Kerberos is a computer network authentication protocol that uses 'tickets' for mutual authentication between clients and servers over non-secure networks. Developed by MIT, it relies on symmetric key cryptography and a trusted third party, known as the Key Distribution Center (KDC), to verify identities and issue time-sensitive tickets to authenticate users without transmitting plaintext passwords. The protocol has evolved through various versions, with significant updates aimed at improving security and encryption methods, and is utilized widely in both academic and commercial applications.


![Kerberos Protocol
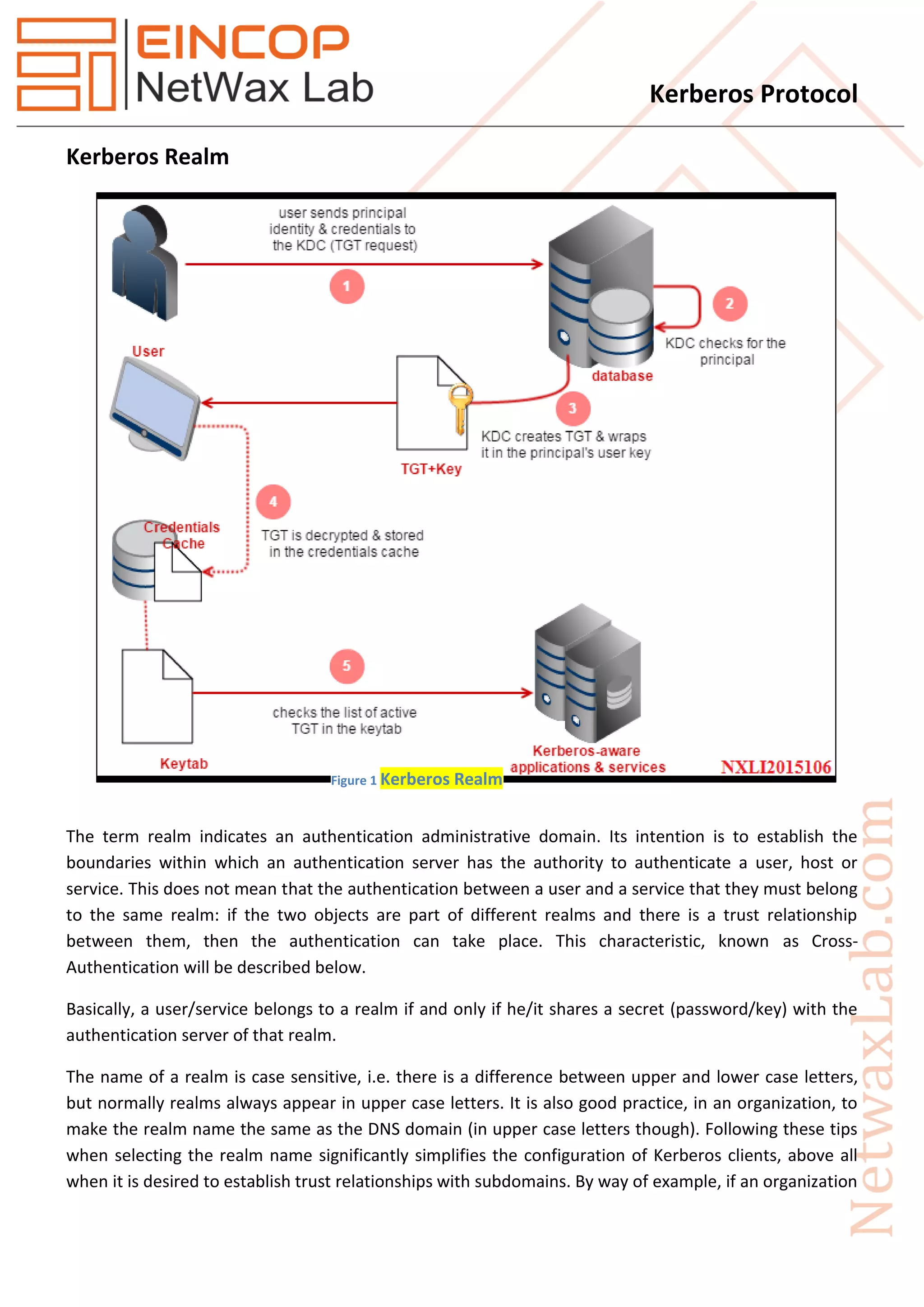
belongs to the DNS domain example.com, it is appropriate that the related Kerberos realm is
EXAMPLE.COM.
