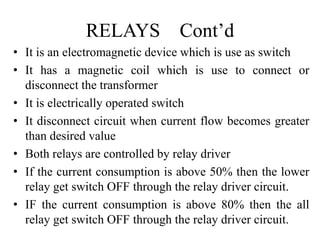
This document describes a project to protect transformers from overload conditions using a microcontroller and GSM technology. It includes a block diagram and explanation of the circuit diagram. The key components are a step-down transformer, rectifier, microcontroller, current transformer, voltage transformer, and relays. The microcontroller monitors the current and voltage, and can trigger the relays to disconnect the transformer if the load exceeds safe levels, while also sending a message via GSM to alert authorities. The objectives are to prevent transformer damage from overloading and allow for load sharing to increase lifespan.