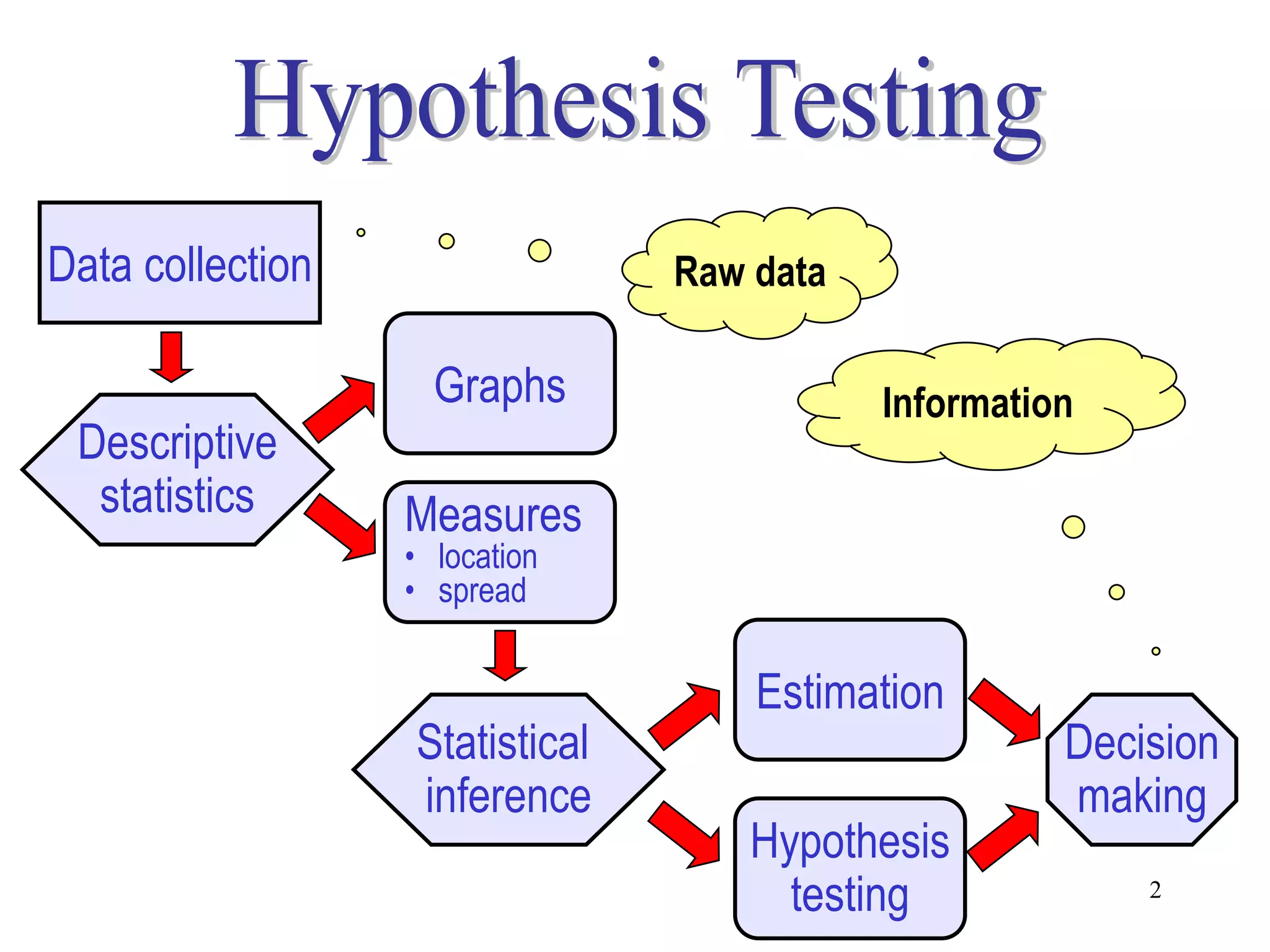
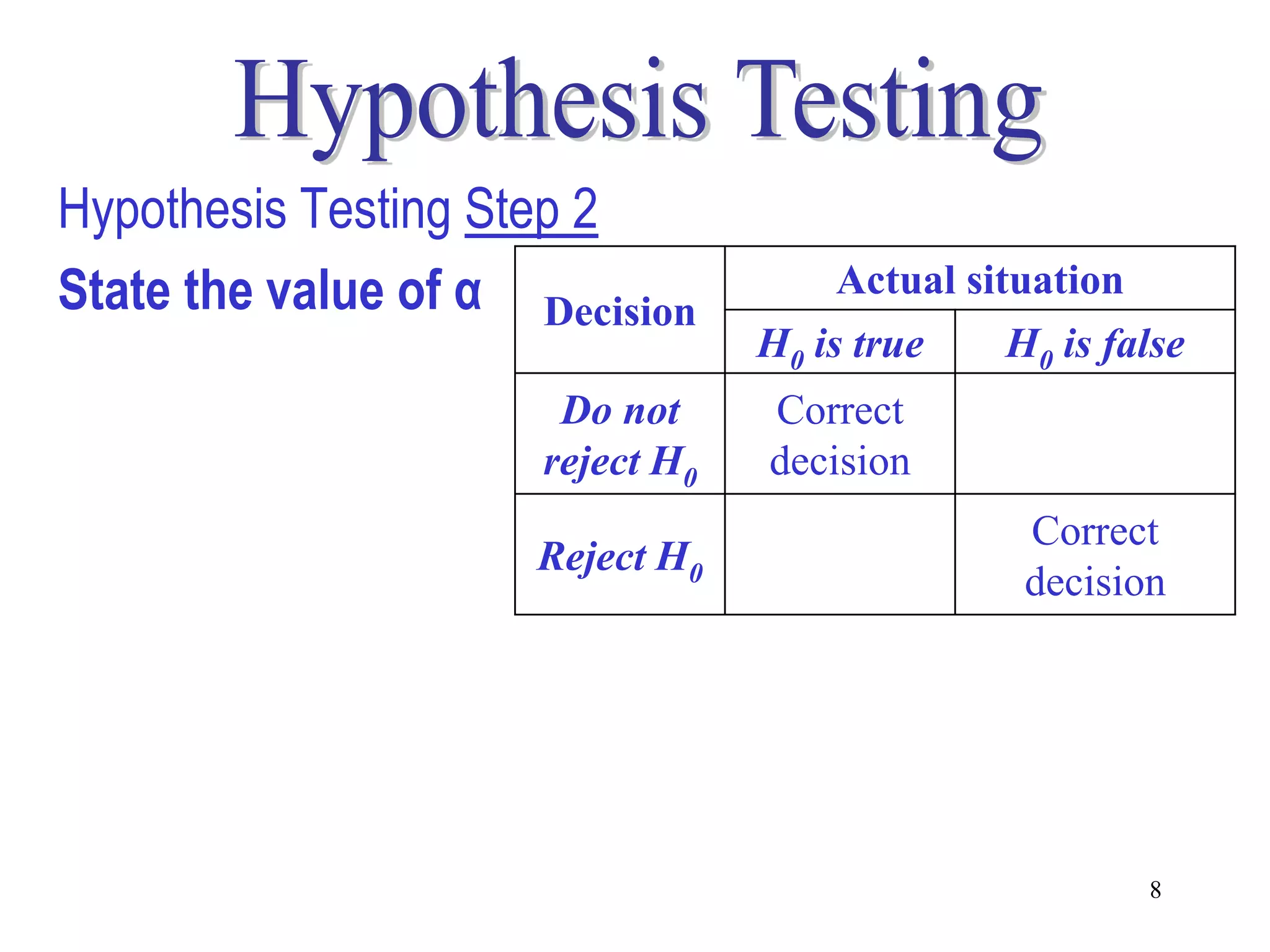
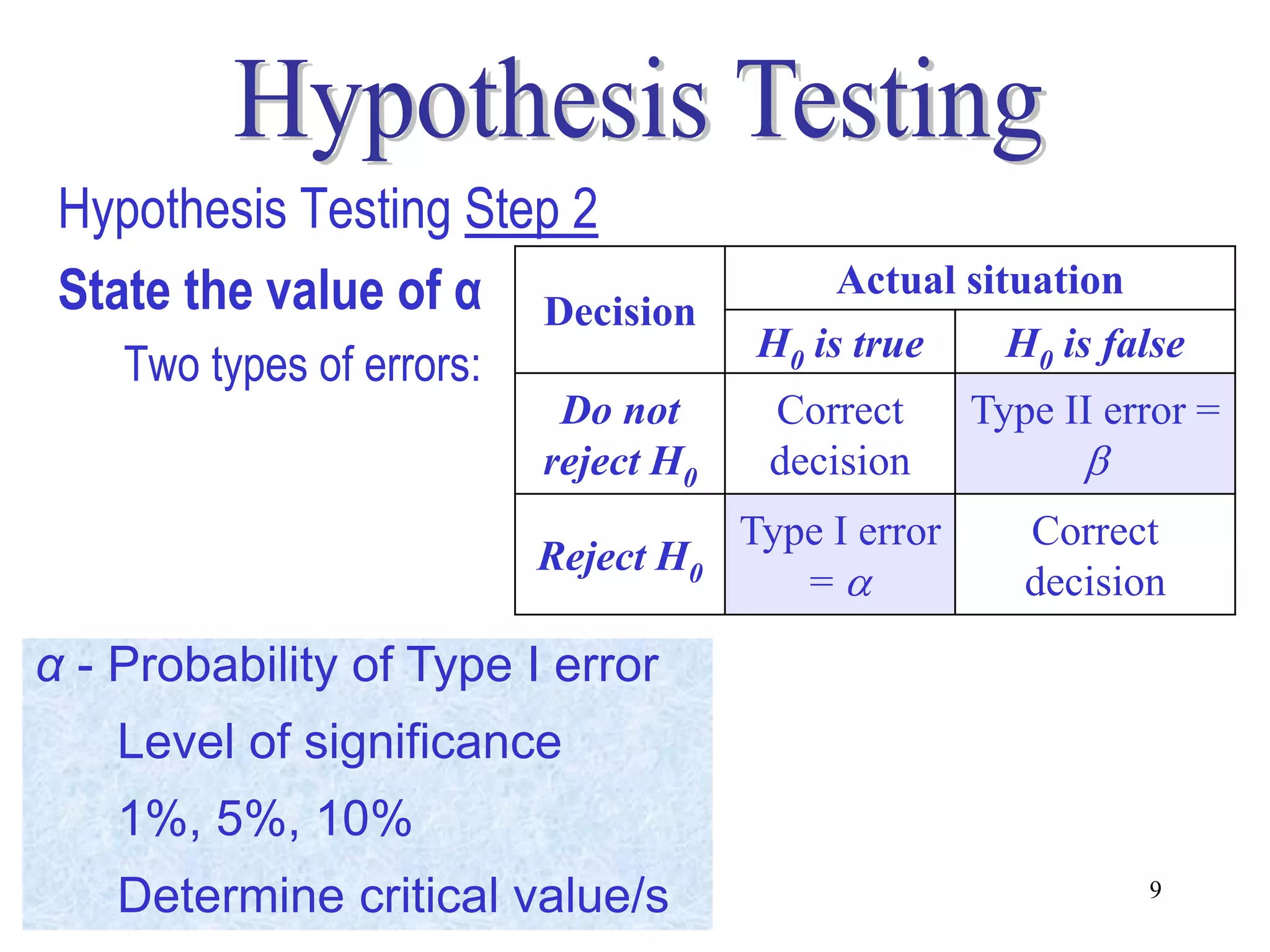
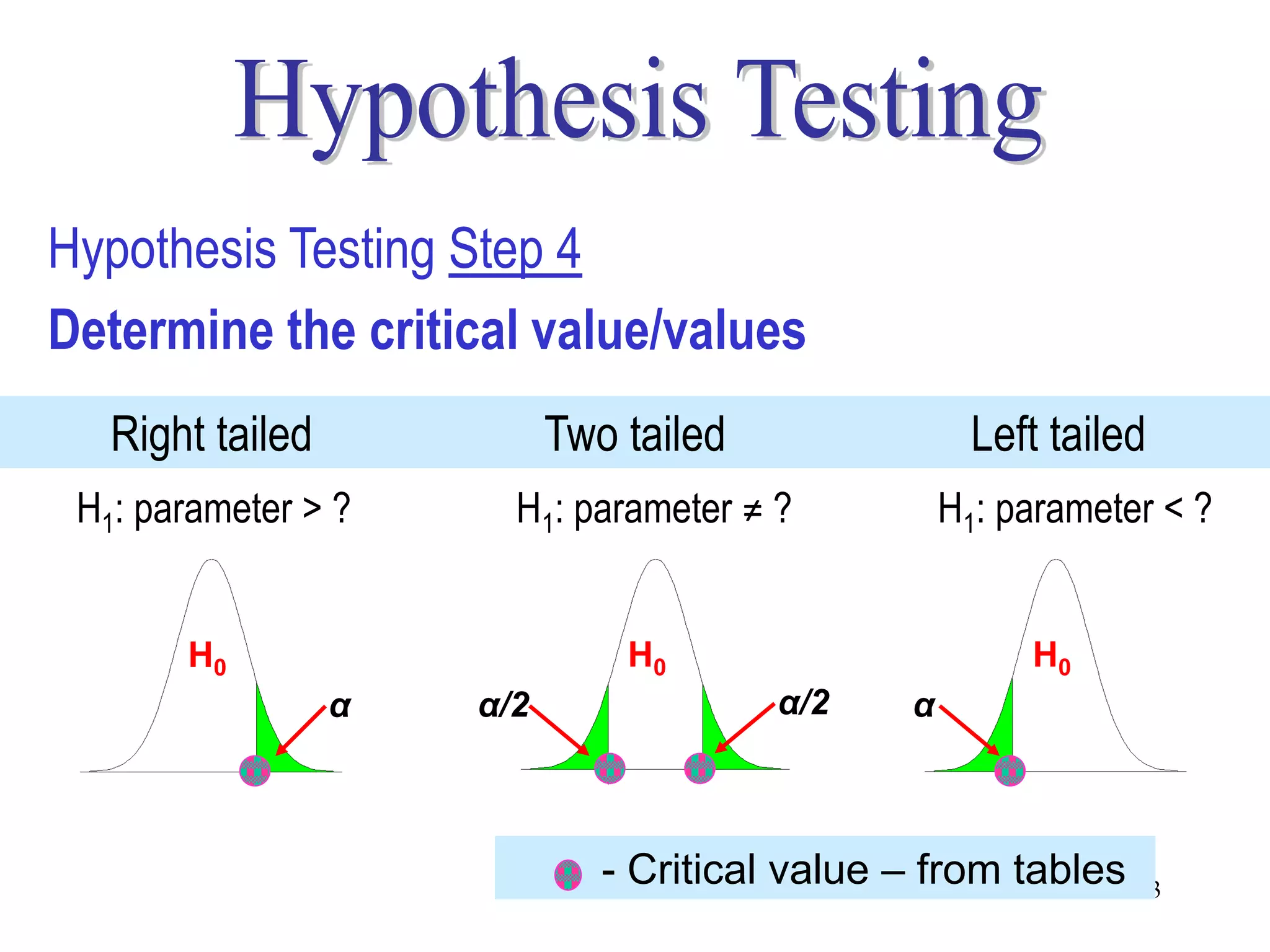
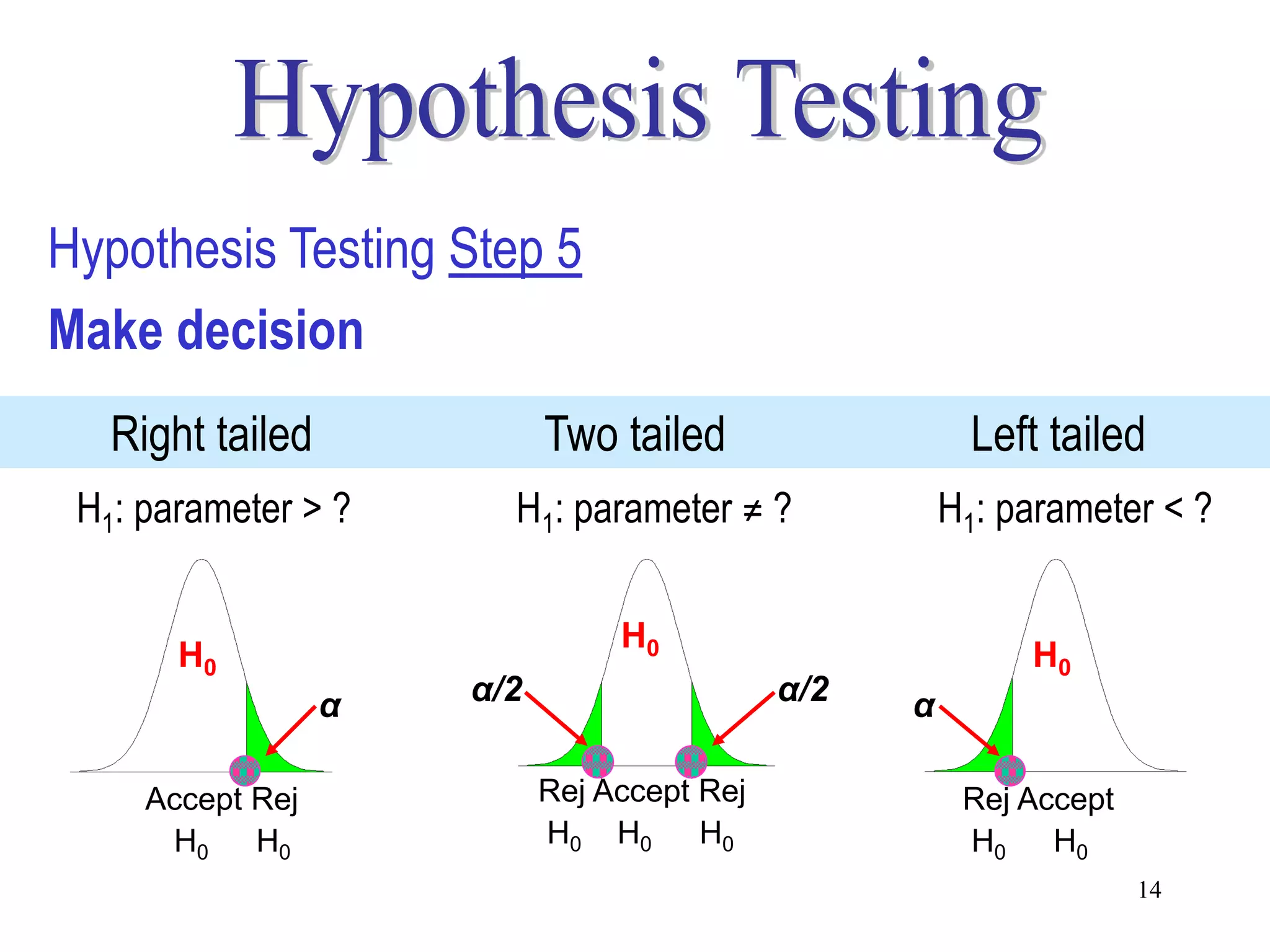
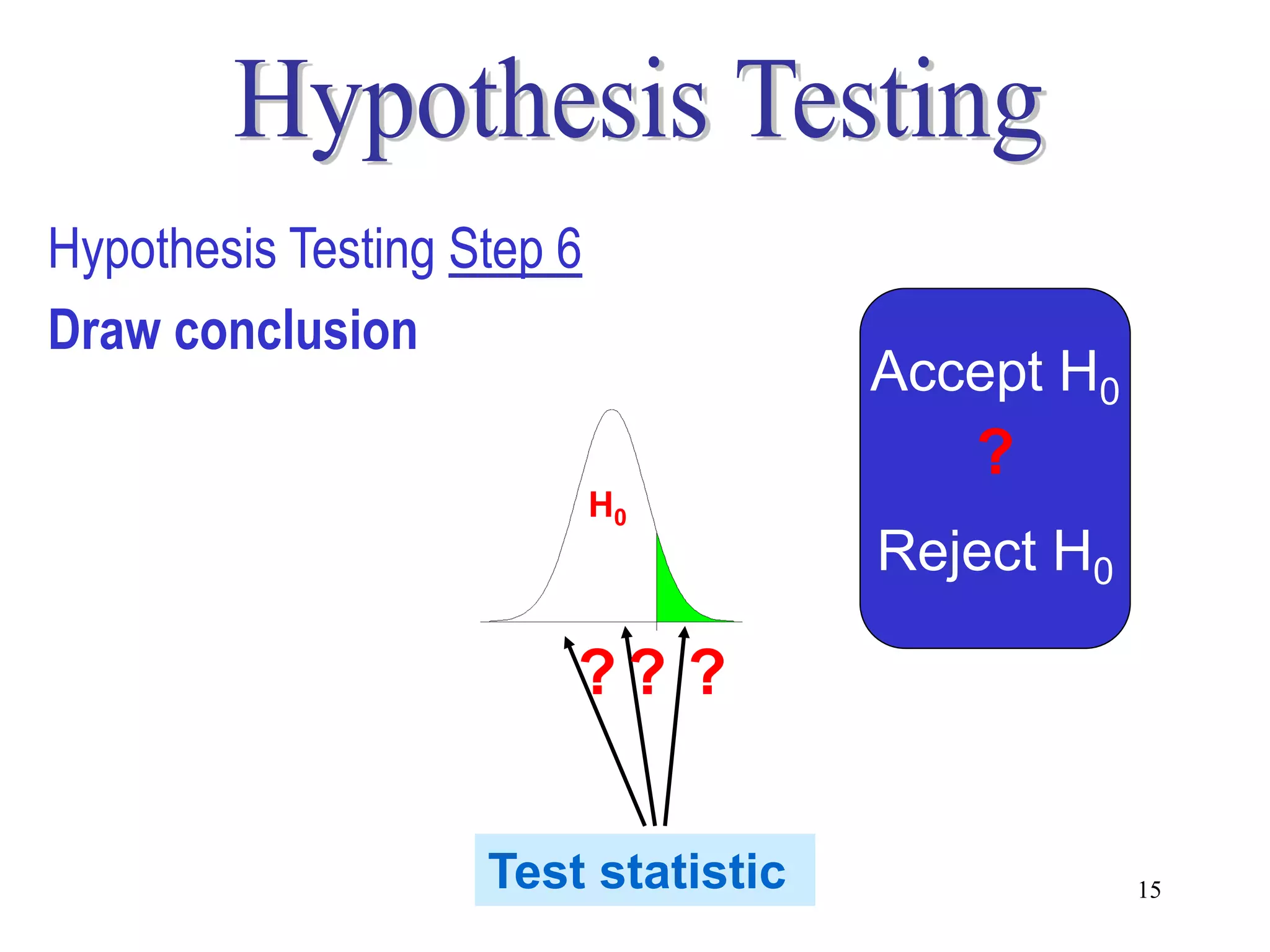