Kerberos Operation
Step 1) Authentication Server to Client
Ticket Granting Ticket : [client, address, validity, Key(client, TGS)]Key(TGS) [Key(client, TGS)]Key(client)
Step 2) Client to Ticket Granting Server
Ticket Granting Ticket : service, [client, client address, validity, Key(client, TGS)]Key(TGS)
Authenticator : [client, timestamp]Key(client, TGS)
Figure 2 Kerberos Operation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nxld80kerberosprotocol-150429020314-conversion-gate02/75/Kerberos-Protocol-4-2048.jpg)
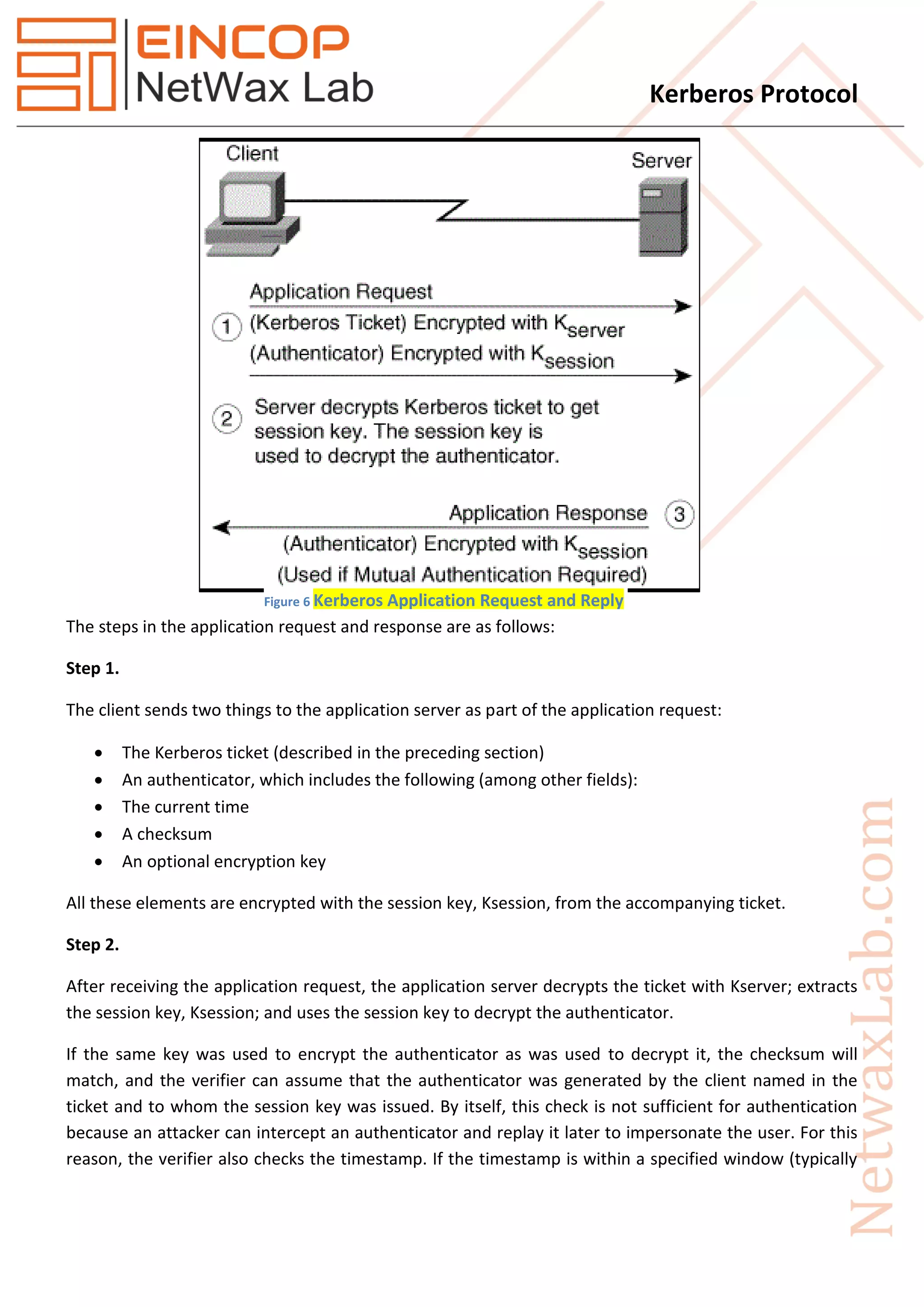
![Kerberos Protocol
Step 3) Ticket Granting Server to Client
Ticket (client, service) : service, [client, client address, validity, Key(client, service)]Key(service)
[Key(client, service)]Key(client, TGS)
Step 4) Client to Service
Ticket (client, service) : service, [client, client address, validity, Key(client, service)]Key(service)
Authenticator : [client, timestamp]Key(client, service)
What follows is a simplified description of the protocol. The following shortcuts will be used: AS =
Authentication Server, TGS = Ticket Granting Server, SS = Service Server.
