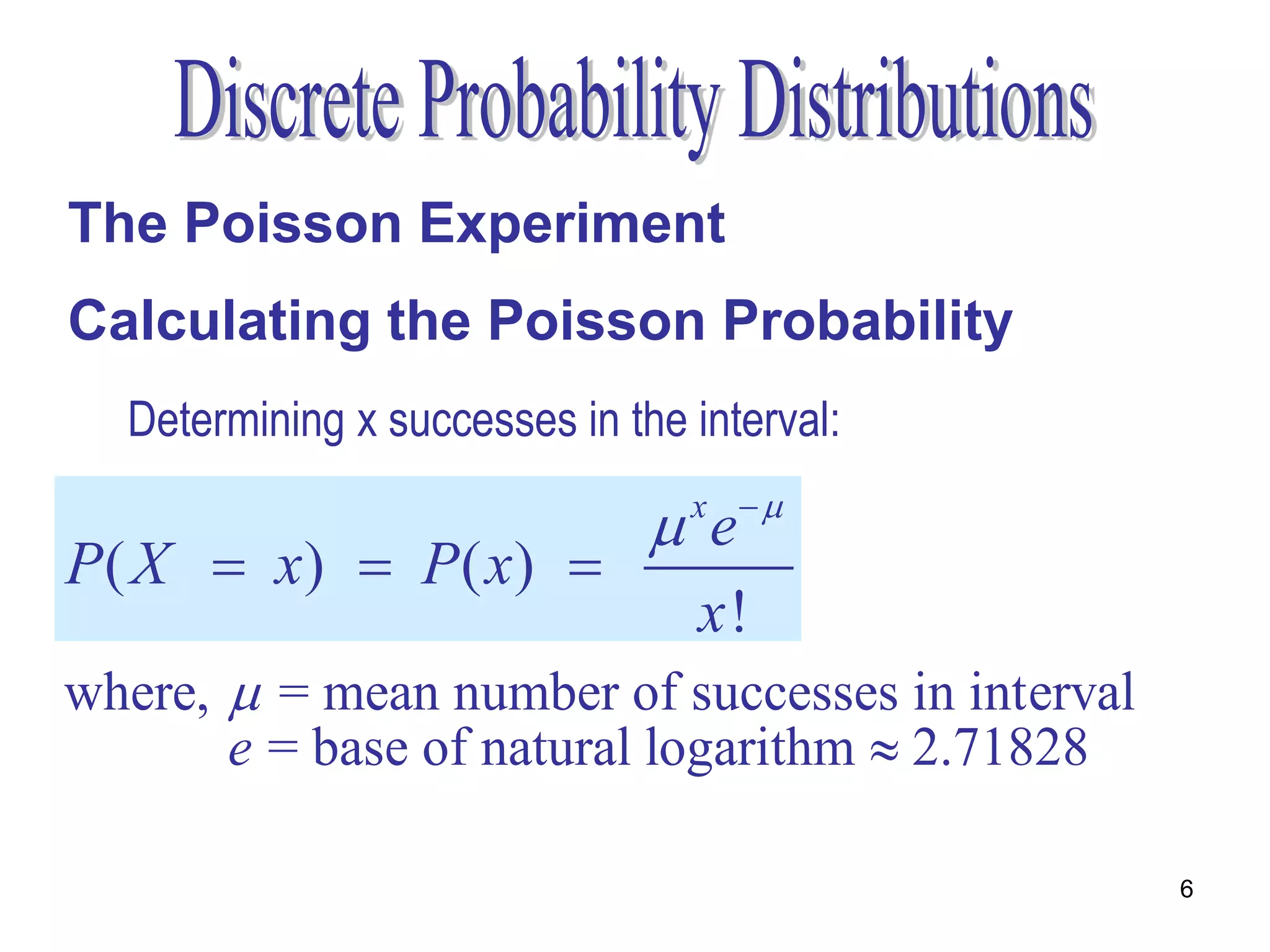
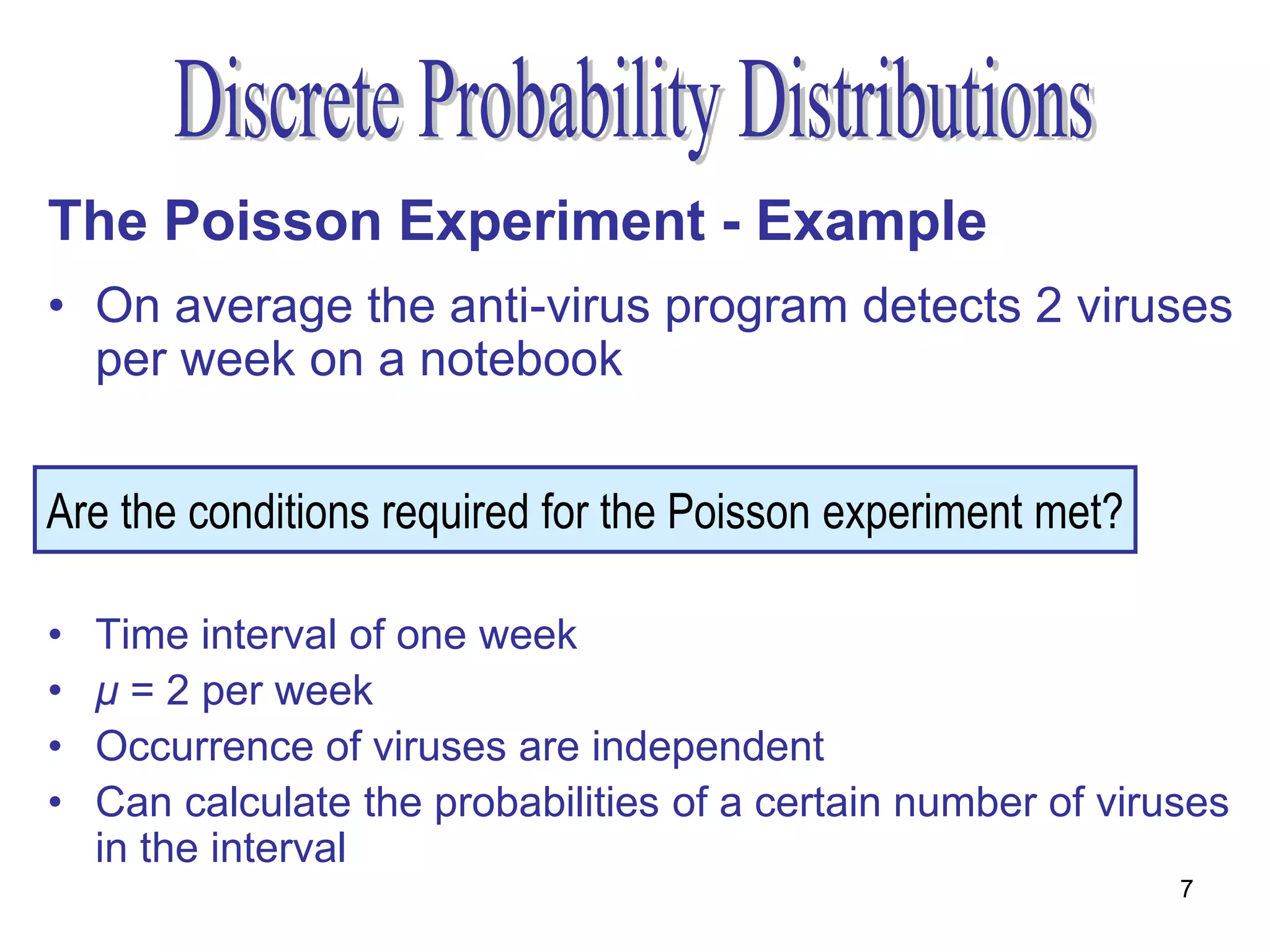
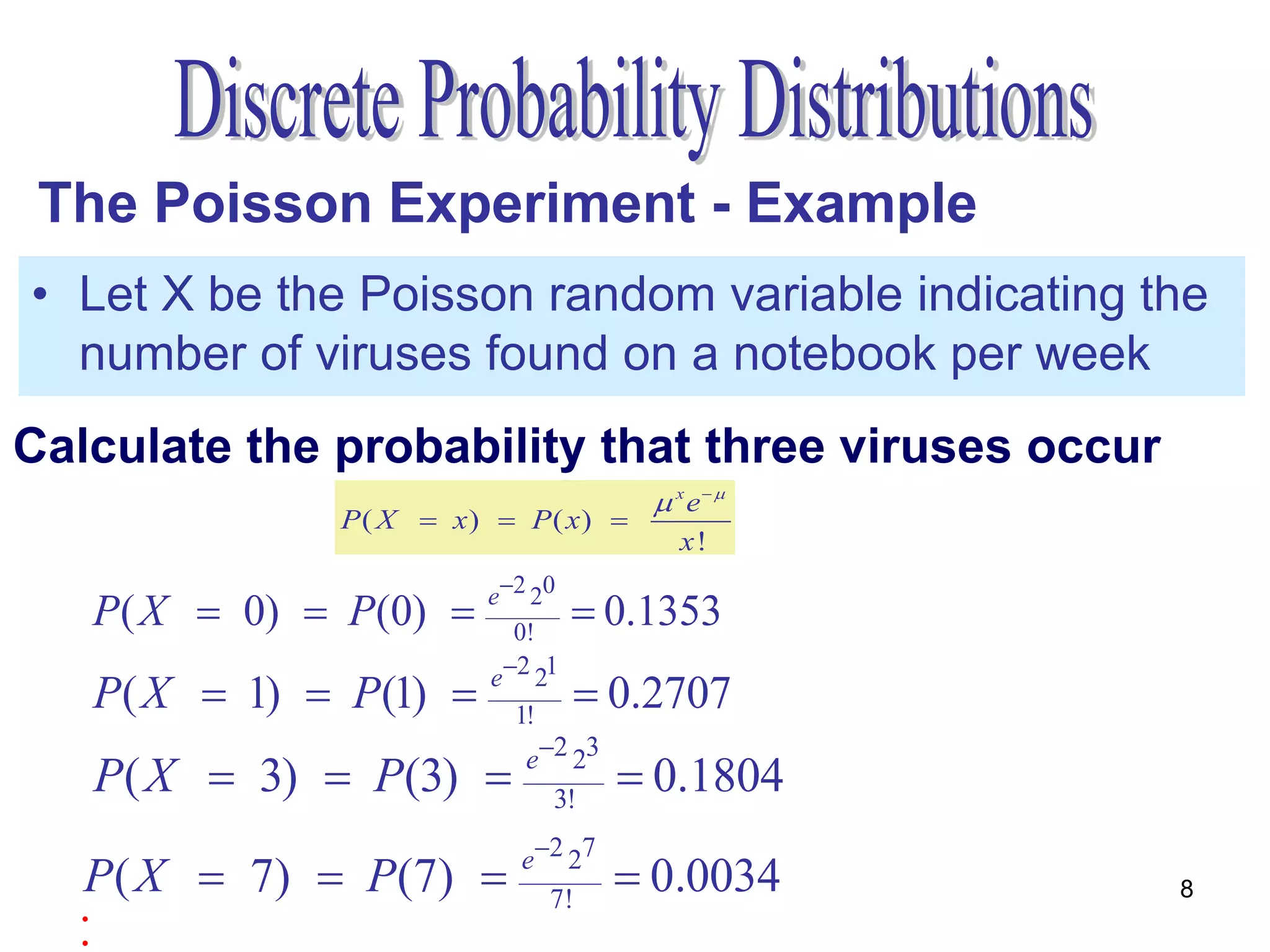