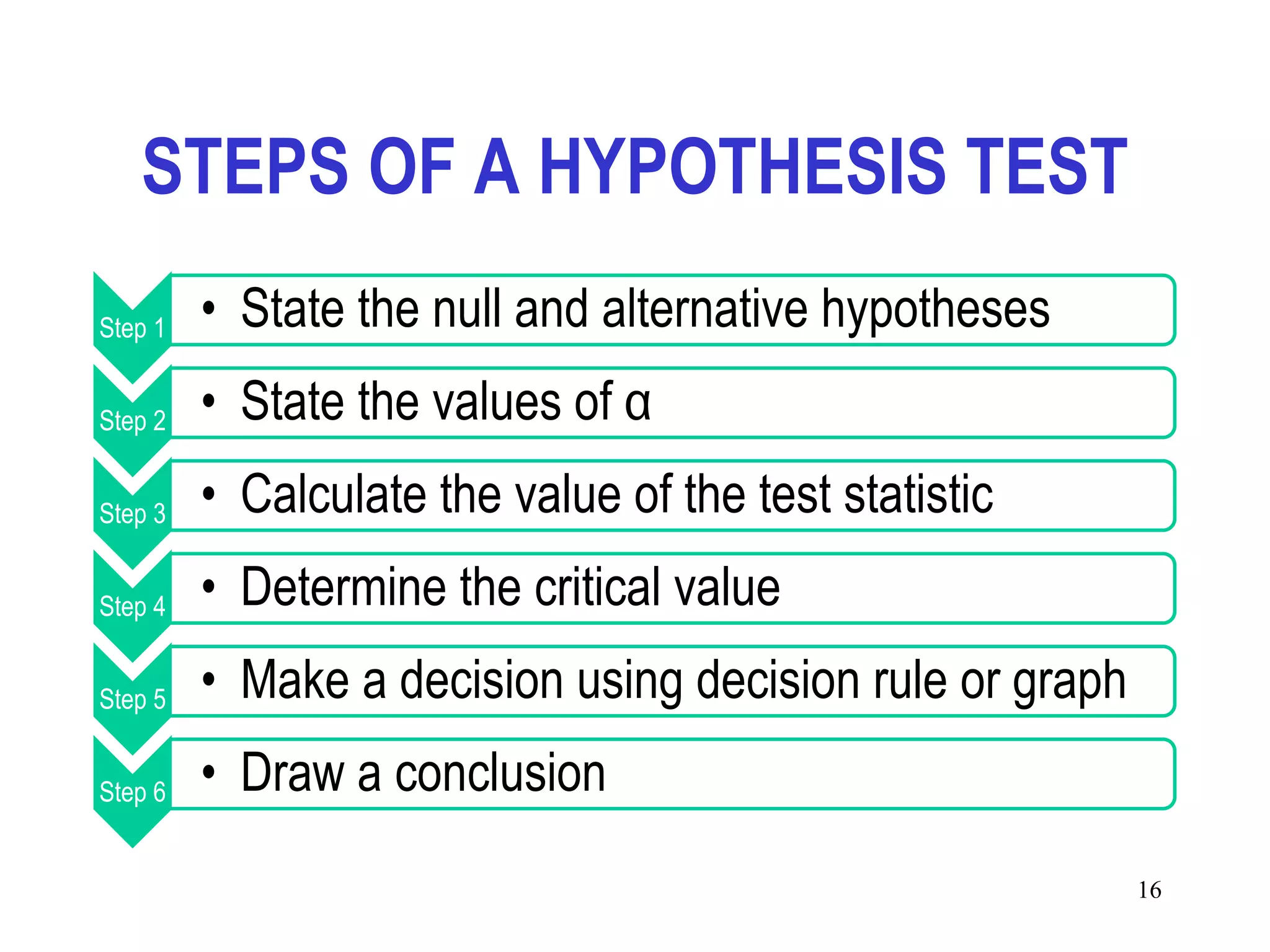
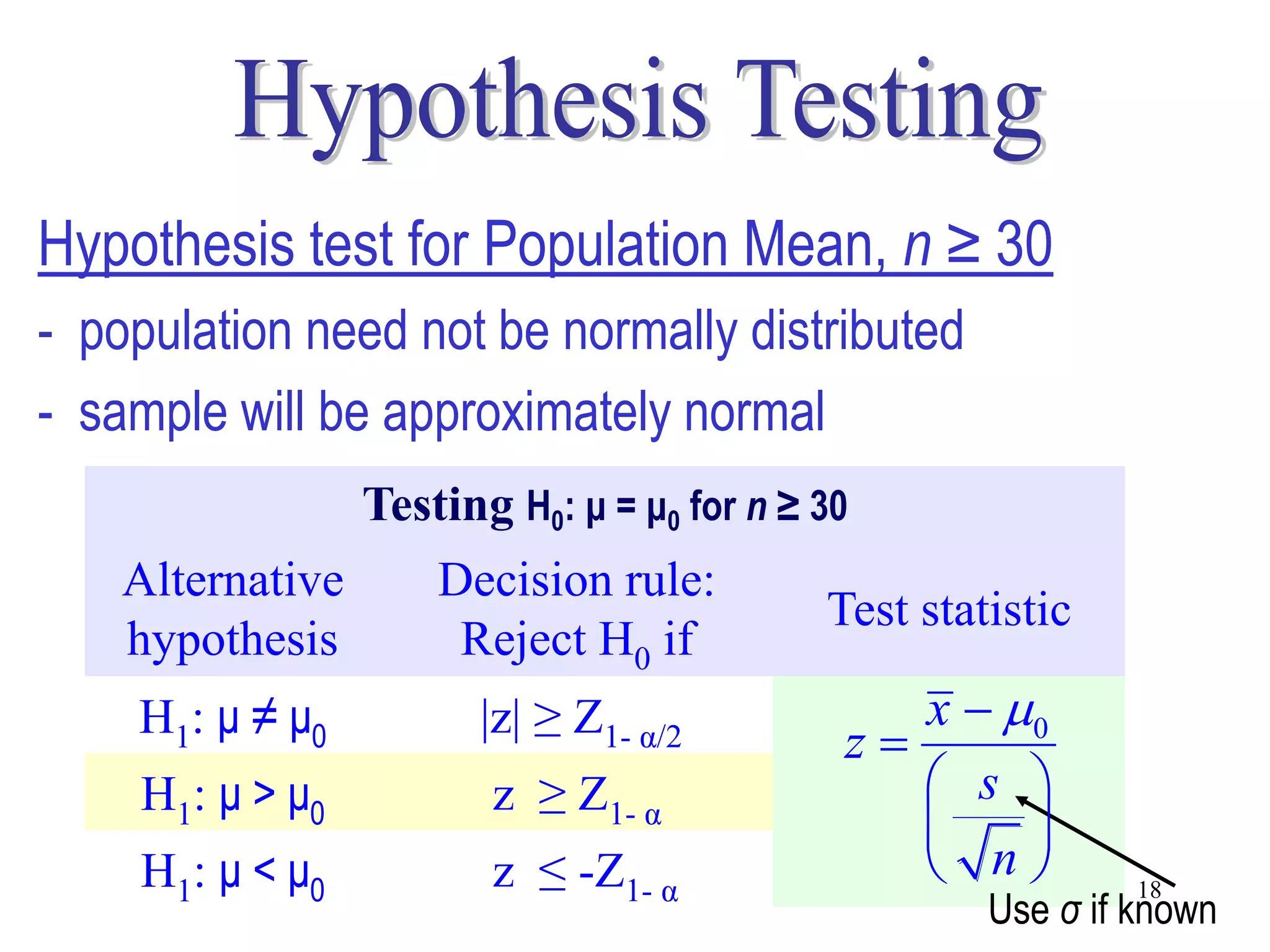
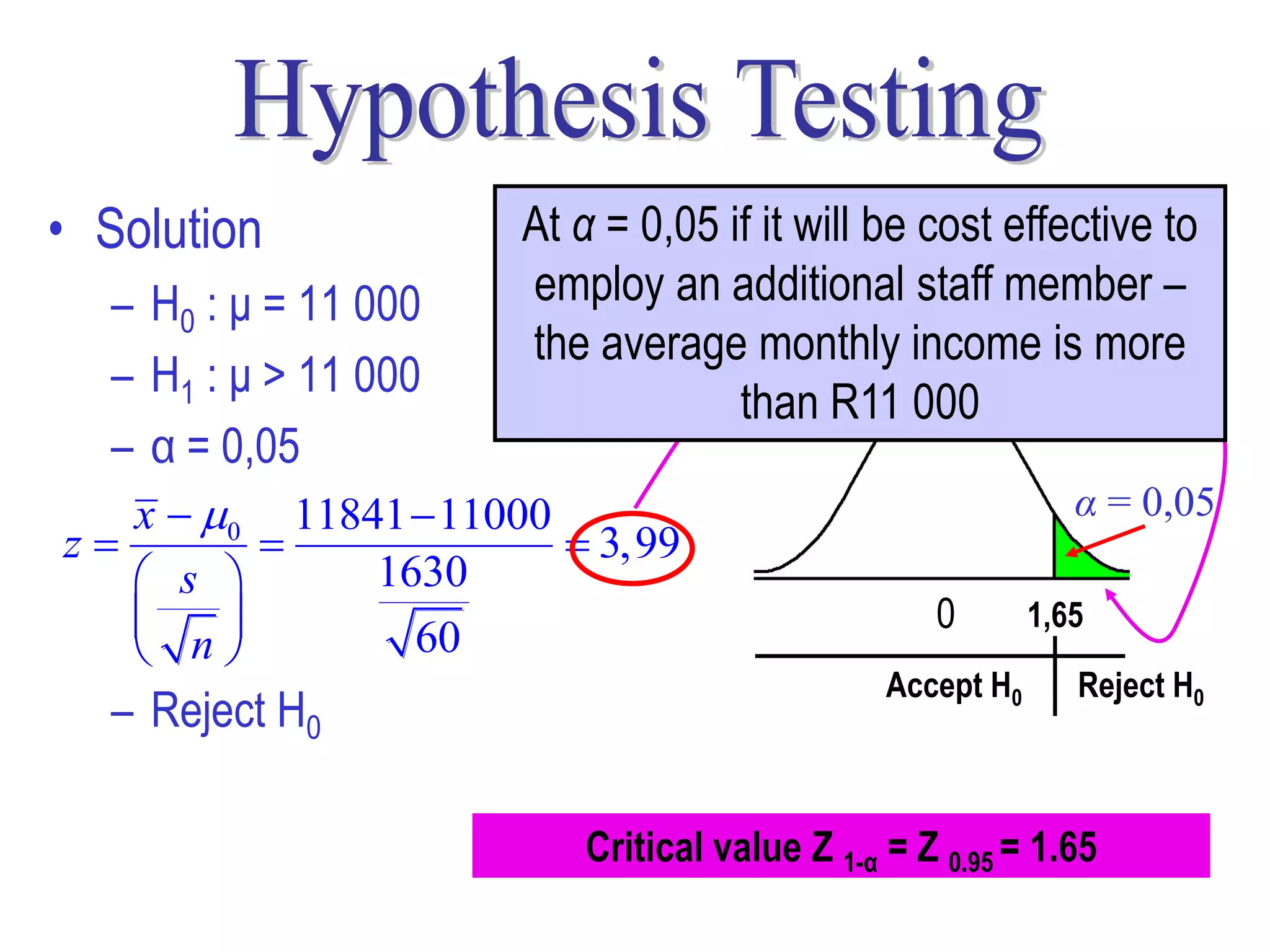
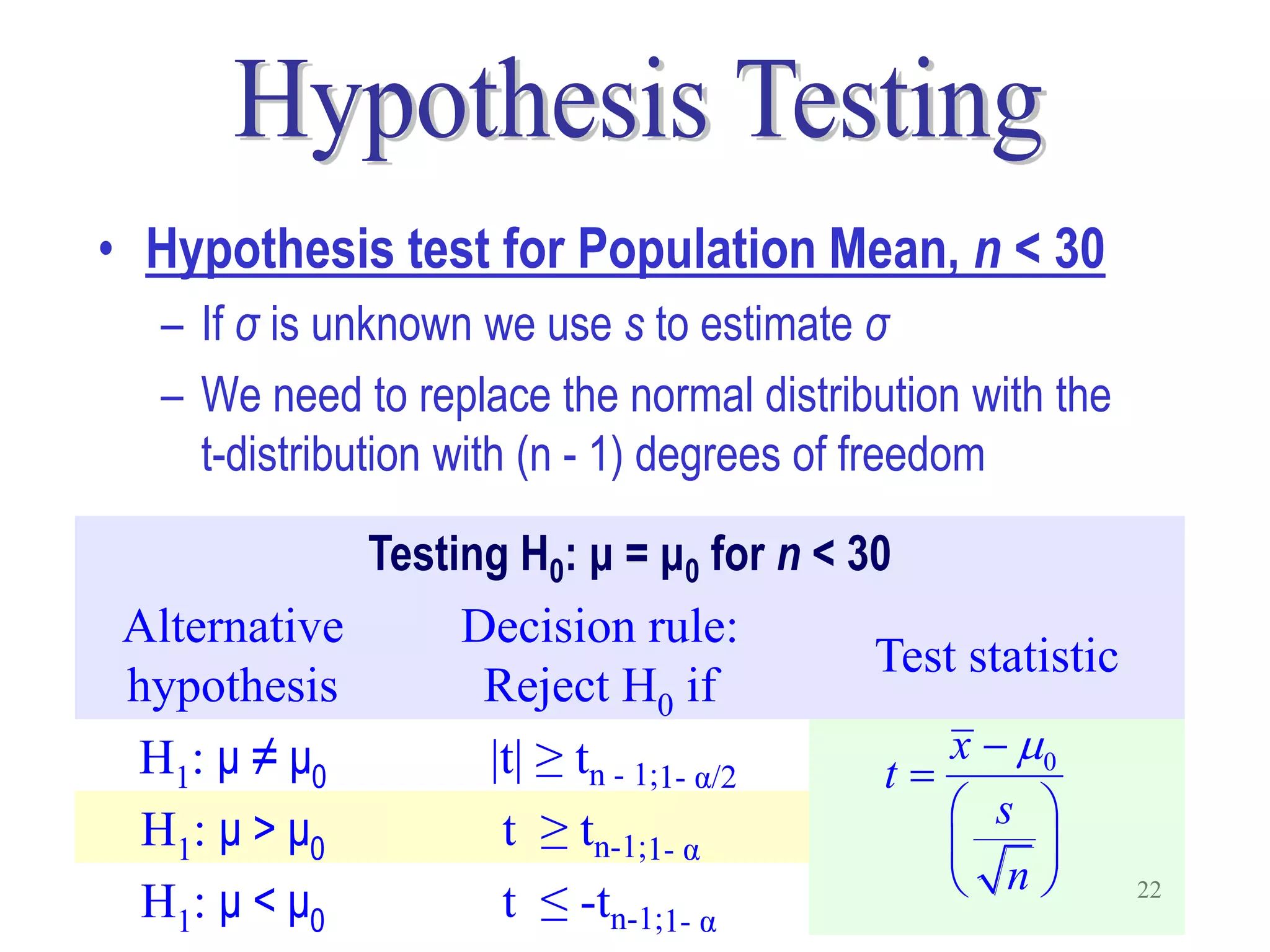
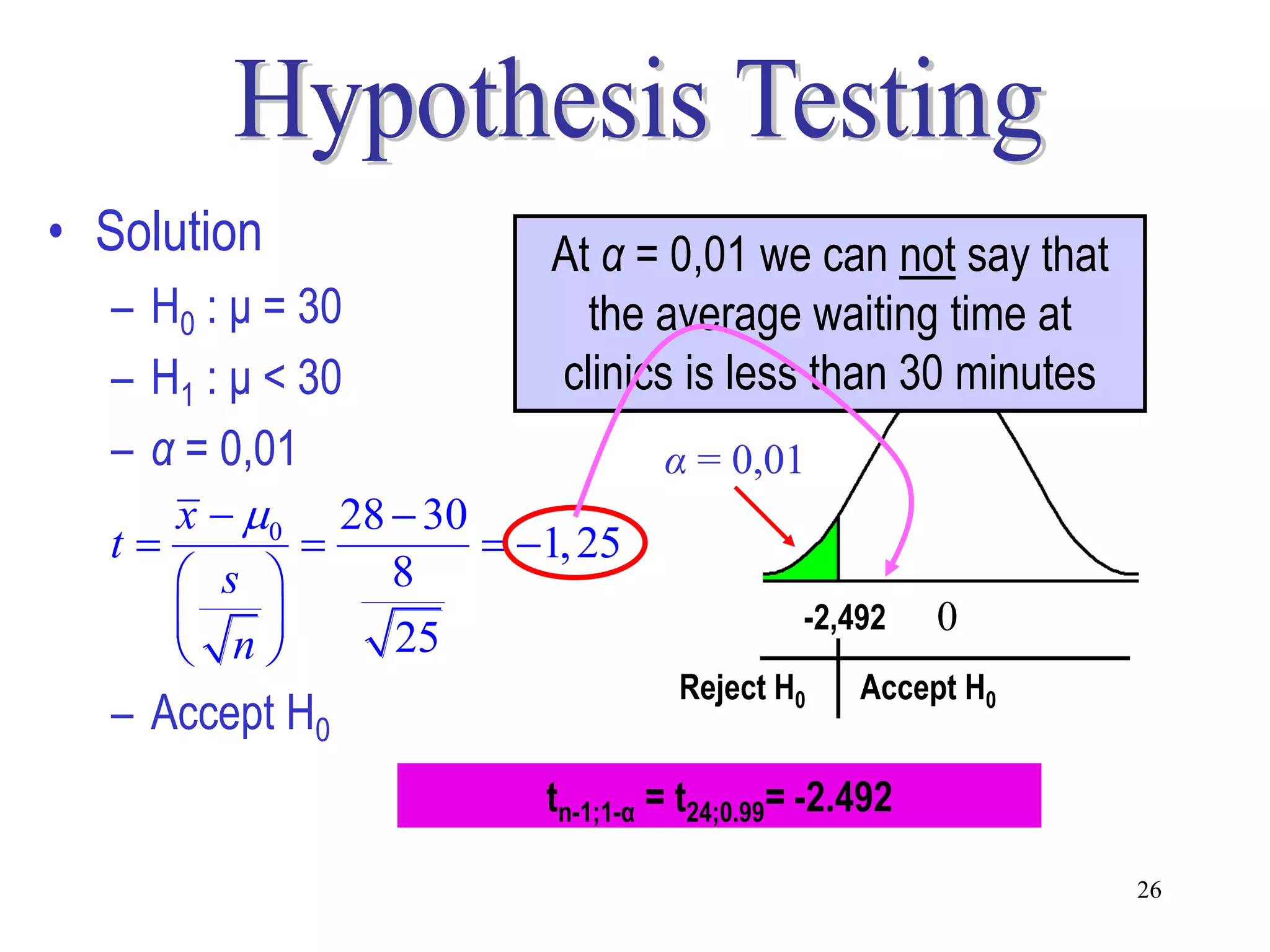