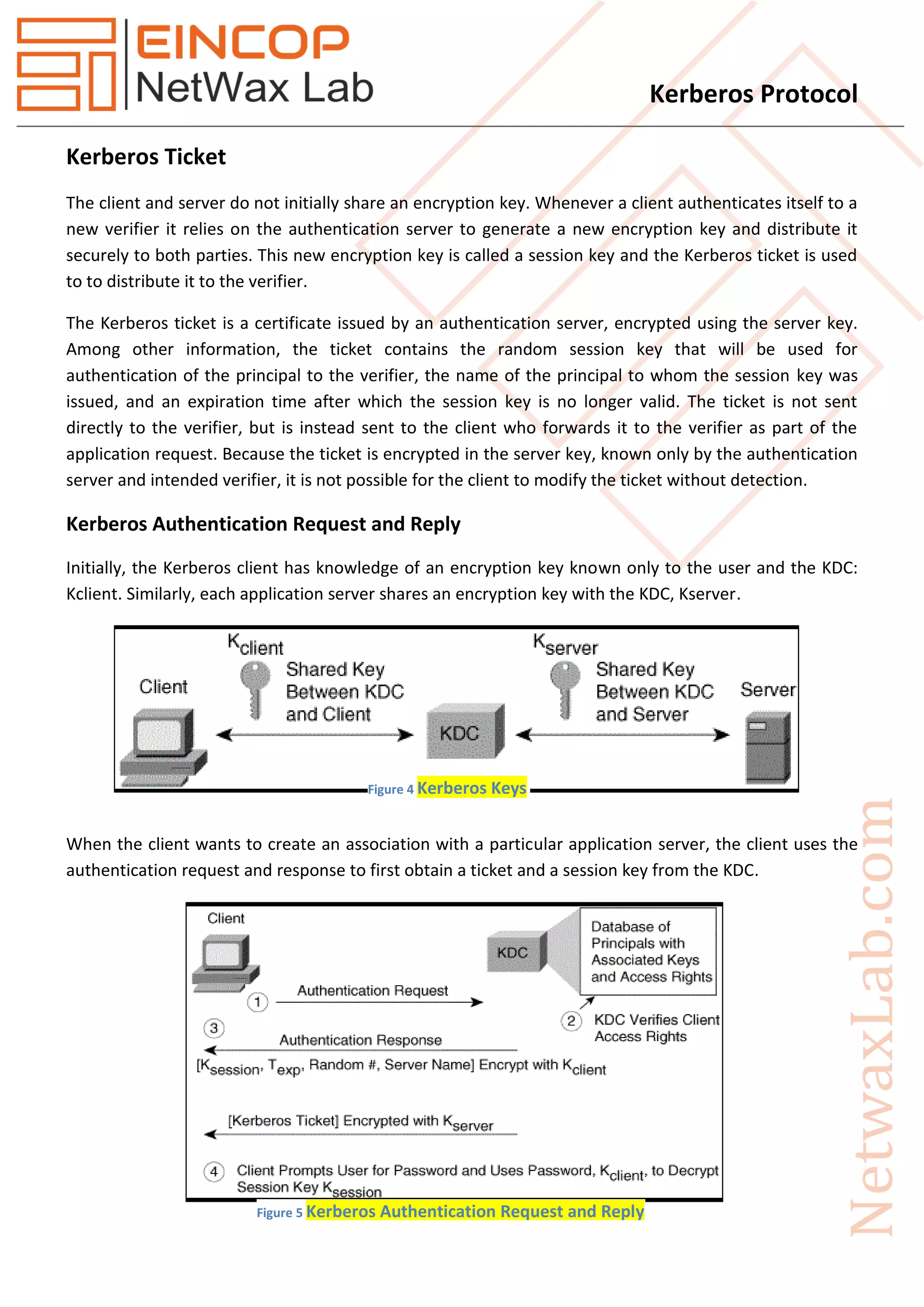
Kerberos Works
The client authenticates itself to the Authentication Server (AS) which forwards the username to a key
distribution center (KDC). The KDC issues a ticket-granting ticket (TGT), which is time stamped, encrypts
it using the user's password and returns the encrypted result to the user's workstation. This is done
infrequently, typically at user logon; the TGT expires at some point, though may be transparently
renewed by the user's session manager while they are logged in.
When the client needs to communicate with another node ("principal" in Kerberos parlance) the client
sends the TGT to the ticket-granting service (TGS), which usually shares the same host as the KDC. After
verifying the TGT is valid and the user is permitted to access the requested service, the TGS issues a
ticket and session keys, which are returned to the client. The client then sends the ticket to the service
server (SS) along with its service request.
Figure 3 Kerberos Negotiations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nxld80kerberosprotocol-150429020314-conversion-gate02/75/Kerberos-Protocol-5-2048.jpg)