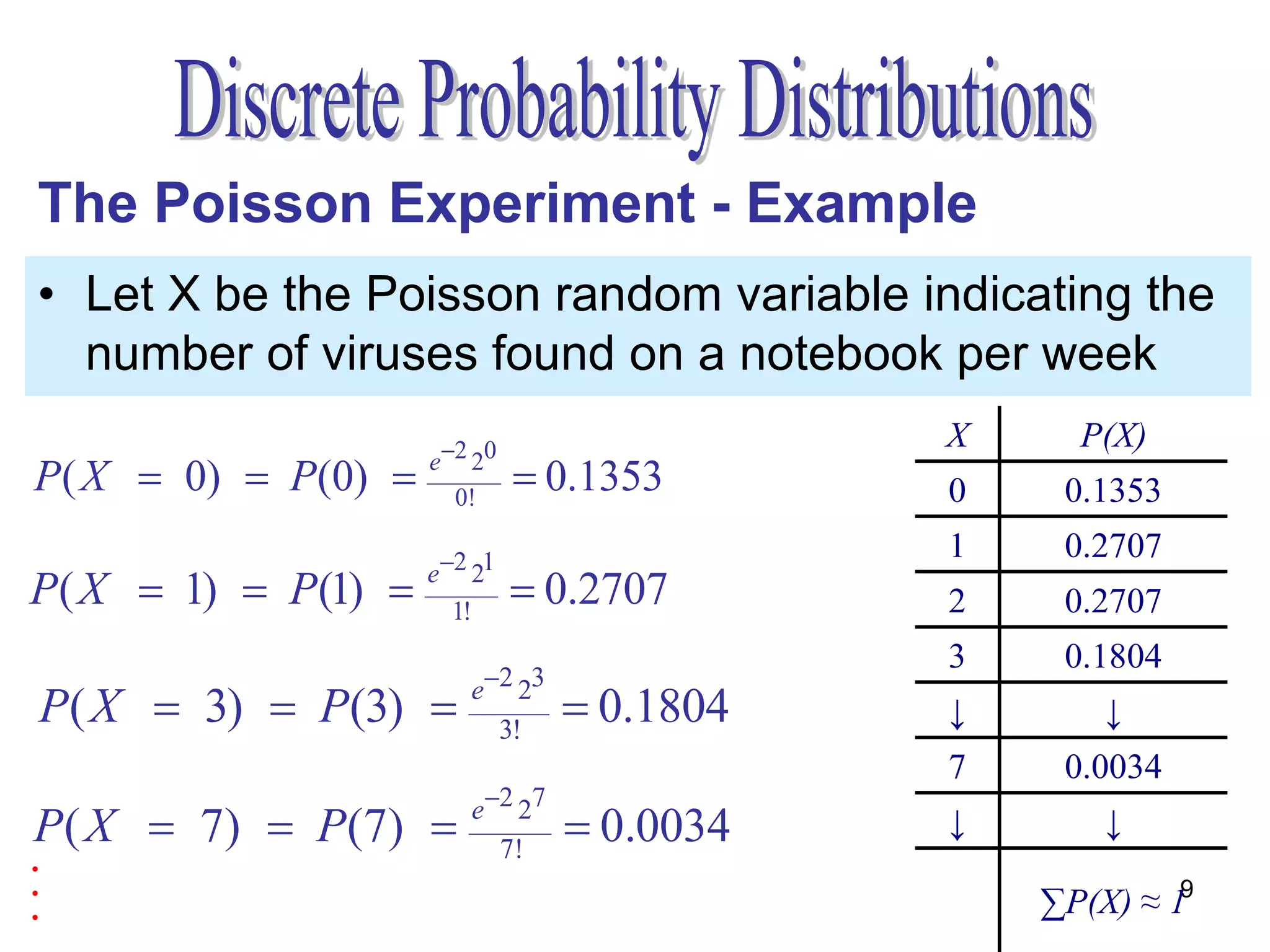
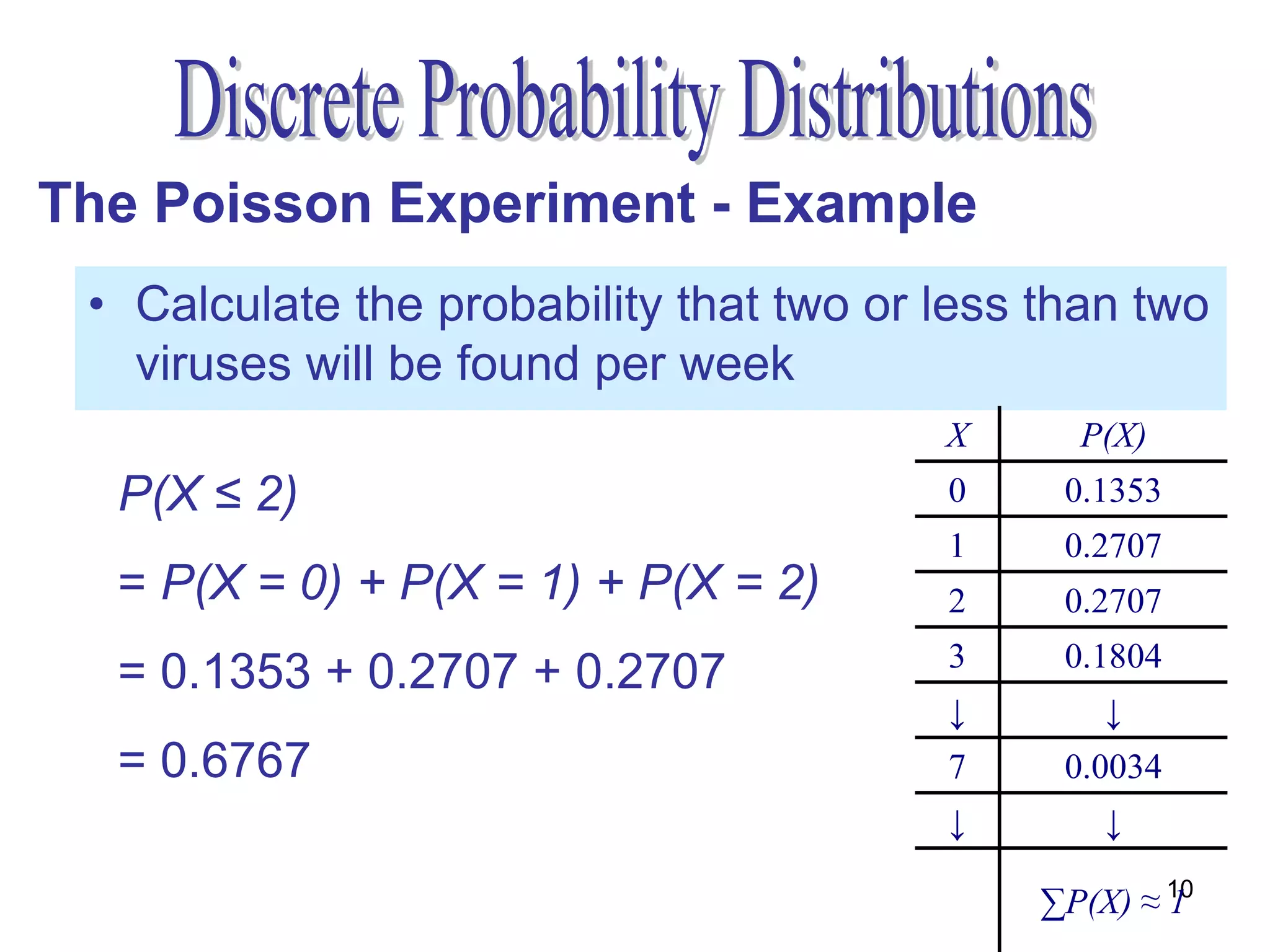
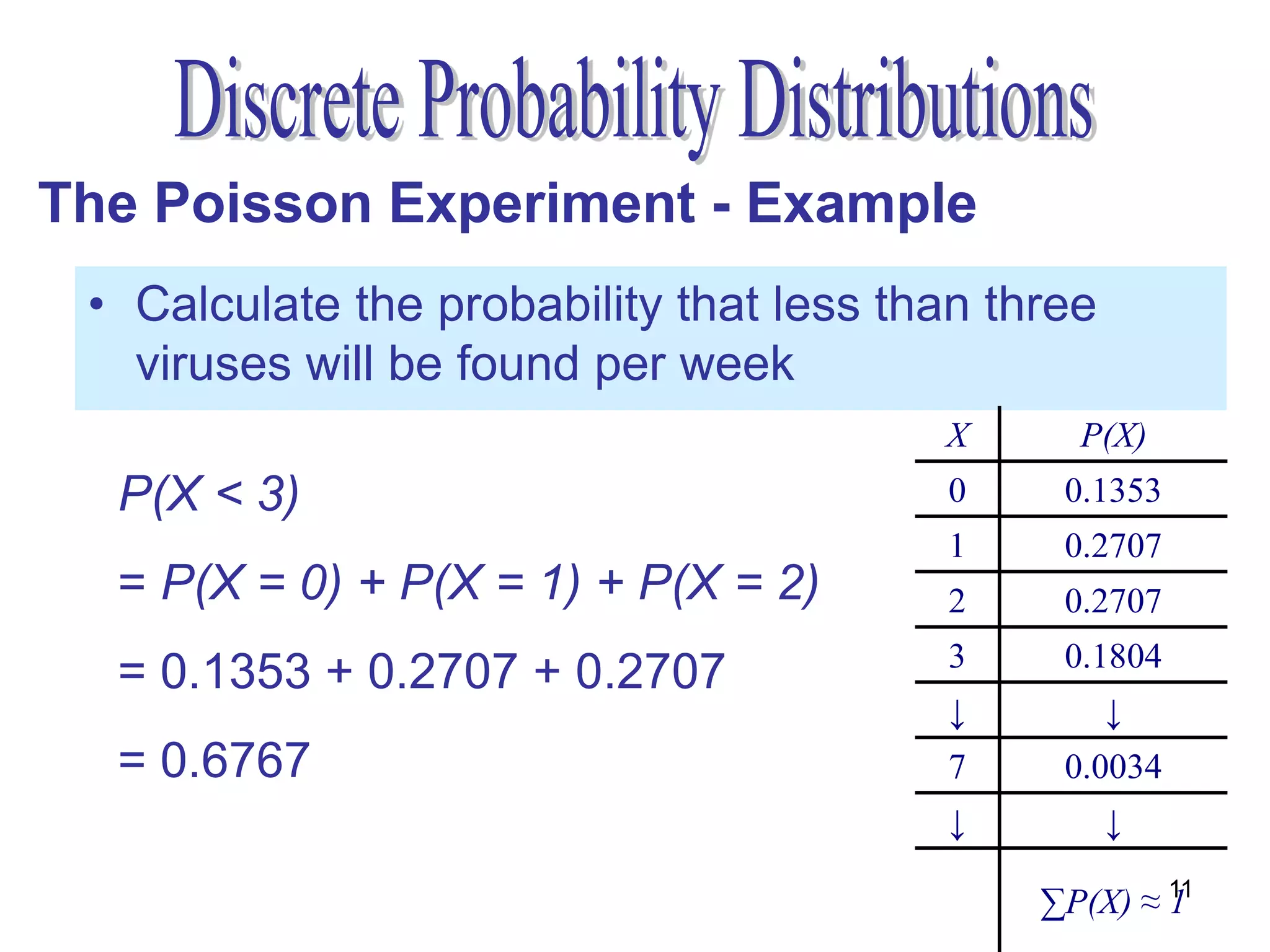
