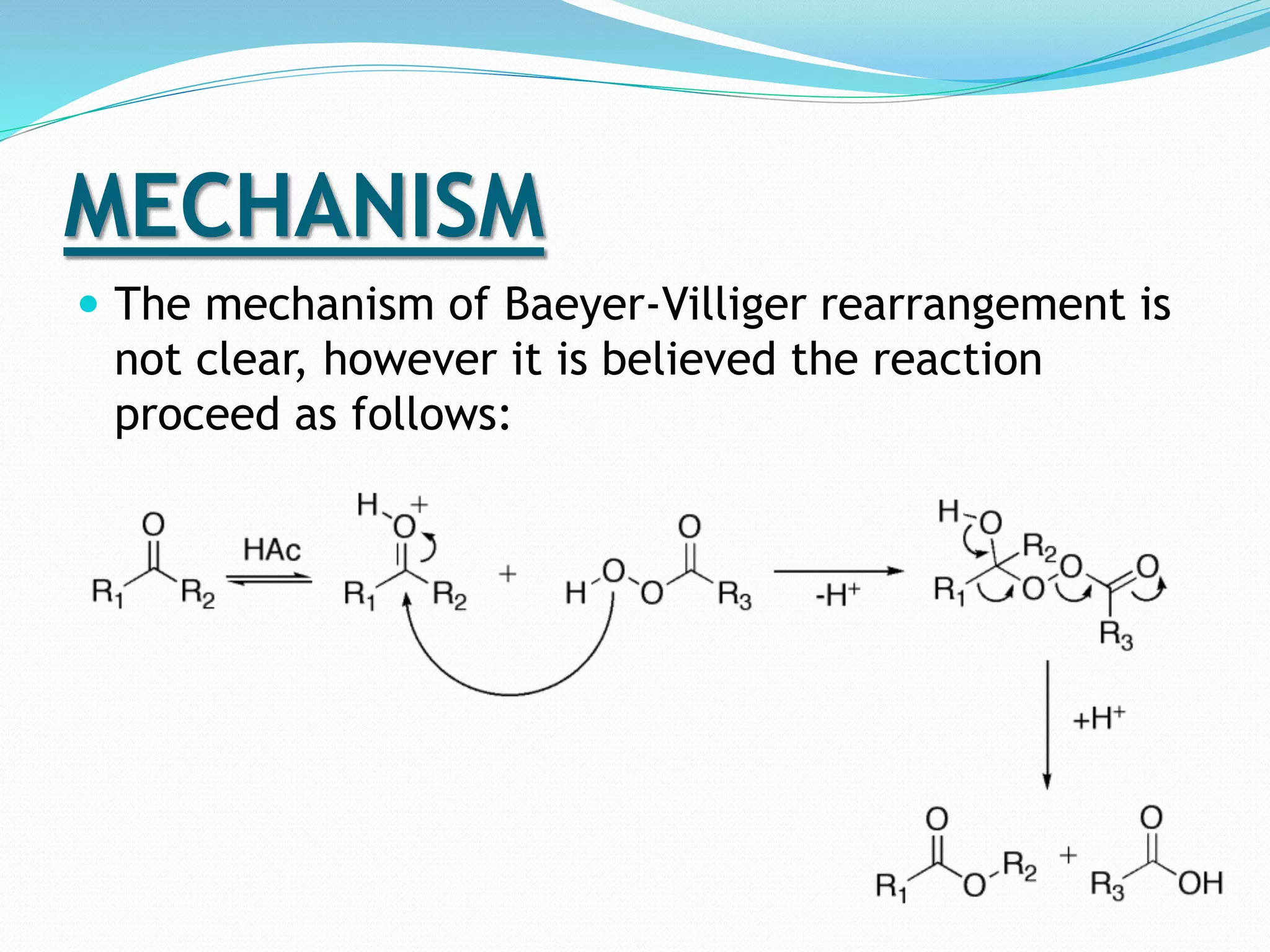
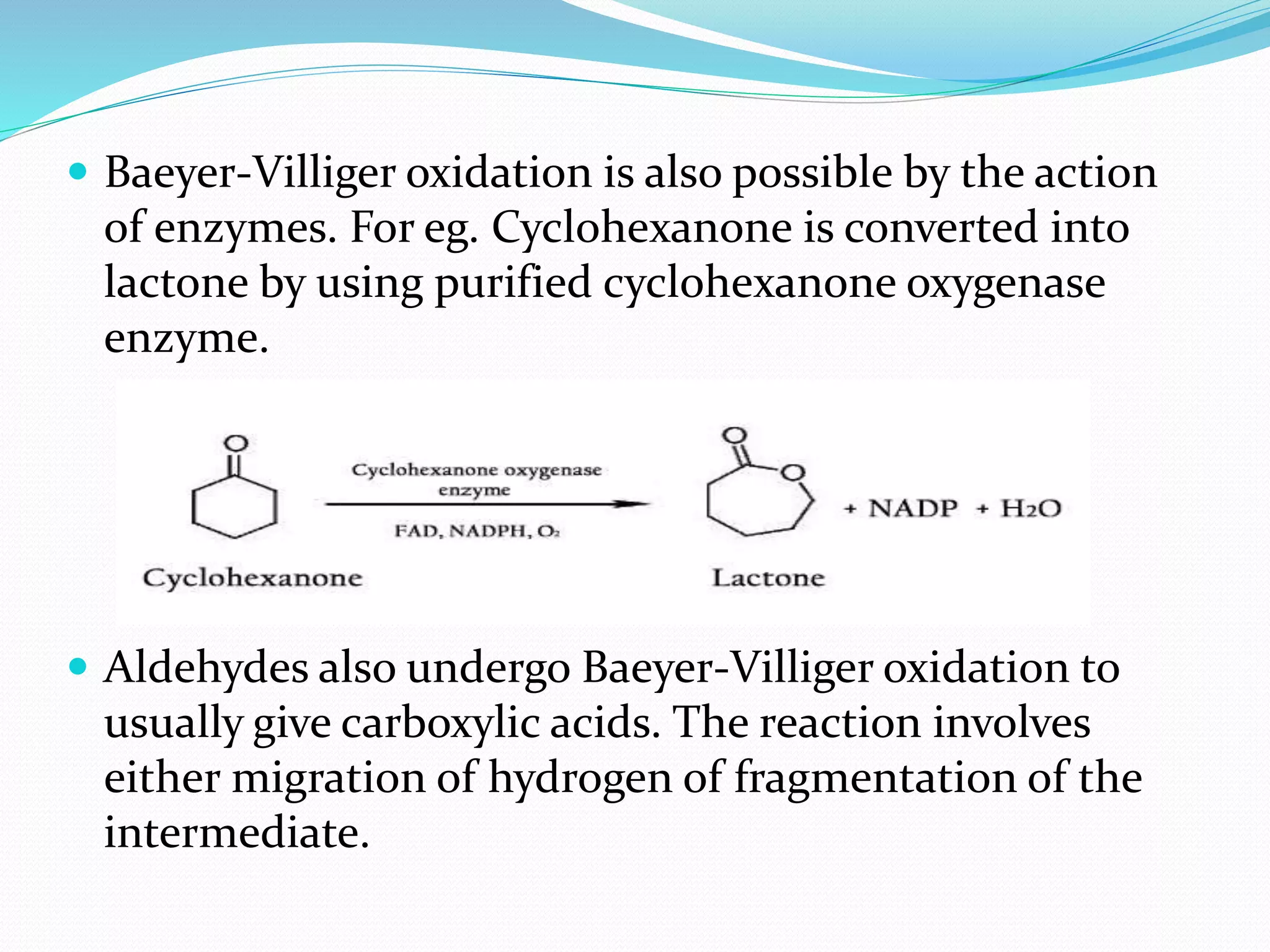
This document discusses the Baeyer-Villiger and Dakin oxidation reactions. The Baeyer-Villiger reaction involves using peroxy acids to oxidize ketones, forming esters and lactones. It is believed to proceed through initial protonation followed by addition and migration of the R group. The Dakin reaction oxidizes aromatic aldehydes and ketones to phenols using oxidizing agents like hydrogen peroxide. It is thought to proceed through a mechanism analogous to the Baeyer-Villiger reaction involving migration of the aryl group. Both reactions have synthetic applications, with the Baeyer-Villiger used to transform ketones and the Dakin employed to synthesize benzenediols, catechol, and other compounds.