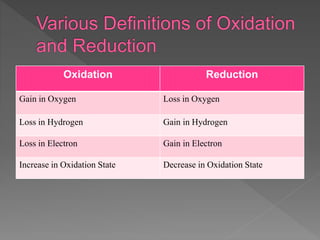
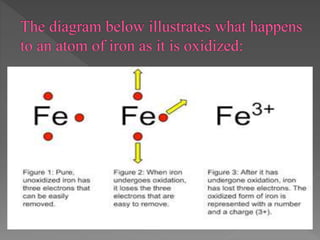
Magnesium and methane undergo oxidation reactions in the examples provided. In the magnesium reaction, magnesium atoms are oxidized when they lose electrons to form magnesium ions. In the methane reaction, hydrogen atoms gain oxygen and are oxidized to form water, while carbon gains oxygen and is oxidized to carbon dioxide. Oxidation causes a loss of electrons or gain of oxygen. Reduction is the opposite, with a gain of electrons or loss of oxygen. Oxidizing agents become reduced by causing other reactants to be oxidized, while reducing agents become oxidized by causing other reactants to be reduced.