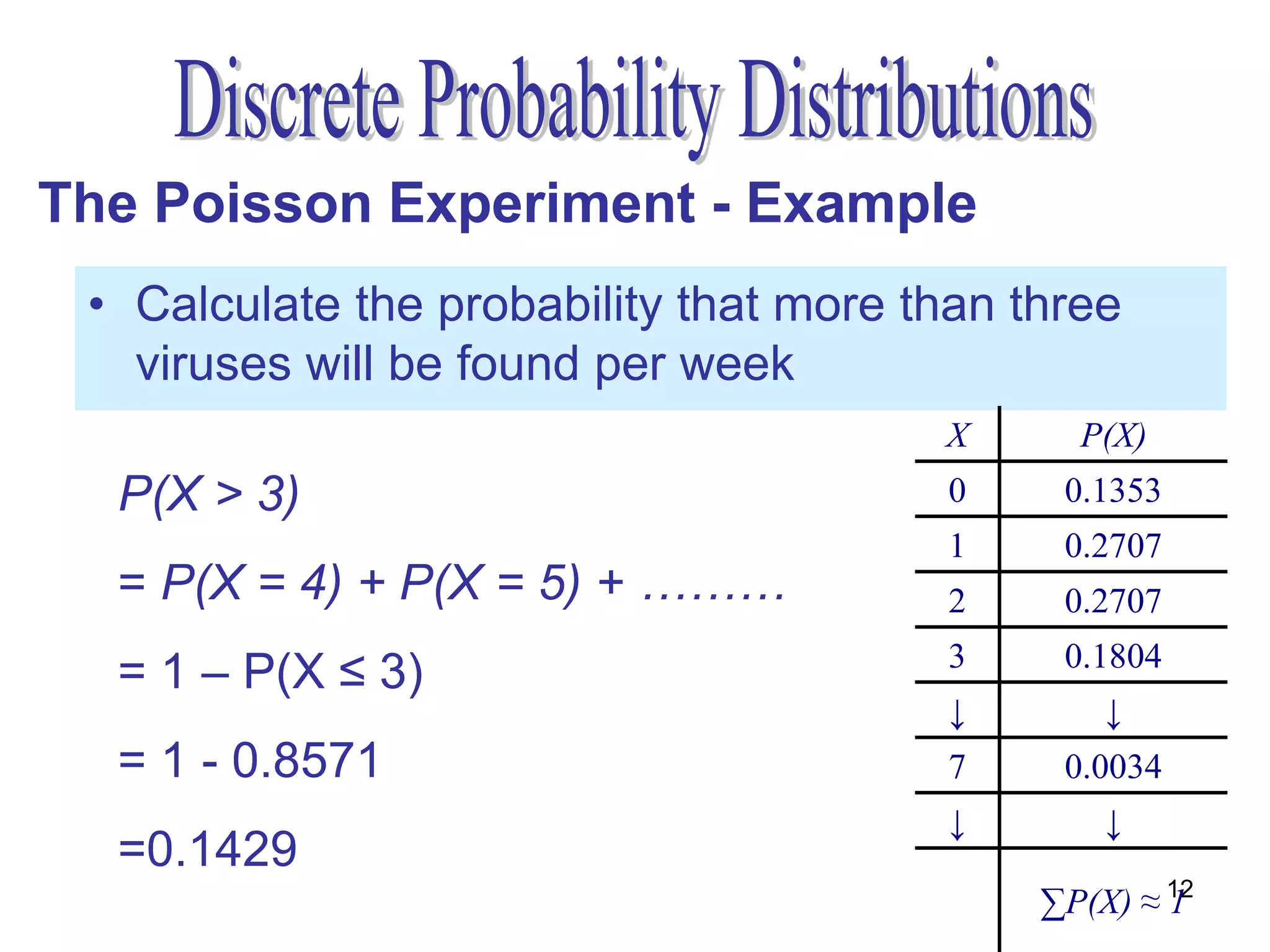
The document discusses the Poisson experiment, which is used to model rare, random events that occur independently within intervals of a specified metric like time, distance, or volume. Some key properties are that the probability of an event is the same across equal intervals and independent between intervals. Examples given include accidents, bacteria, or computer viruses. The document provides an example of calculating probabilities of certain virus counts using the Poisson distribution and defines that for a Poisson random variable, the expected value and variance are equal to the mean.