Embed presentation
Downloaded 41 times





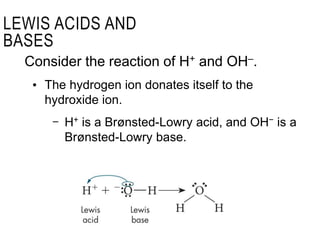
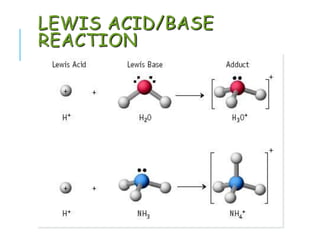
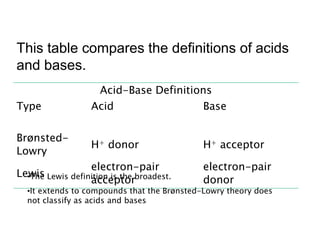

This document discusses Lewis acid-base theory. It defines a Lewis acid as a substance that can accept an electron pair to form a covalent bond, while a Lewis base is a substance that can donate an electron pair to form a covalent bond. The Lewis definitions include all Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases. According to Lewis, an acid accepts an electron pair during a reaction and a base donates an electron pair.







