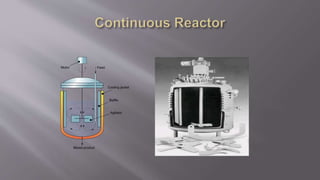
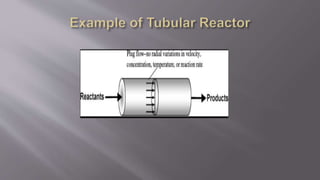
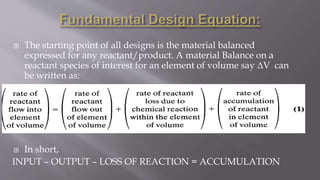
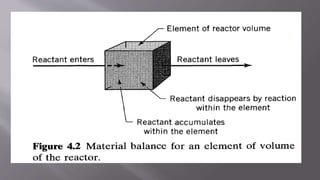
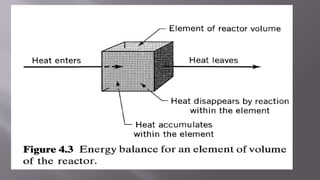
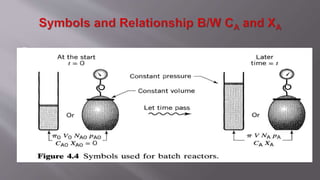
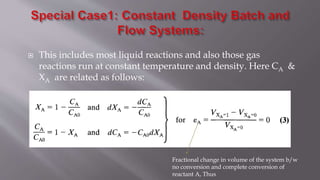
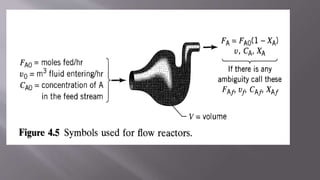
Chemical reaction engineering (CRE) focuses on the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions and reactor design, including key factors like phase, temperature, pressure, and agitation. It covers four reactor types: batch, continuous stirred tank, tubular, and packed bed, each with distinct characteristics regarding inflow and outflow. Material and energy balances are crucial for understanding reactor performance, particularly concerning temperature gradients and composition changes.