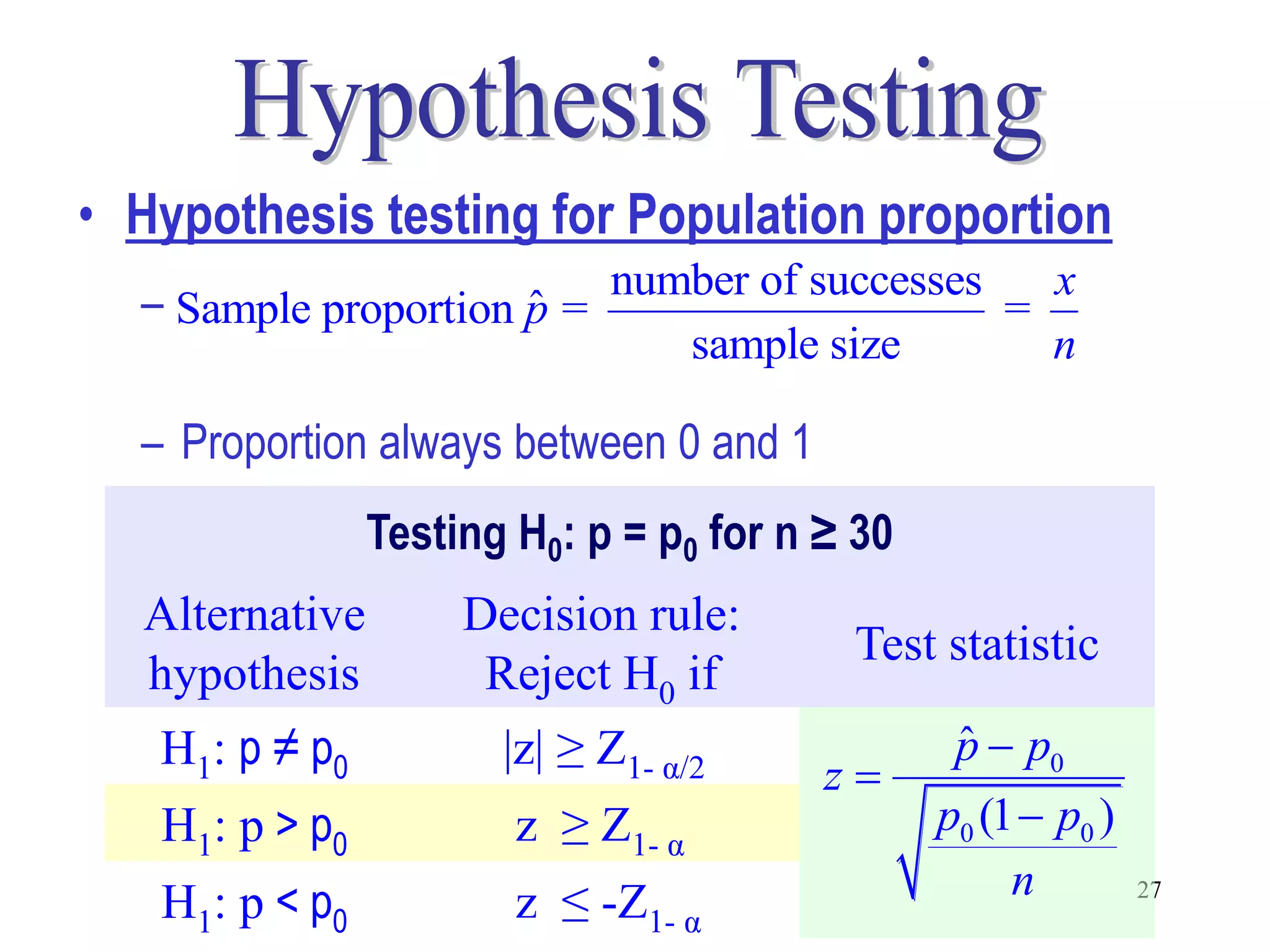
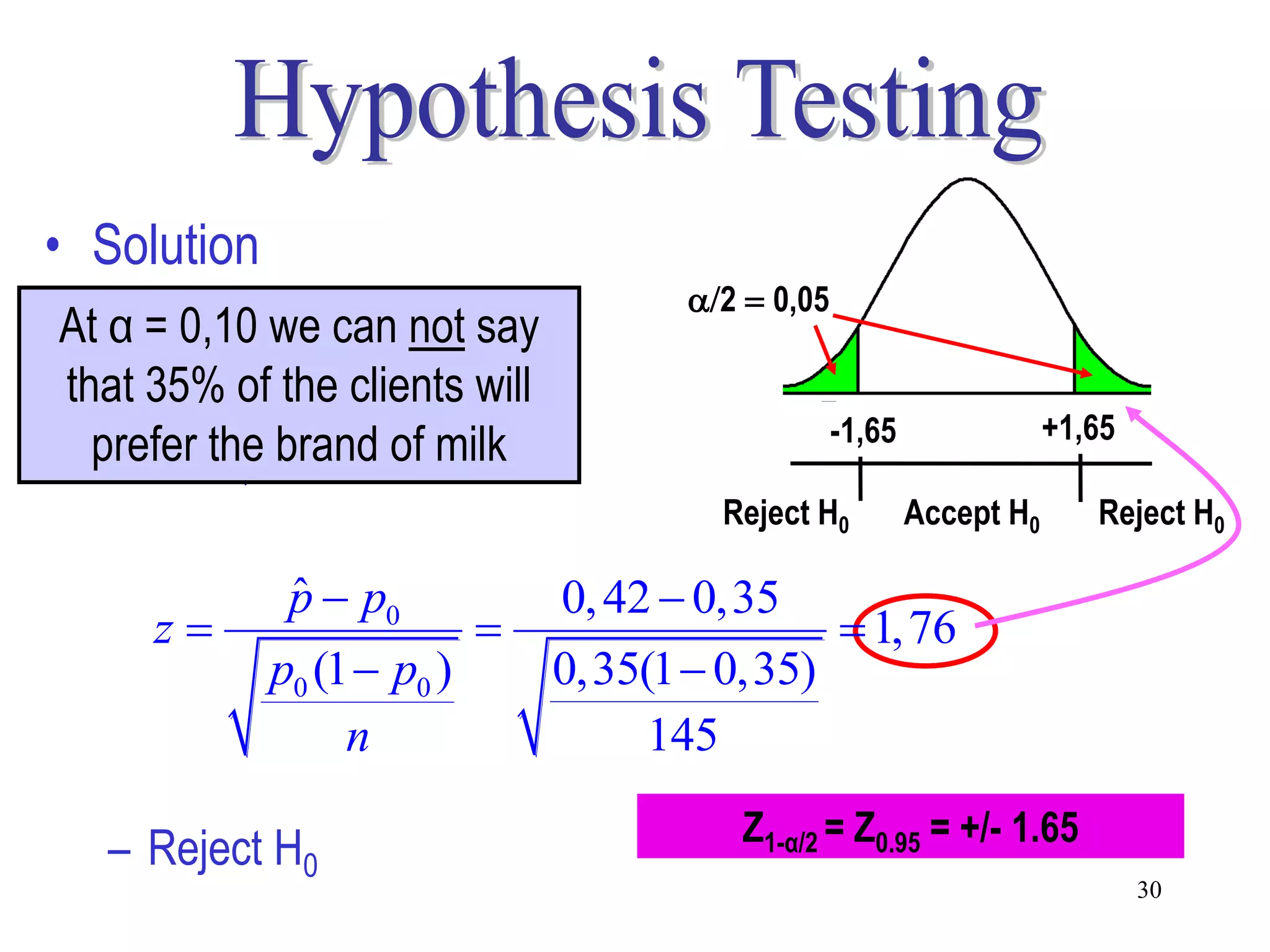
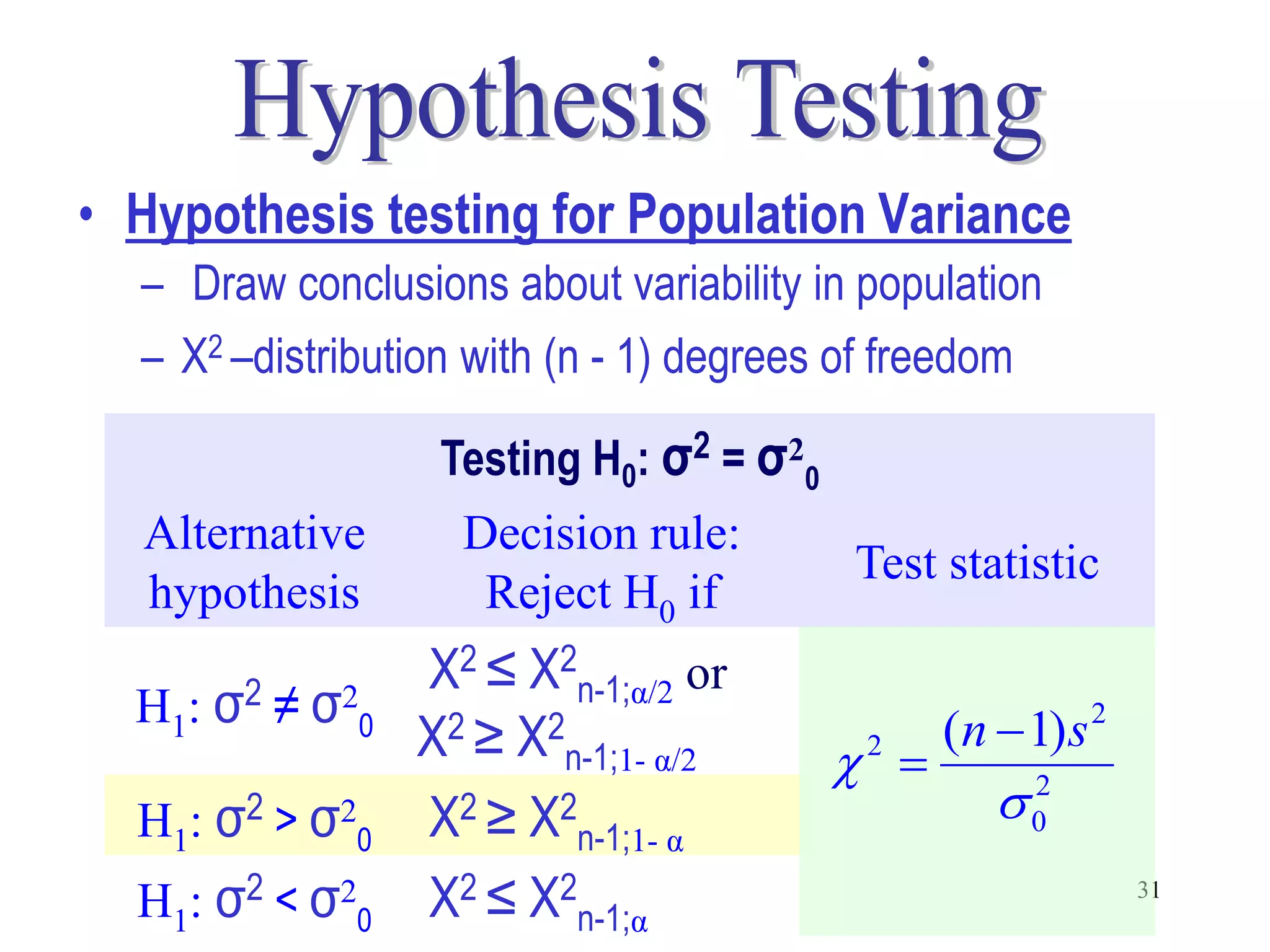
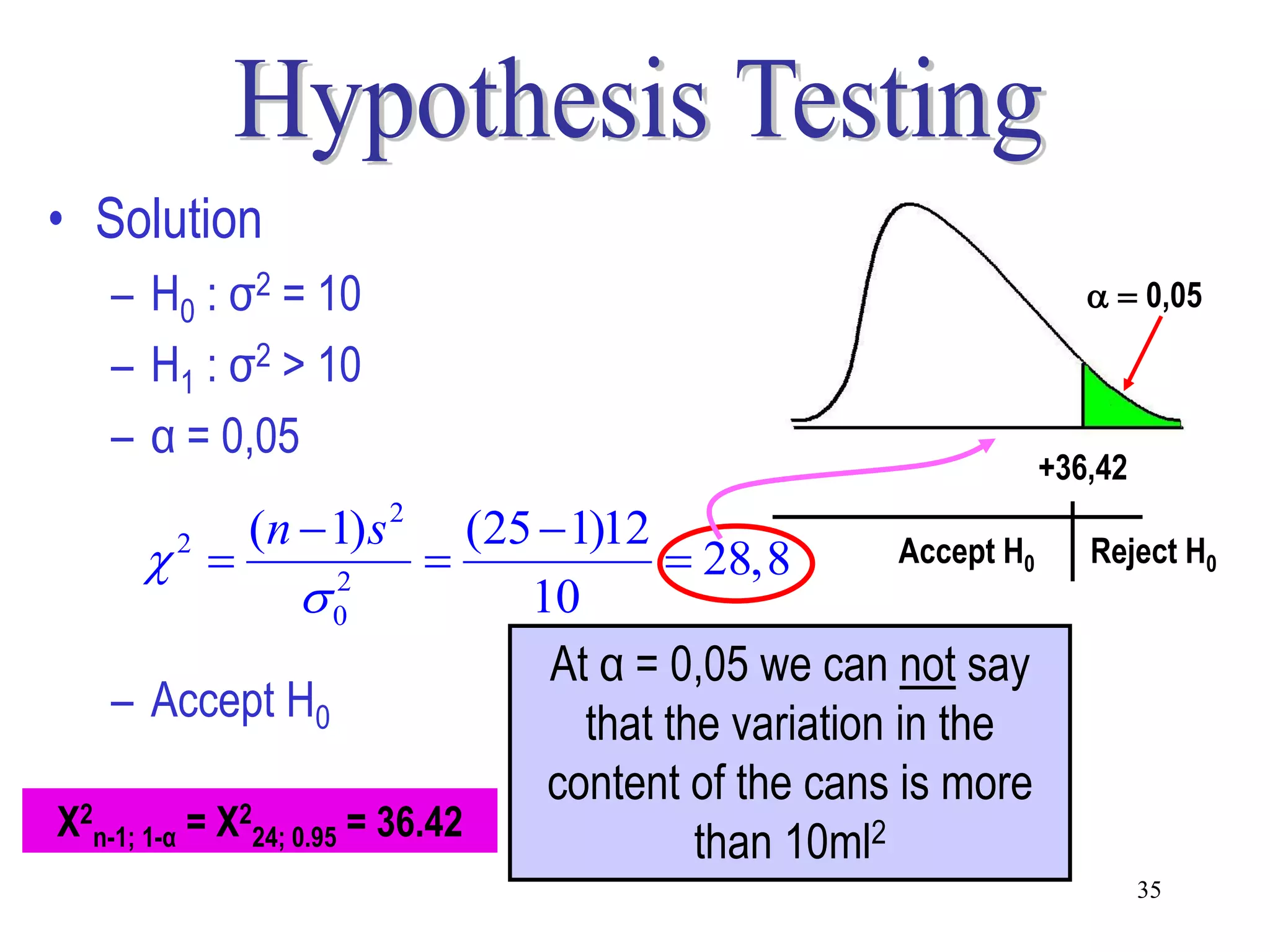
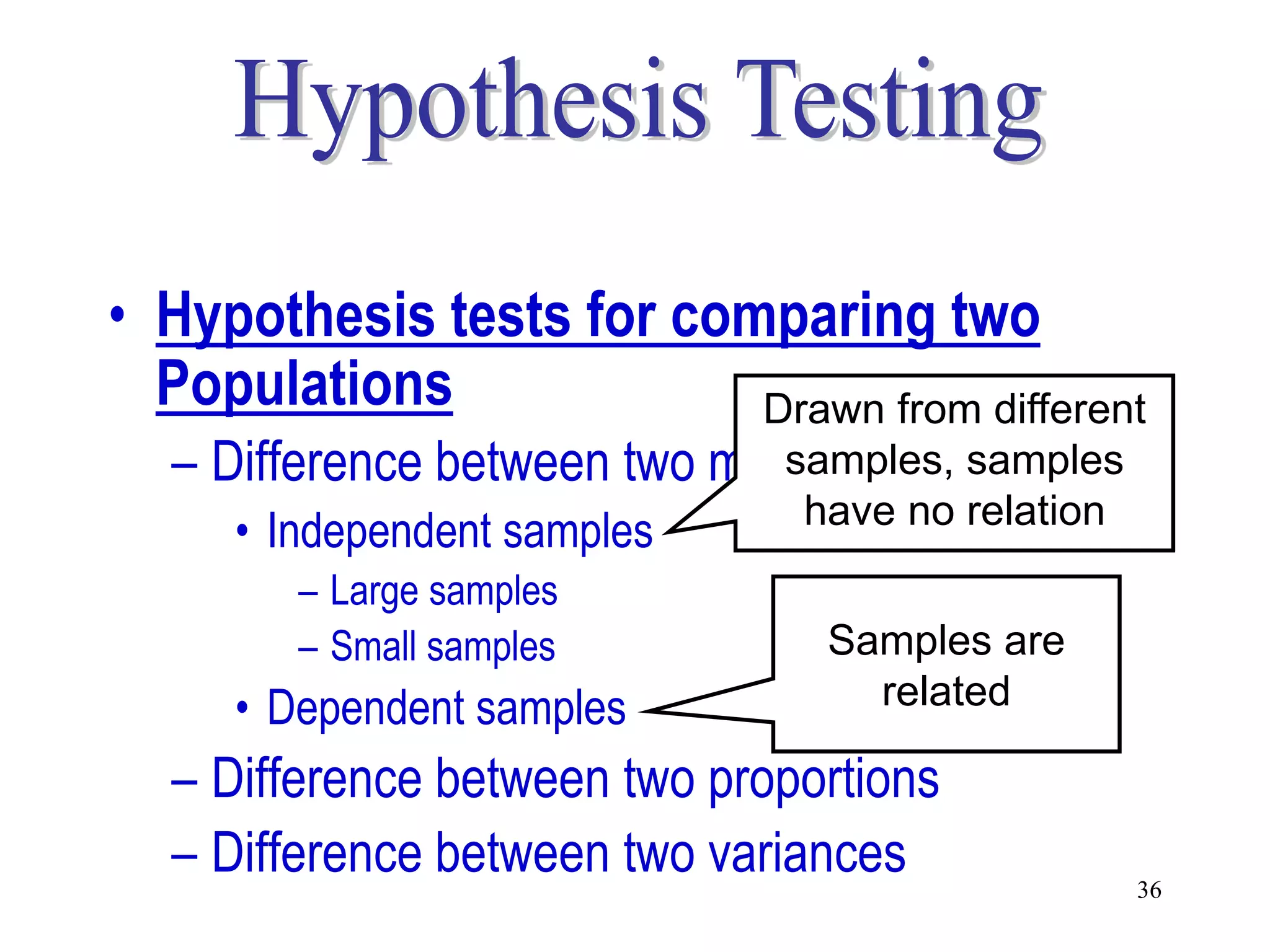
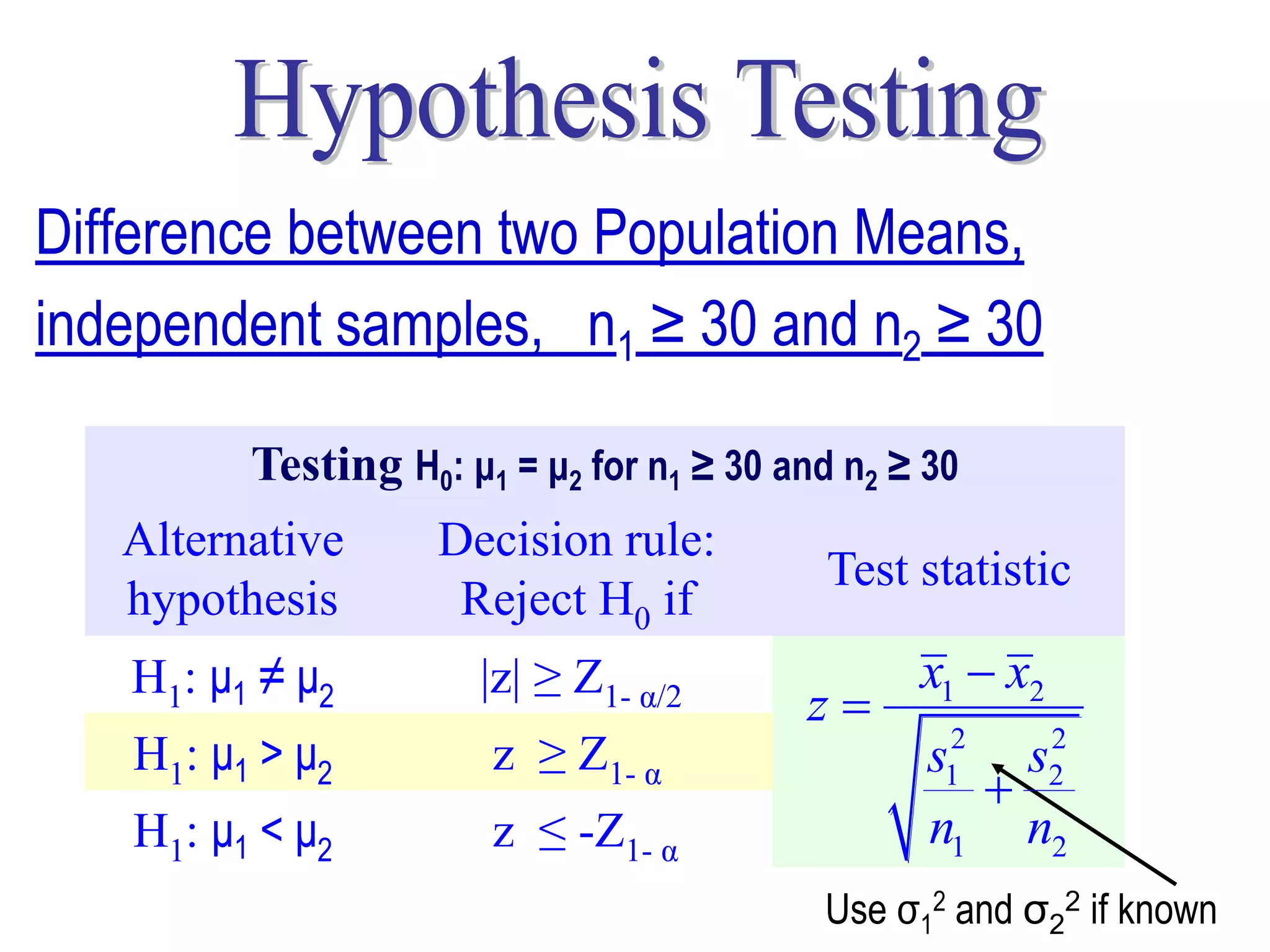
