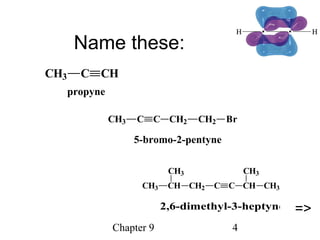
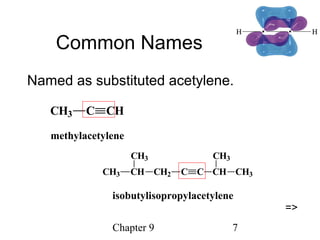
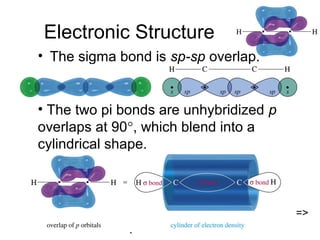
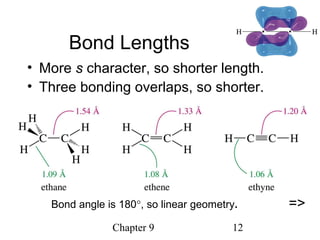
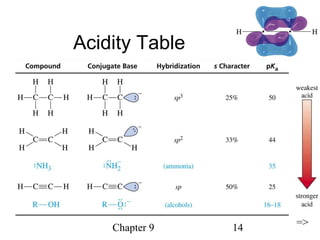
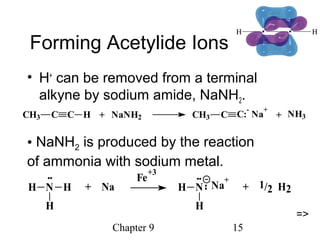
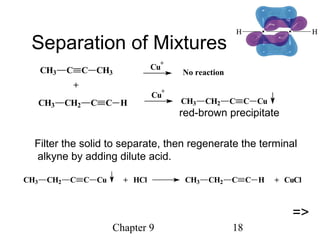
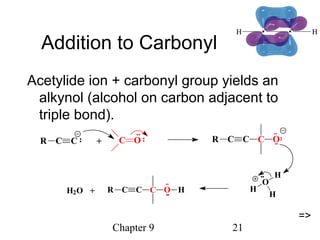
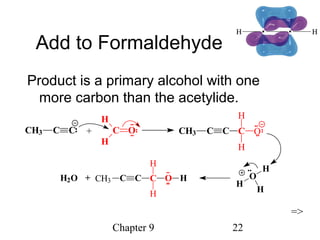
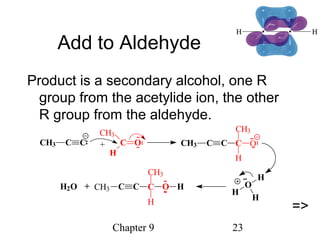
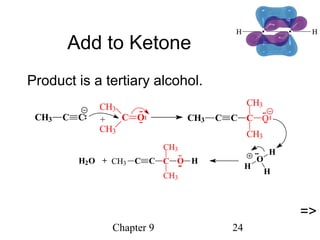
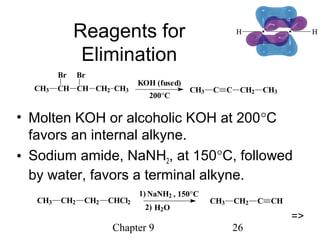
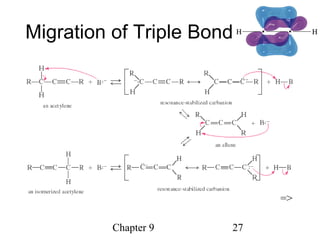
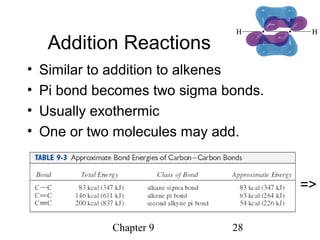
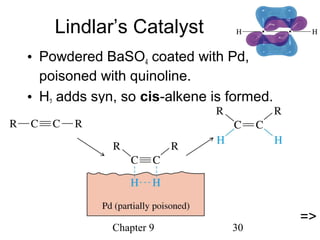
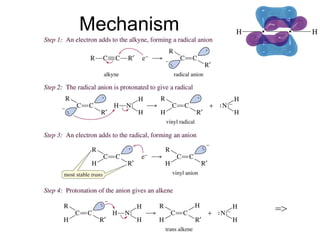
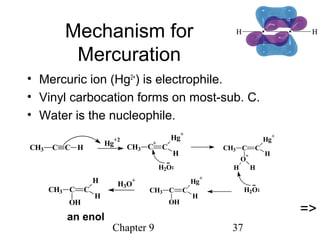
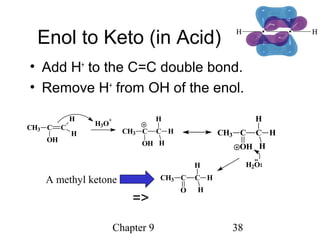
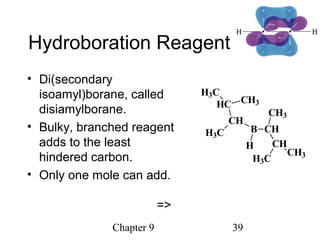
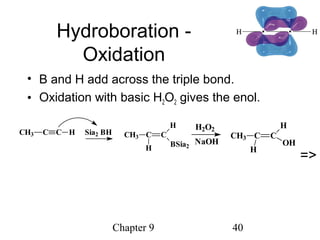
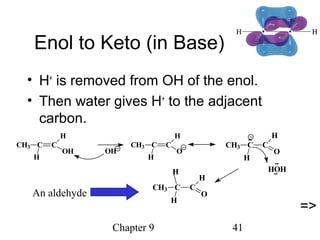
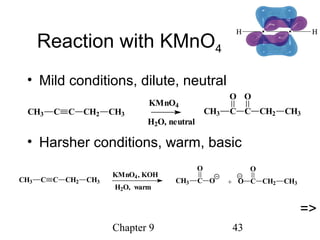
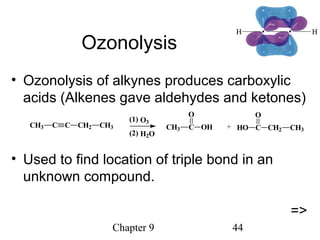
This chapter discusses alkynes, carbon-carbon triple bonds. Alkynes contain two pi bonds and have the general formula CnH2n-2. They can be named using IUPAC nomenclature by changing the -ane ending of the parent alkane to -yne. Alkynes undergo addition reactions like alkenes but also have unique reactions like forming acetylide ions. They can be synthesized through elimination and by reactions of acetylide ions. Oxidation and ozonolysis reactions of alkynes cleave the triple bond.