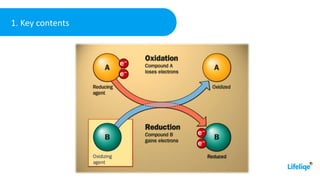
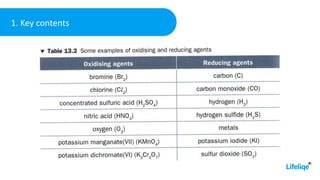
This chemistry class lesson introduces the concepts of oxidation and reduction reactions. It defines oxidizing and reducing agents and explains how to identify them in chemical equations. Examples are provided of assigning oxidation numbers and representing electron transfer processes. The lesson also demonstrates tests for identifying the presence of oxidizing and reducing agents in solutions. Practice problems are included for students to determine oxidizing and reducing agents in example reactions.