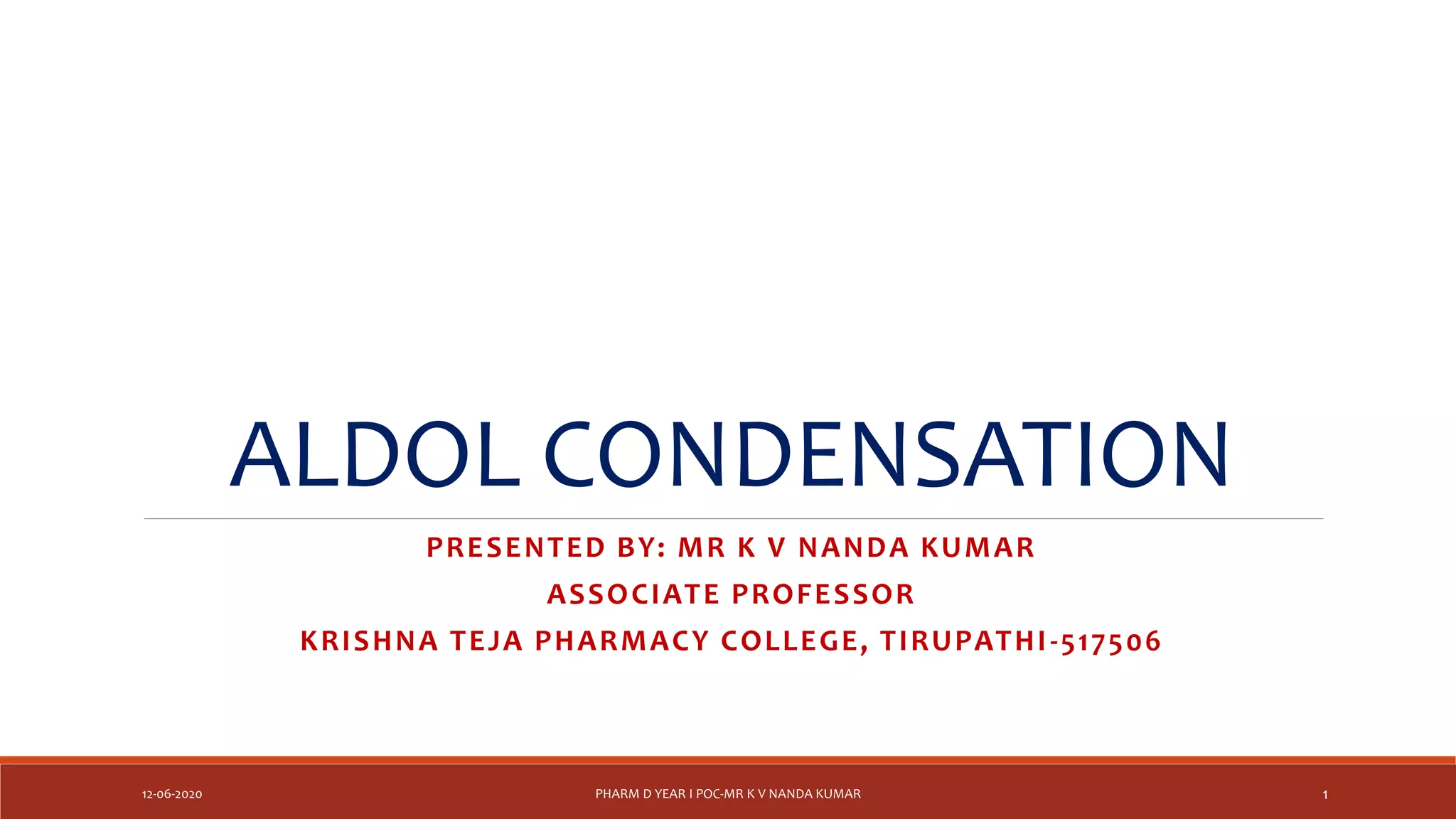
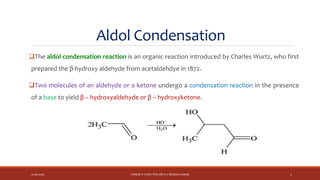
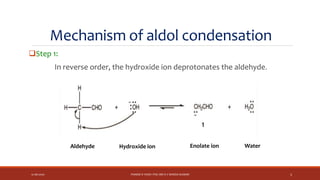
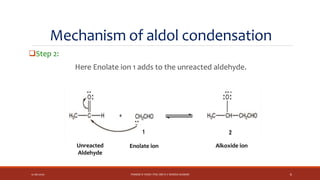
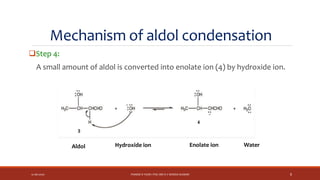
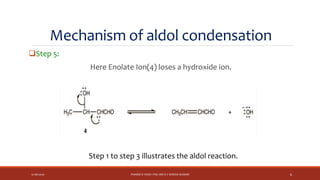
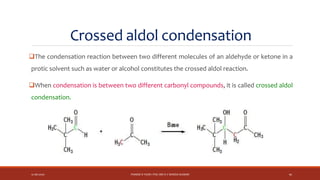
The document discusses aldol condensation, an organic reaction where two molecules of an aldehyde or ketone undergo a condensation reaction in the presence of a base to yield a β–hydroxyaldehyde or β–hydroxyketone. It involves the reaction of an enolate ion, formed from deprotonation of an aldehyde, with a carbonyl compound to form an aldol. This may then undergo dehydration to form a conjugated enone. The mechanism proceeds through enolate formation, carbon-carbon bond formation between the enolate and carbonyl, and protonation to form the aldol intermediate. Crossed aldol condensation refers to the reaction between two different aldehyde or ketone