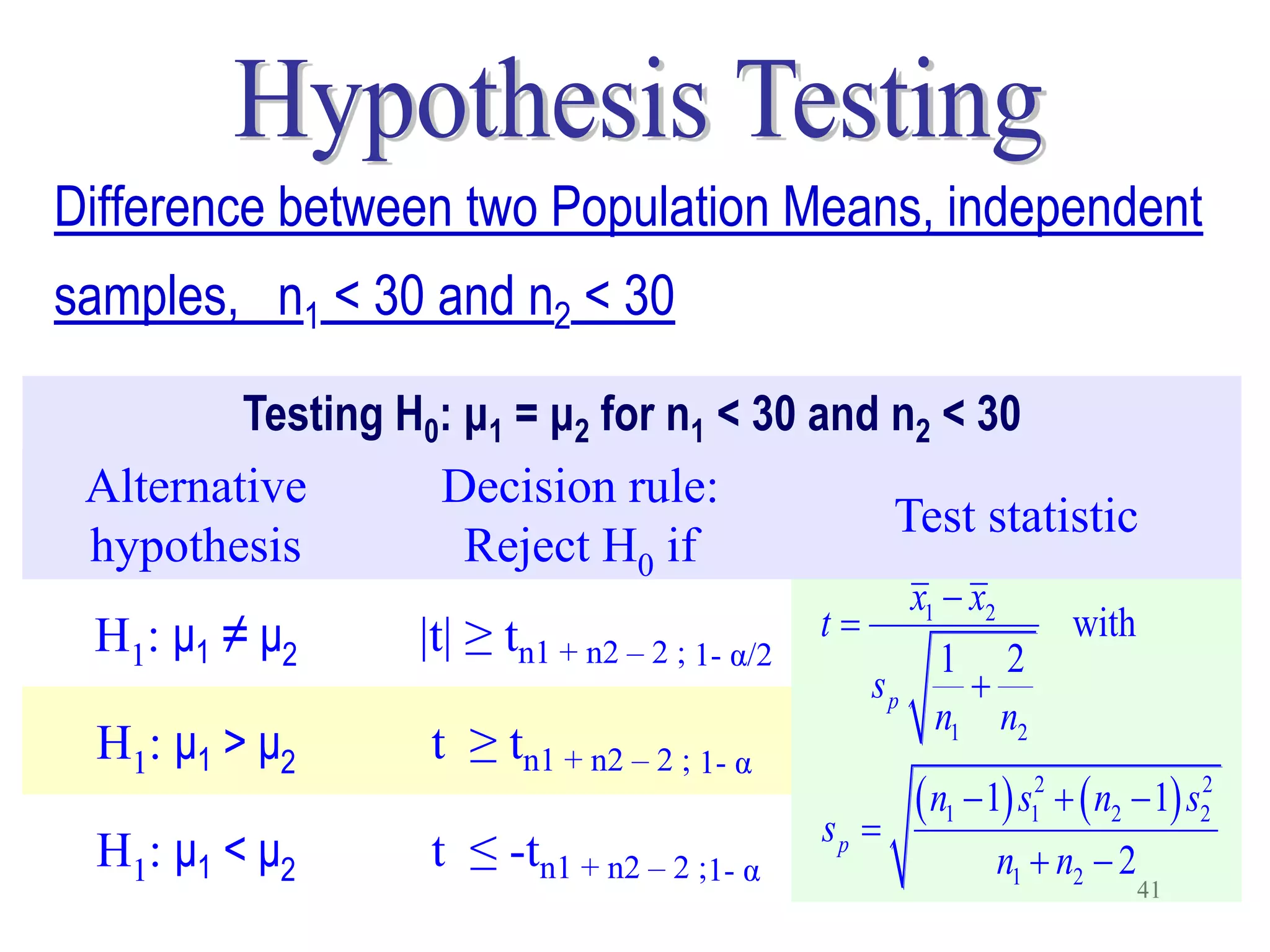
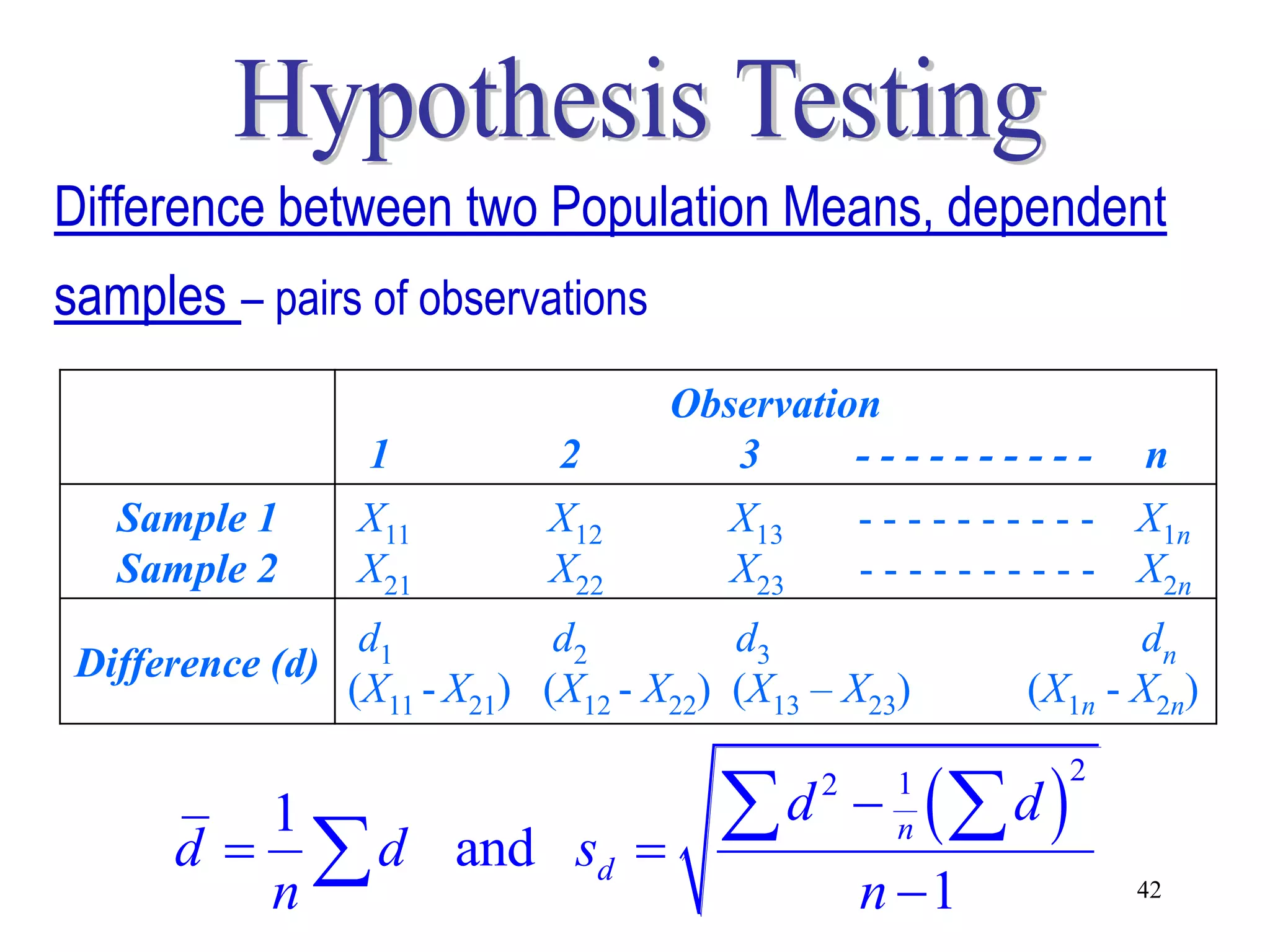
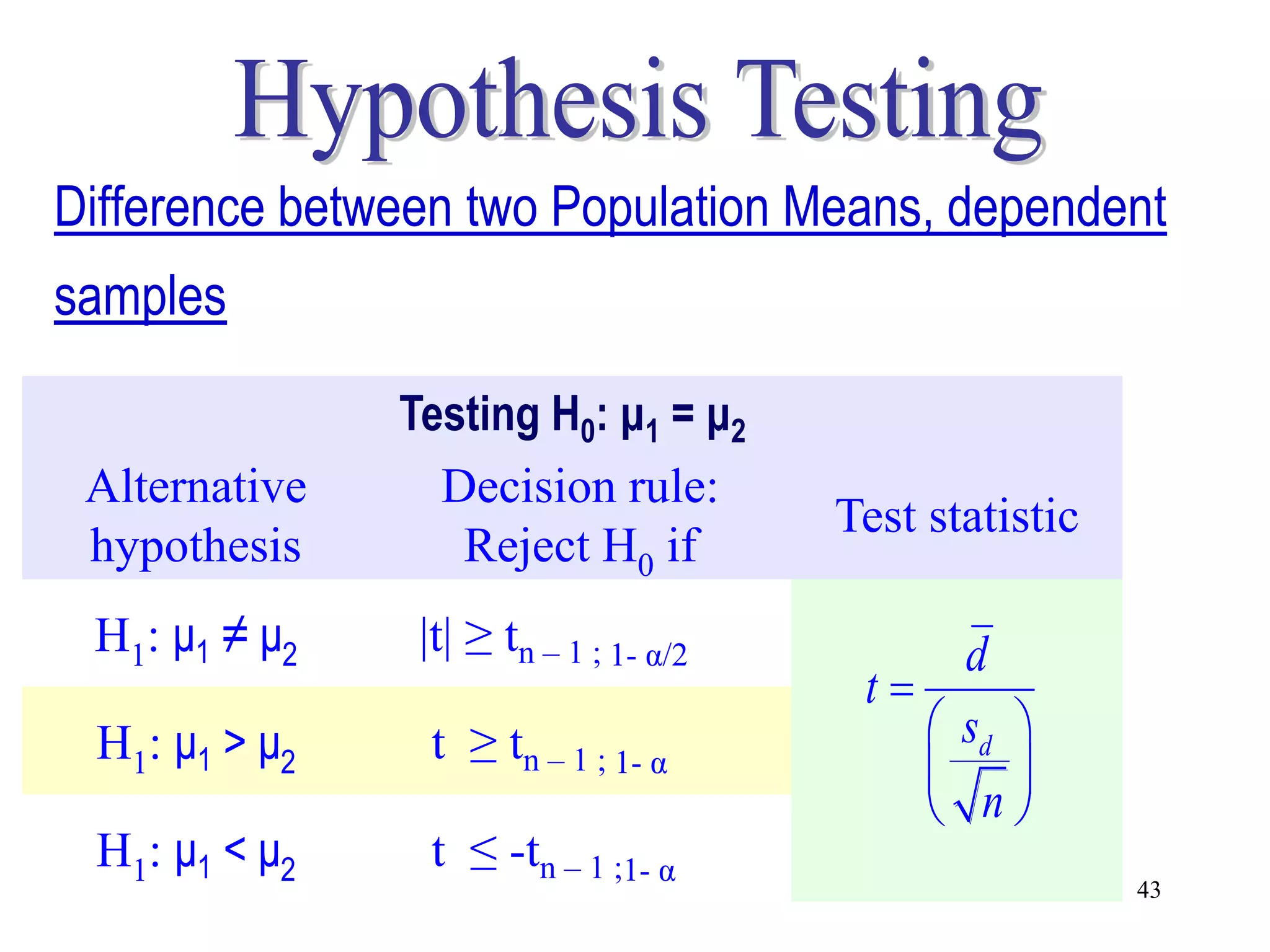
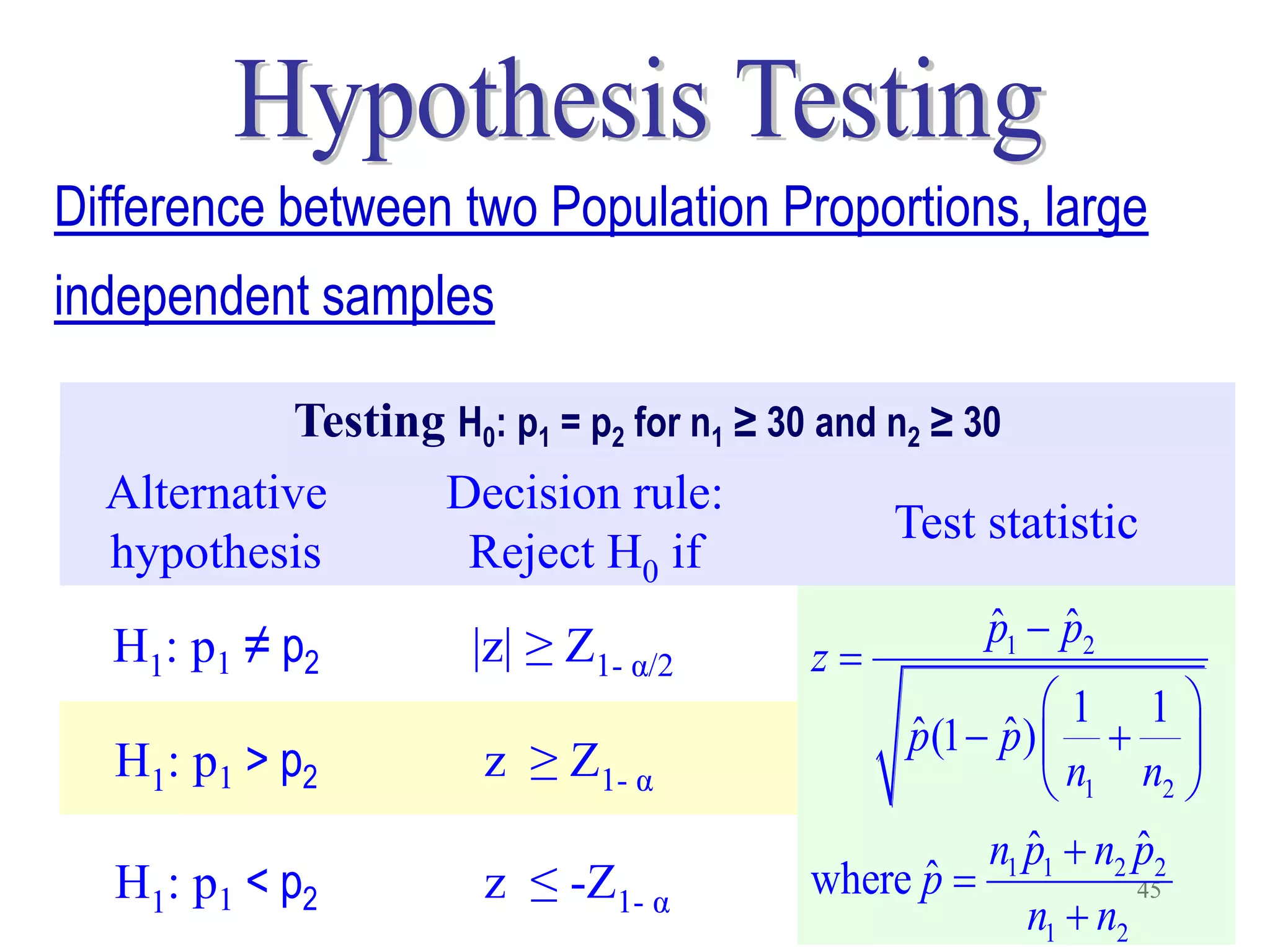
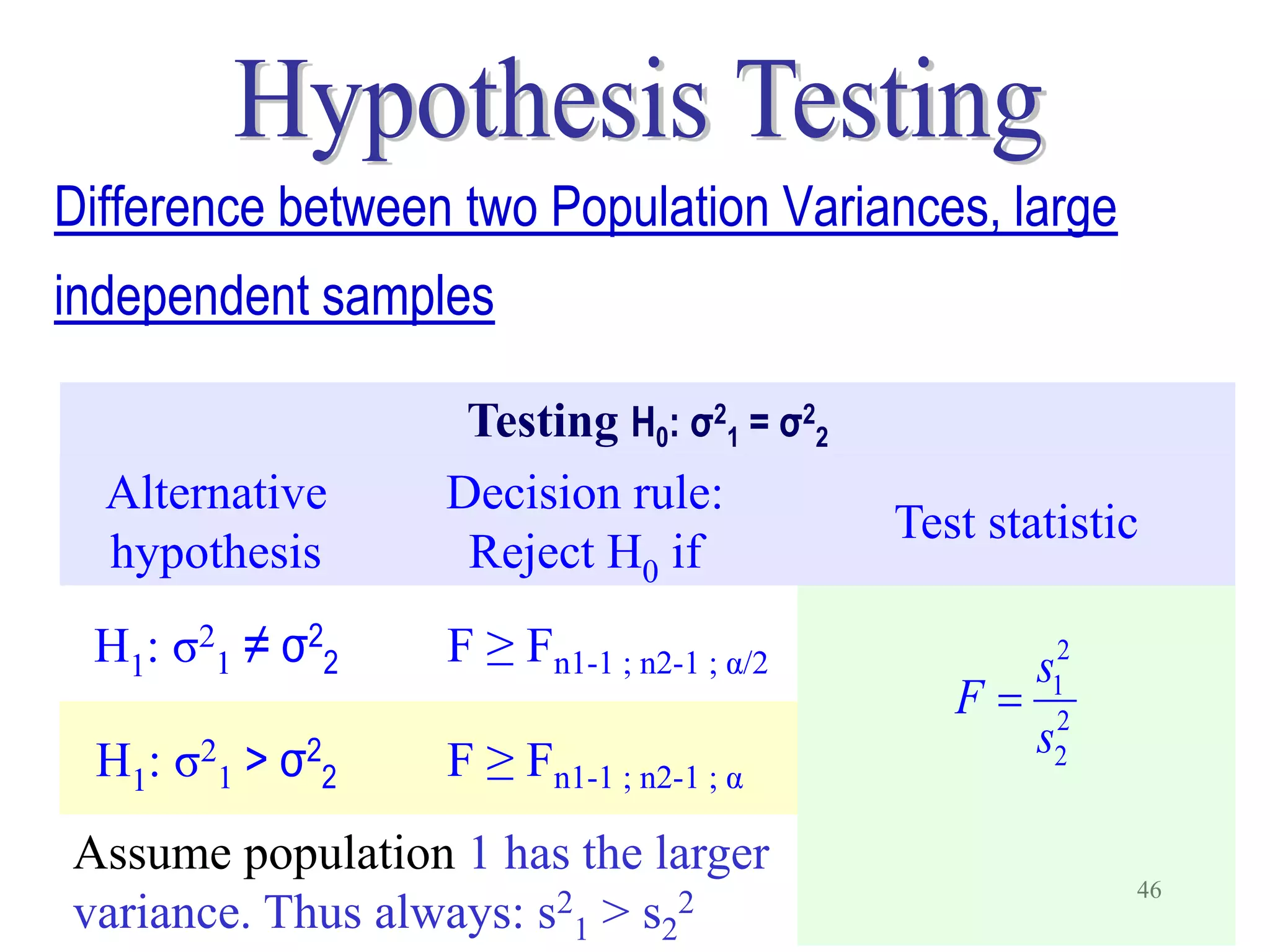
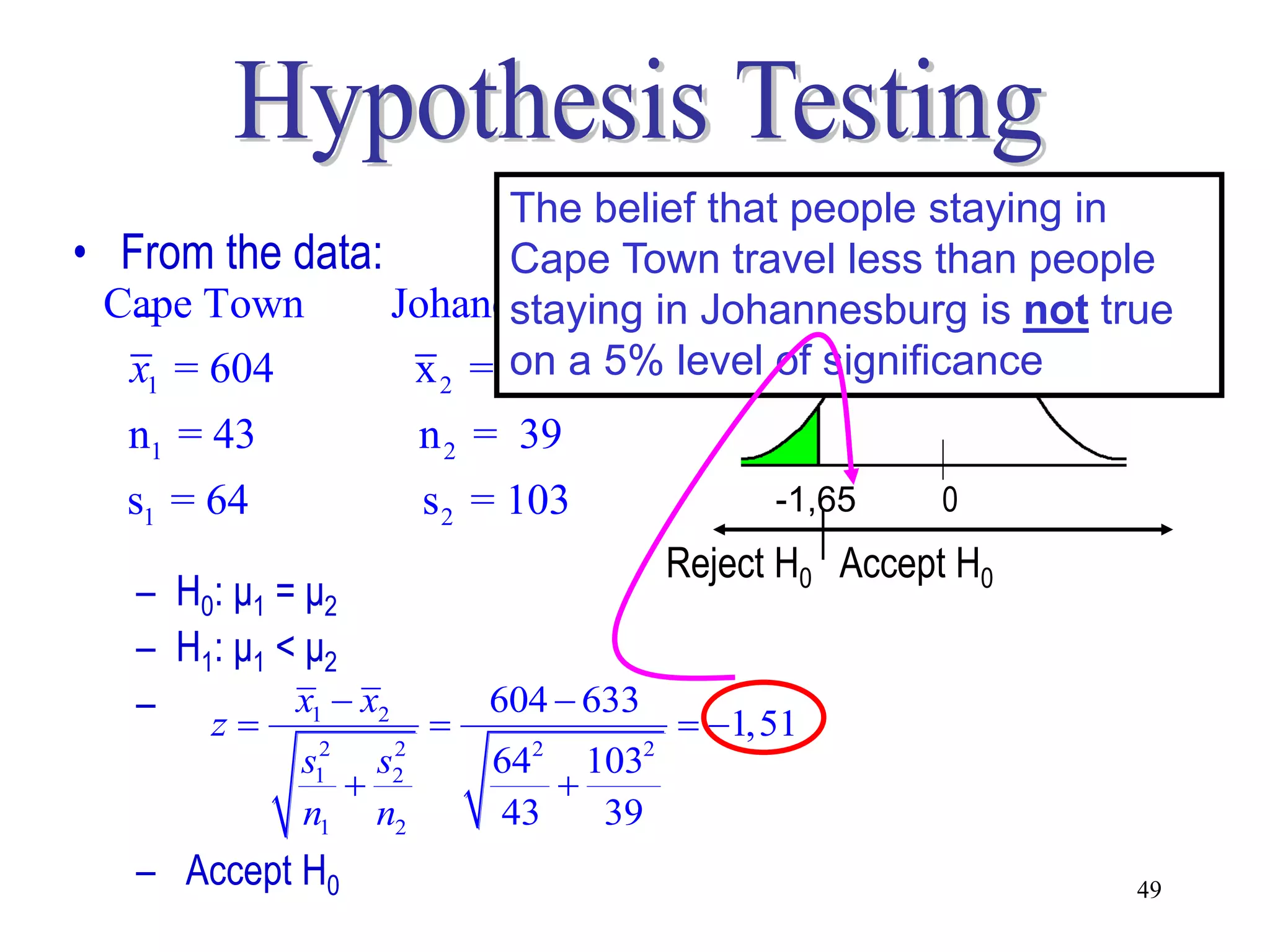
