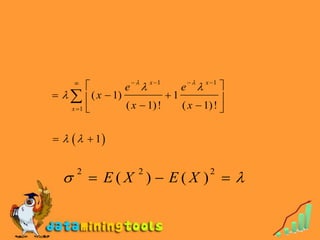The document discusses several probability distributions:
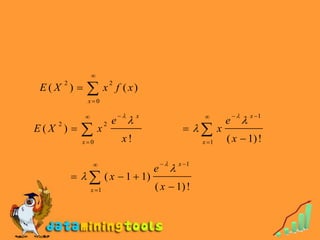
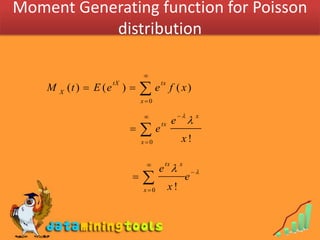
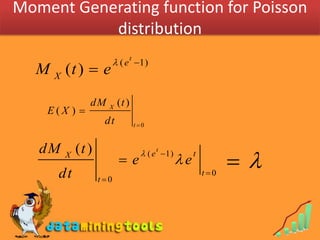
1) The Poisson distribution, which models the number of discrete events occurring in a fixed interval of time or space, with a single parameter λ representing the expected number of occurrences.
2) The Poisson process, which assumes events occur continuously with a constant average rate λ and the time between events is exponentially distributed.
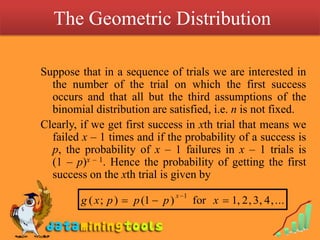
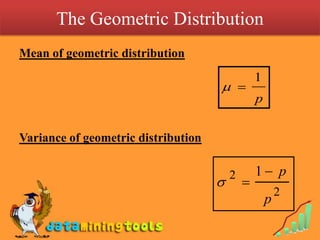
3) The geometric distribution, which models the number of trials needed for the first success in a sequence of Bernoulli trials, with probability of success p on each trial.