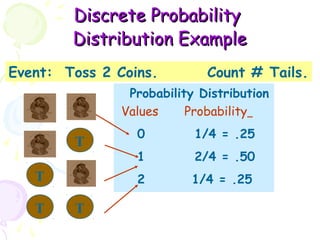
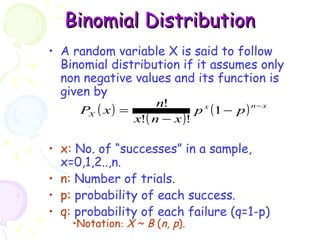
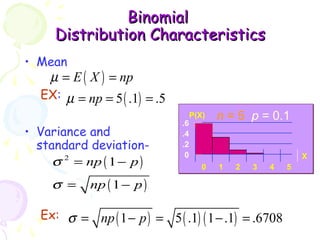
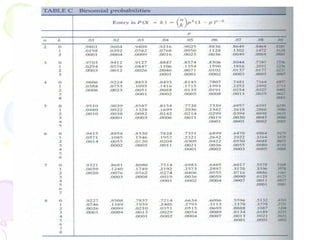
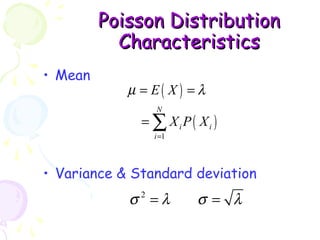
This document provides information on probability distributions, including discrete and binomial distributions. It discusses the assumptions and characteristics of binomial distributions, using examples to show how they work. It also covers the Poisson distribution, its assumptions and function, and gives an example of calculating probabilities using the Poisson. The document ends with questions for practice with binomial and Poisson distributions.