This document discusses discrete random variables. It begins by defining a random variable as a function that assigns a numerical value to each outcome of an experiment. There are two types of random variables: discrete and continuous. Discrete random variables have a countable set of possible values, while continuous variables can take any value within a range. Examples of discrete variables include the number of heads in a coin flip and the total value of dice. The document then discusses how to describe the probabilities associated with discrete random variables using lists, histograms, and probability mass functions.














![18/09/2017
15
The mean of these data is the statistic, ݔഥwhere
Sample mean=̅ݔ= (2+1…..+1+3) / 10 =1.6 heads
If you observed X indefinitely, what would X be on
the average?
Following are the list of possible values of X along
with their corresponding probabilities.
x1 = 0 with probability 1/8
x2 = 1 with probability 3/8
x3 = 2 with probability 3/8
x4 = 3 with probability 1/8
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 29
So the average value of X , is
(0)(1/8) + (1)(3/8) + (2)(3/8) + (3)(1/8) = 1.5 heads
Notice that X cannot be 1.5, this is merely the value
of X on the average.
The following formula can be used to compute the
mean of a discrete random variable
µµµµ ==== ΣΣΣΣ [[[[ xxxxiiii **** P(xP(xP(xP(xiiii)))) ]]]]
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discreteprobabilitydistributioncomplete-181223032728/85/Discrete-probability-distribution-complete-15-320.jpg)
![18/09/2017
16
A personnel manager in a large production facility
is investigating the number of reported on the job
accidents over a period of 1 month. We define the
random variable
X = Number of reported accidents per month.
Based on past records, she has derived the
following probability distribution for X:
0 with probability 0.50
1 with probability 0.25
2 with probability 0.10
3 with probability 0.10
4 with probability 0.05
1.0
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 31
During 50 % of the months there were no
reported accidents, 25 % of the months had
one accident, and so on.
What is the mean or average value of X?
SolutionSolutionSolutionSolution
µ = Σ [ xi * P(xi) ]
µ = (0)*(.5) +(1)*(.25) +(2)(.1)+(3)(.1)+(4)*(.05)
==== 0000....95959595 reportedreportedreportedreported accidentaccidentaccidentaccident onononon averageaverageaverageaverage perperperper
monthmonthmonthmonth....
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discreteprobabilitydistributioncomplete-181223032728/85/Discrete-probability-distribution-complete-16-320.jpg)

![18/09/2017
18
For the con flipping example
σ2222 ==== ΣΣΣΣxxxx2222P(x)P(x)P(x)P(x) ---- 2222
= [(0)2*(1/8) +(1)2*(3/8) +(2)2.
(3/8)+(3)2*(1/8)] –(1.5)2
= 3-2.25 = 0.75
EXAMPLEEXAMPLEEXAMPLEEXAMPLE 5555....5555
DetermineDetermineDetermineDetermine thethethethe variancevariancevariancevariance andandandand standardstandardstandardstandard deviationdeviationdeviationdeviation
ofofofof thethethethe randomrandomrandomrandom variablevariablevariablevariable describeddescribeddescribeddescribed inininin exampleexampleexampleexample
5555....4444 concerningconcerningconcerningconcerning onononon thethethethe jobjobjobjob accidentsaccidentsaccidentsaccidents
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 35
A personnel manager in a large production facility is
investigating the number of reported on the job accidents
over a period of 1 month. We define the random variable
X = Number of reported accidents per month.
Based on past records, she has derived the following
probability distribution for X:
0 with probability 0.50
1 with probability 0.25
2 with probability 0.10
3 with probability 0.10
4 with probability 0.05
1.0
Determine the variance and the standard deviation of the
random variable X defined above.
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discreteprobabilitydistributioncomplete-181223032728/85/Discrete-probability-distribution-complete-18-320.jpg)
![18/09/2017
19
XXXX P(x)P(x)P(x)P(x) x.Px.Px.Px.P(x)(x)(x)(x) XXXX2222.P(x).P(x).P(x).P(x)
0 0.5 0 0
1 0.25 0.25 0.25
2 0.1 0.2 0.4
3 0.1 0.3 0.9
4 0.05 0.2 0.8
Total 1.0 0.95 2.35
So, µ = Σ [ xi * P(xi) ]= 0.95 accident
σ2222 ==== ΣΣΣΣx2P(x) - 2 = 2.35 – (.95)2 = 1.45 accident 2222
σ = 1.45 ൌ 1.20 accidents
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 37
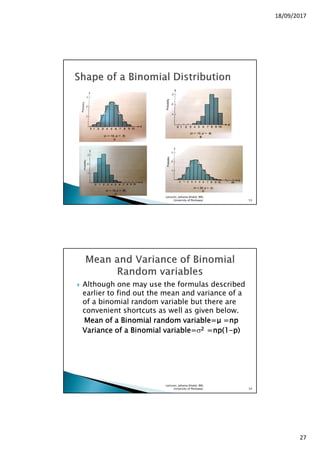
Three popular discrete random variables are
Binomial, hypergeometric and Poisson
random variables.
We will study only Binomial Random variable.
A binomial random variable counts the
number of successes out of n independent
trials.
The random variable X representing the
number of heads in three flips of a coin is a
special type of discrete random variable,
called a binomial random variable.
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discreteprobabilitydistributioncomplete-181223032728/85/Discrete-probability-distribution-complete-19-320.jpg)











![18/09/2017
32
X = no of vouchers in error out of 20 randomly
selected vouchers.
n=20, p= 0.10, 1-p = 0.90
1111---- WhatWhatWhatWhat isisisis thethethethe probabilityprobabilityprobabilityprobability thatthatthatthat atatatat leastleastleastleast threethreethreethree
vouchersvouchersvouchersvouchers willwillwillwill containcontaincontaincontain anananan errorerrorerrorerror????
If there are 3 or more than 3 vouchers with error
then this condition will satisfy, that is
P(X≥3) = P(x=3) +P(x=4)+ P(x=5)+….+P(x=20)
OR we may write it as
P(X≥3) = 1- P(X<3) = 1- [P(x=0) +P(x=1)
+P(x=2)]
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 63
P(X≥3) = 1- [P(0) +P(1) +P(2)]
P(X≥3) = 1- [0.122 +0.270+0.285]
P(X≥3) = 0.323
The probability that at leas three vouchers will
contain an error is 32.3%
2222---- WhatWhatWhatWhat isisisis thethethethe probabilityprobabilityprobabilityprobability thatthatthatthat nononono moremoremoremore thanthanthanthan
oneoneoneone containscontainscontainscontains anananan error?error?error?error?
P(X≤1) = P(x=0) +P(x=1)
P(X≤1) = 0.122 +0.270 =0.392
Lecturer, Johaina Khalid, IMS,
University of Peshawar. 64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discreteprobabilitydistributioncomplete-181223032728/85/Discrete-probability-distribution-complete-32-320.jpg)

