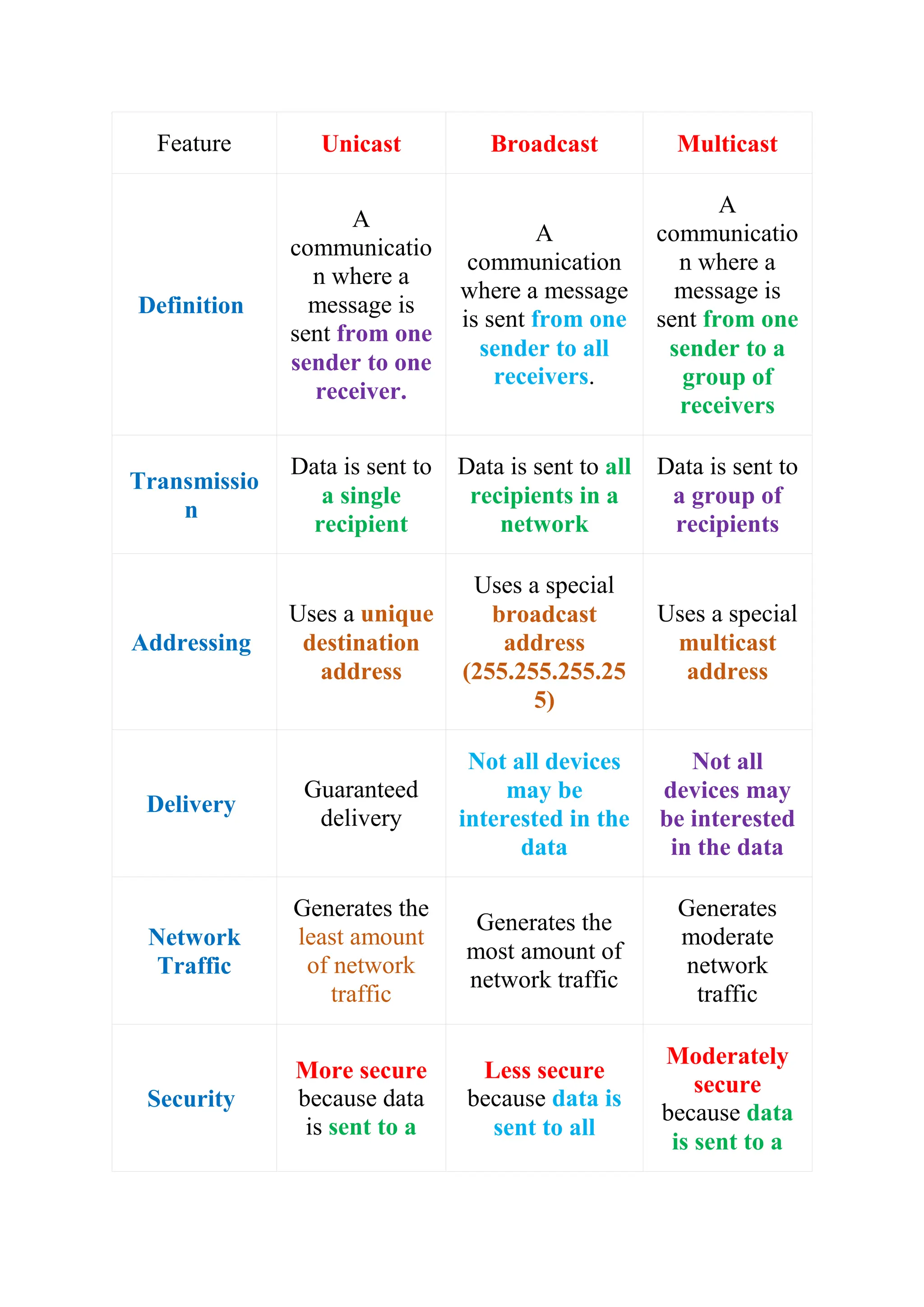
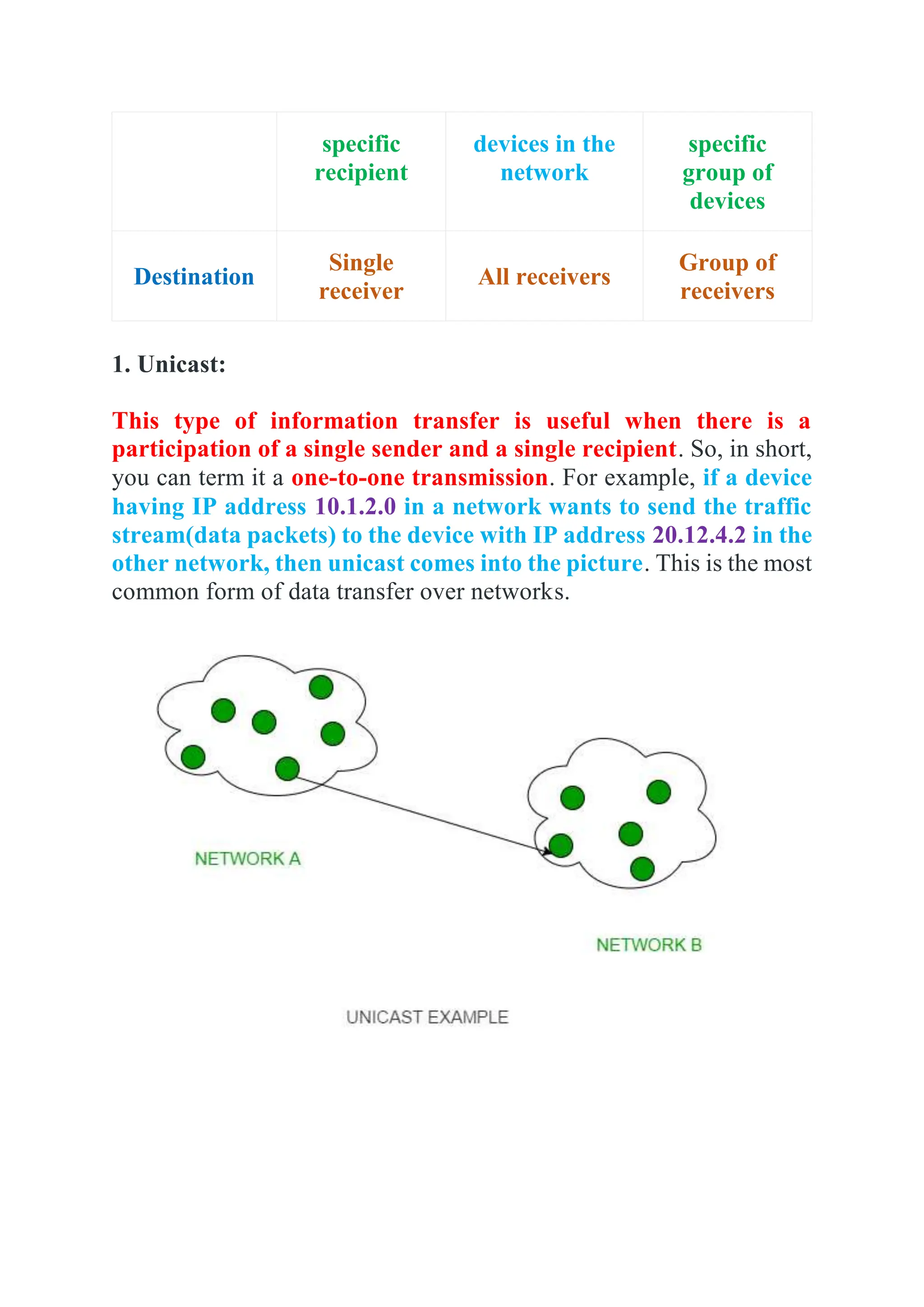
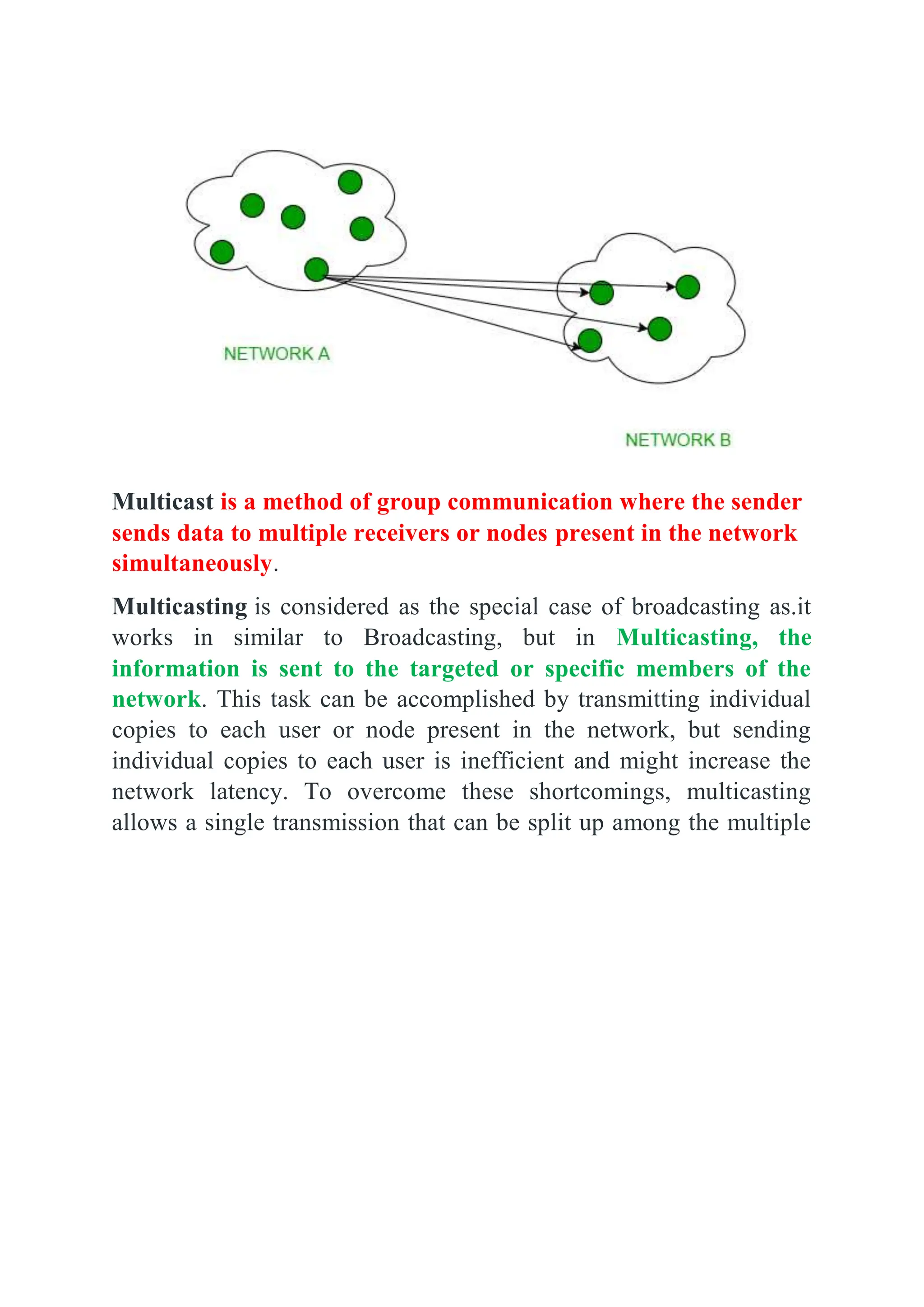