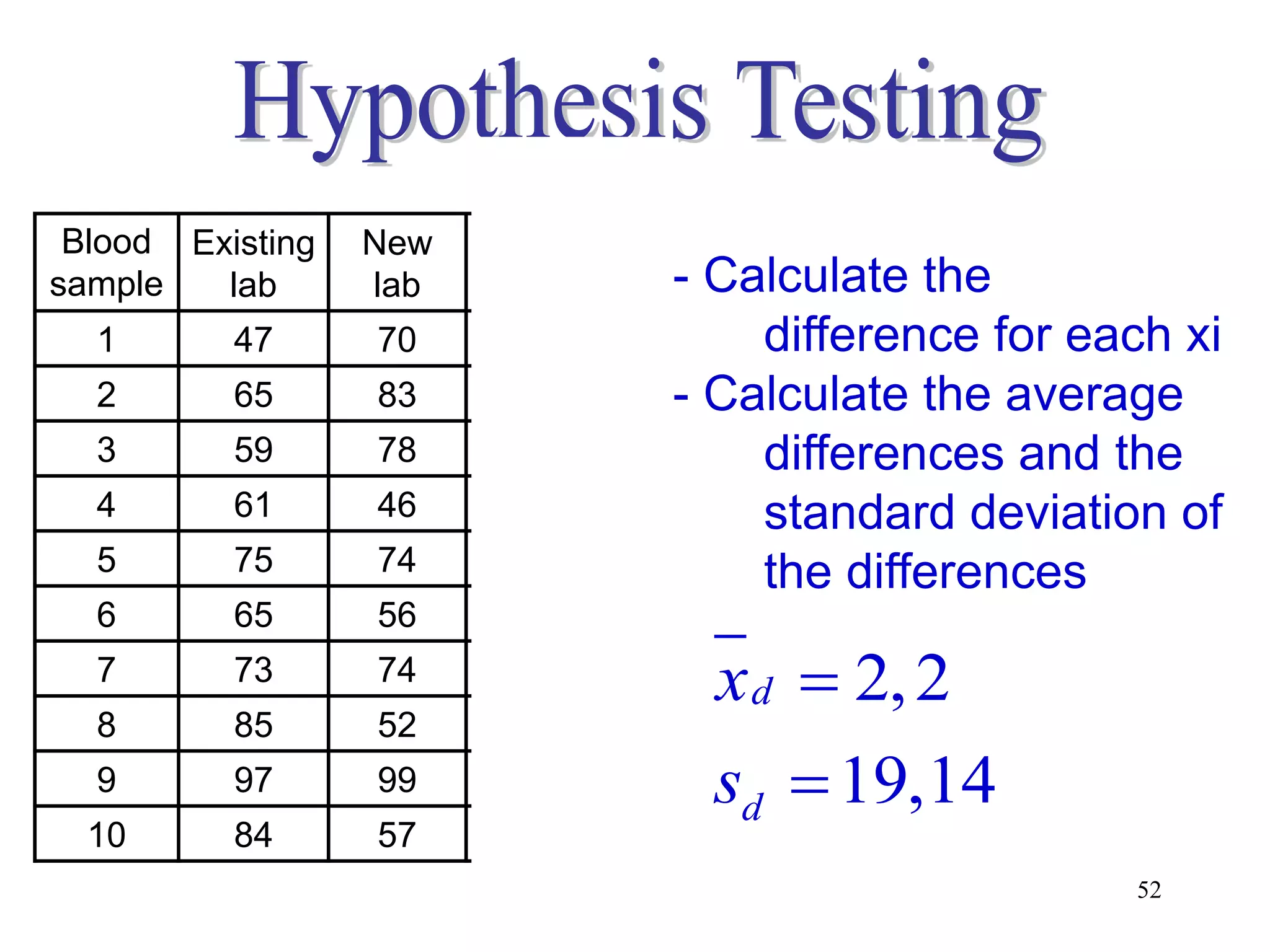
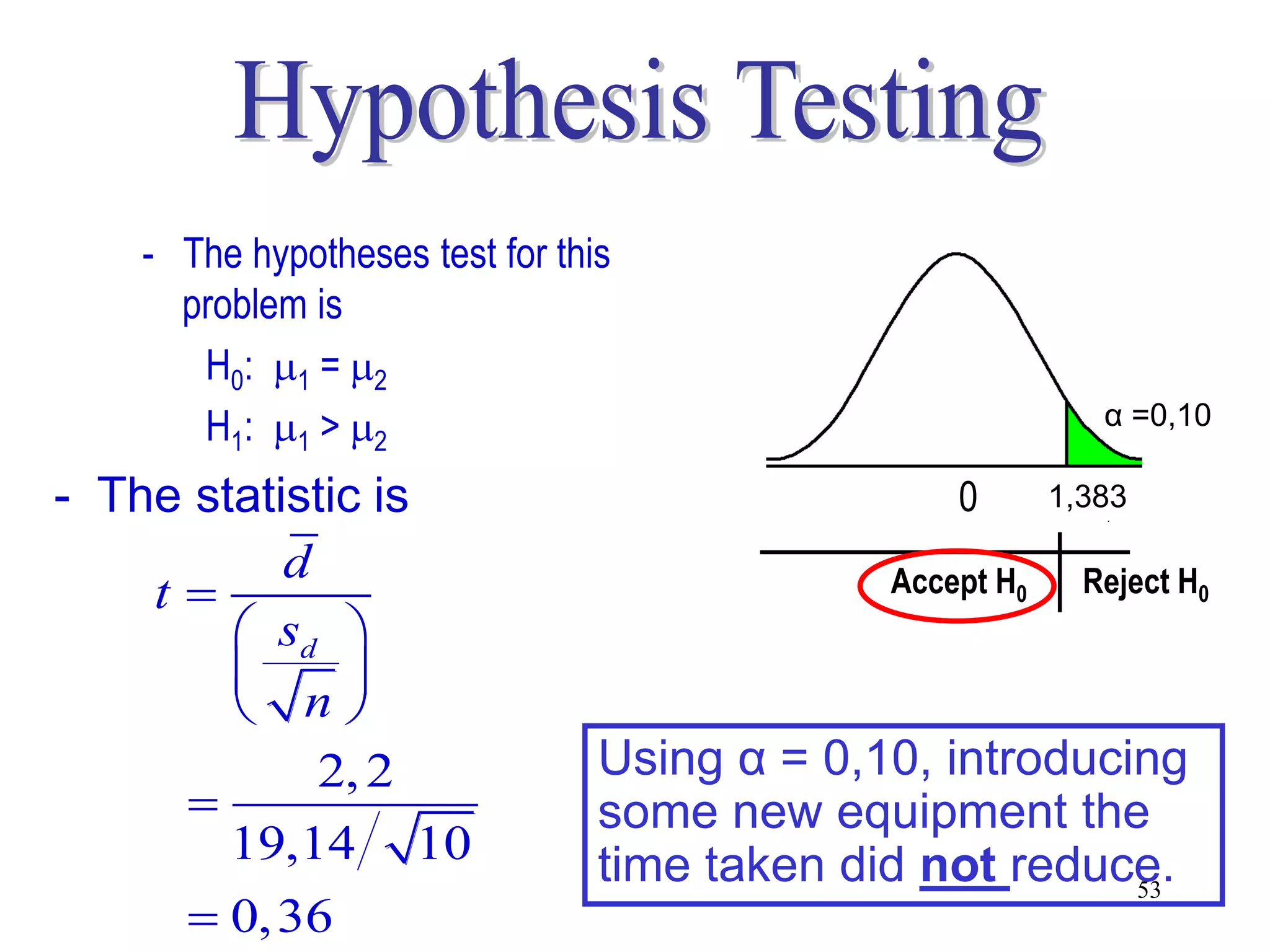
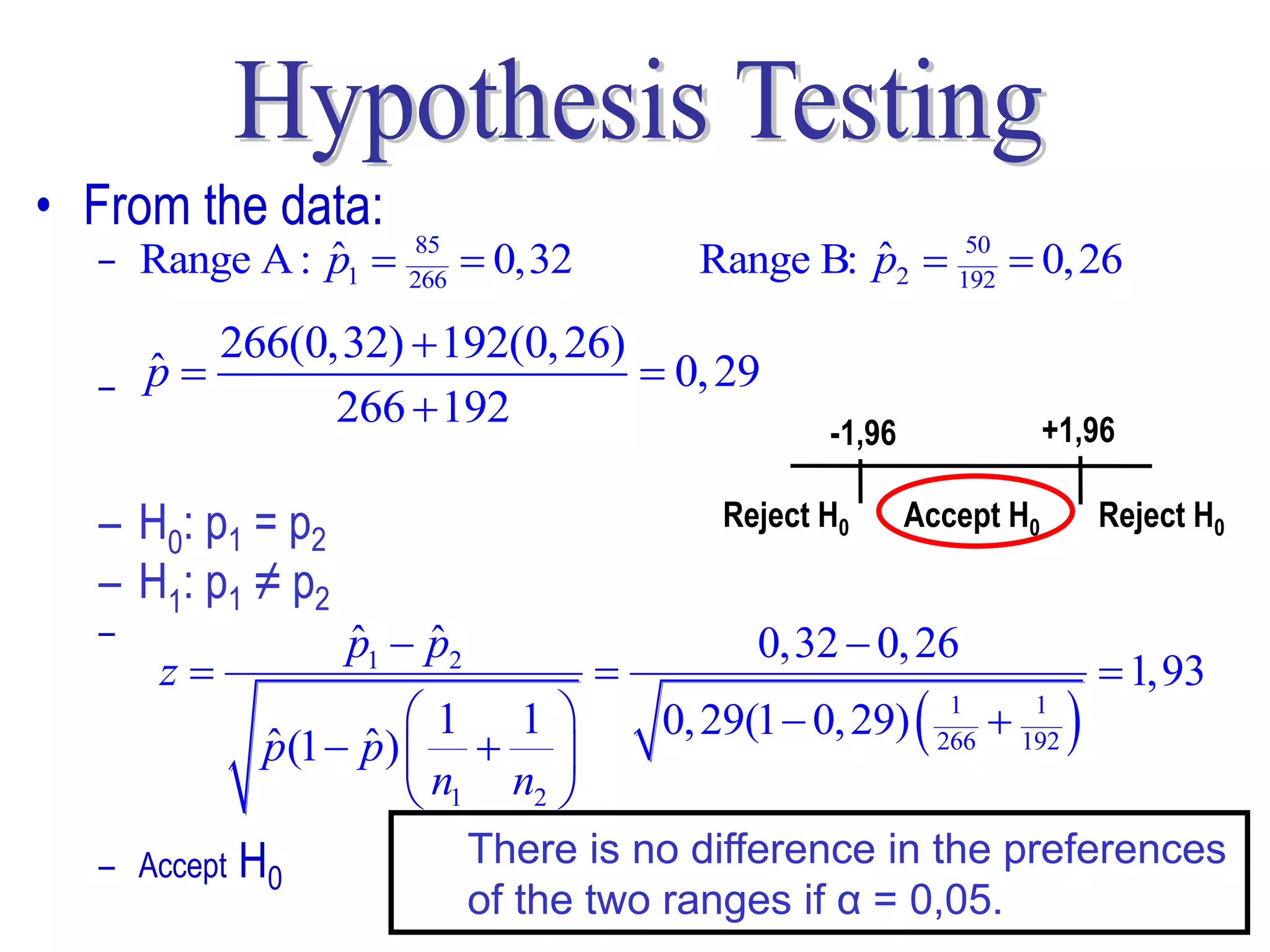
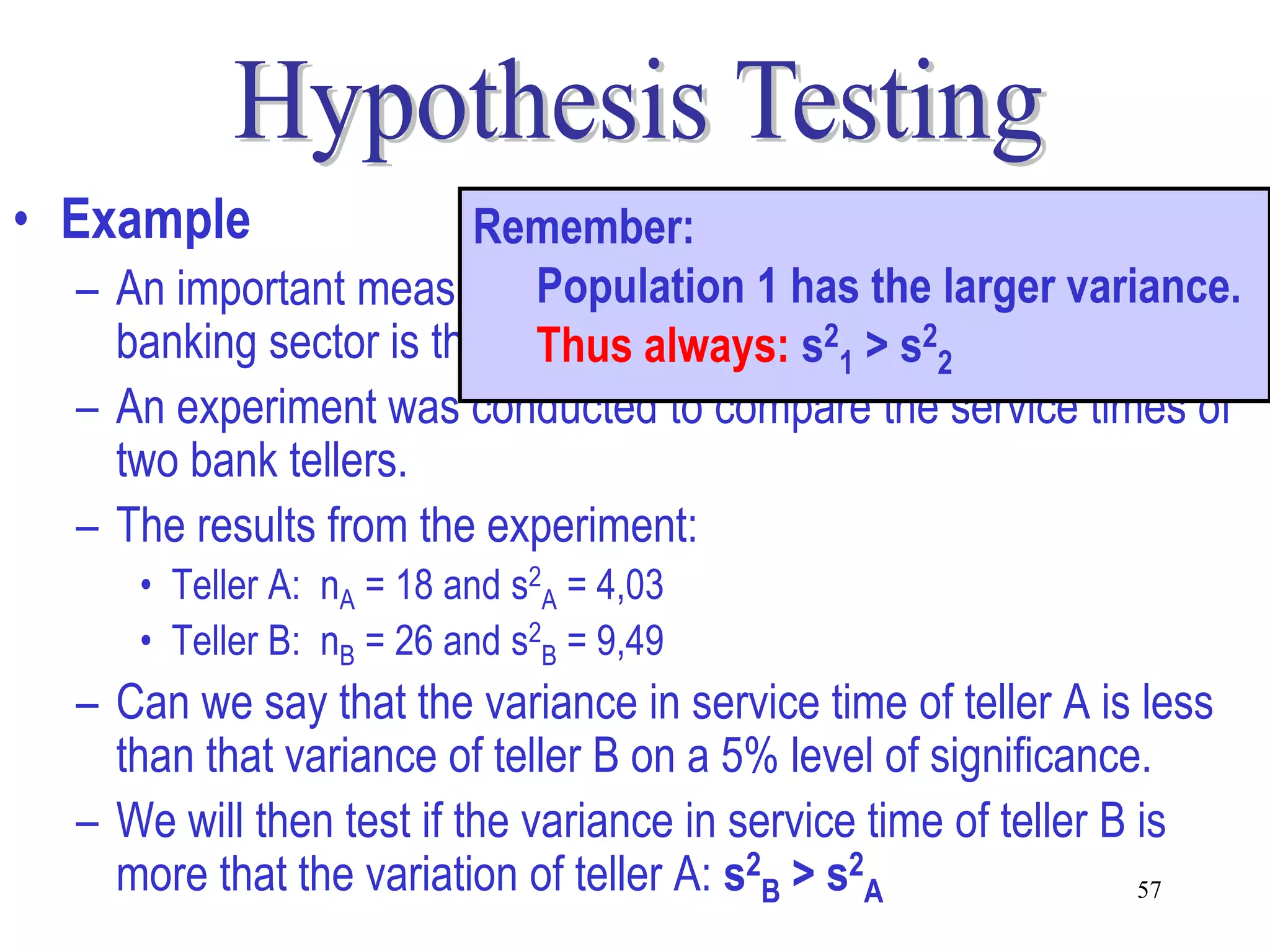
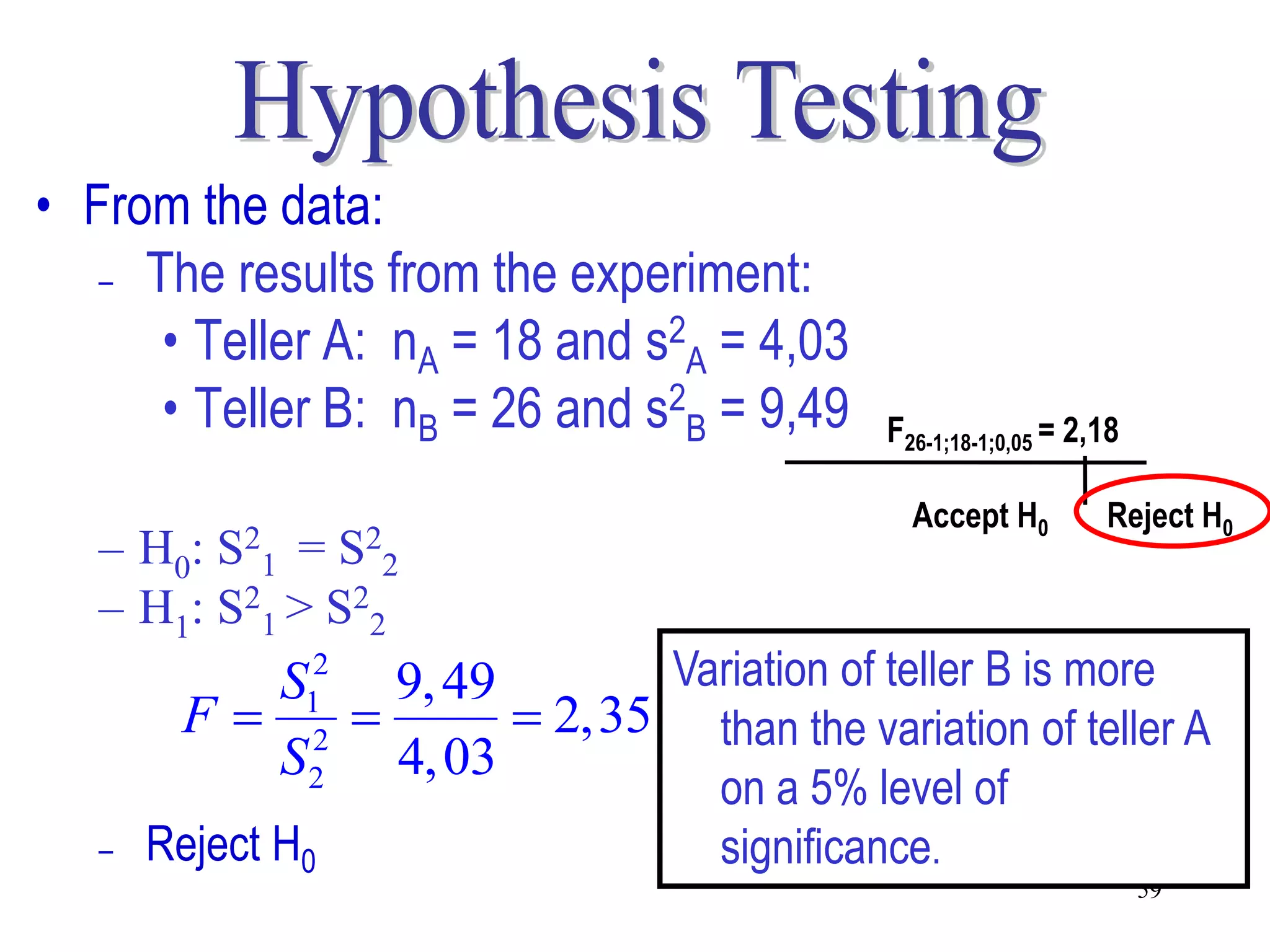
This document discusses hypothesis testing, which is a statistical procedure used to make inferences about populations based on sample data. It involves 6 steps: 1) stating the null and alternative hypotheses, 2) stating the significance level, 3) calculating the test statistic, 4) determining the critical value, 5) making a decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and 6) drawing a conclusion. The key concepts covered are the null and alternative hypotheses, types of errors, significance levels, test statistics, critical values, and decision rules for one-tailed and two-tailed hypothesis tests concerning population means and proportions. Examples are provided to illustrate the application of hypothesis testing.