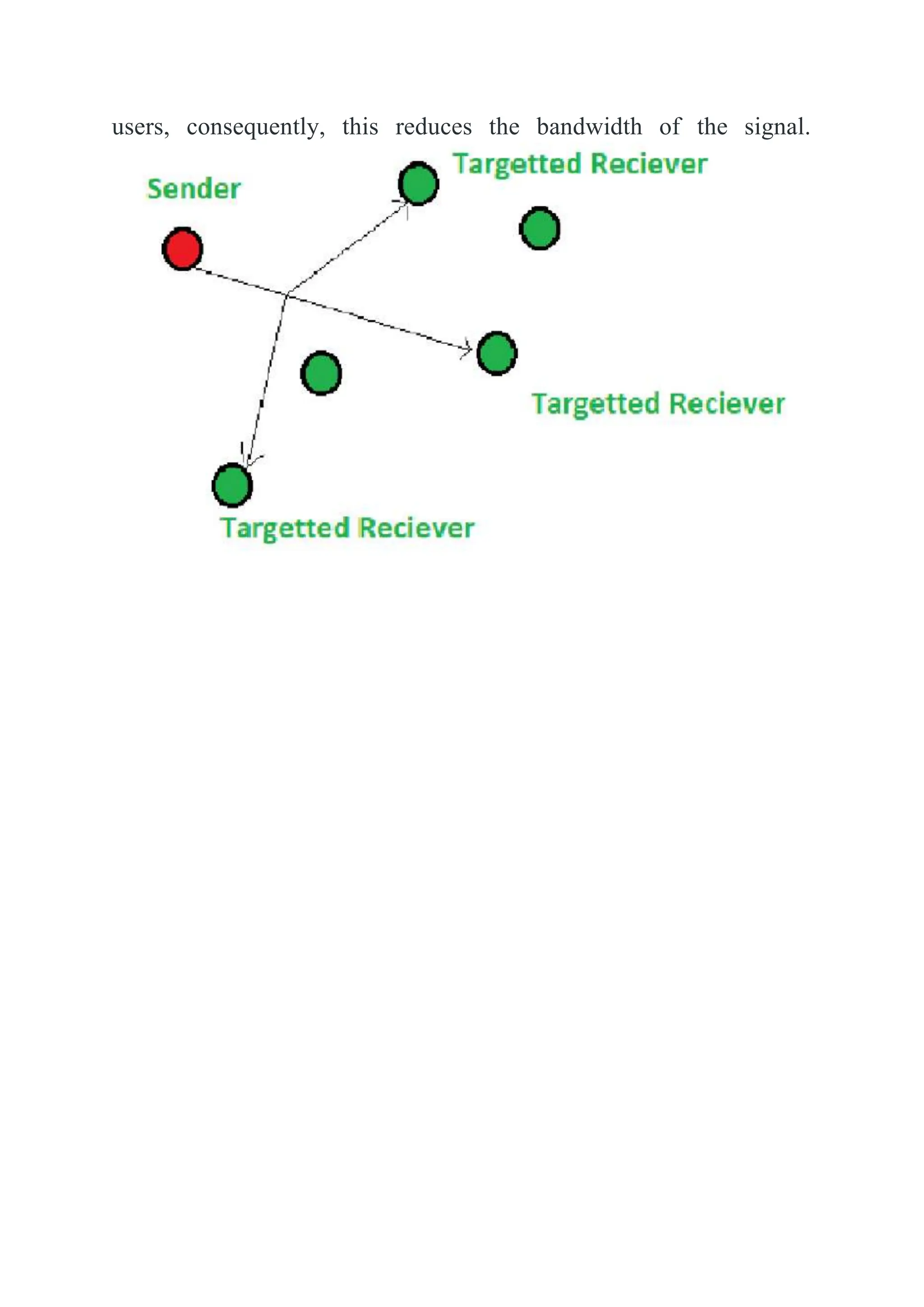
The document explains three types of data transmission: unicast, multicast, and broadcast. Unicast involves one-to-one communication, while broadcast is one-to-all and can be limited or direct, sending data to all devices on a network. Multicast allows data to be sent to specific groups of receivers, reducing network traffic as compared to sending individual copies to each user.