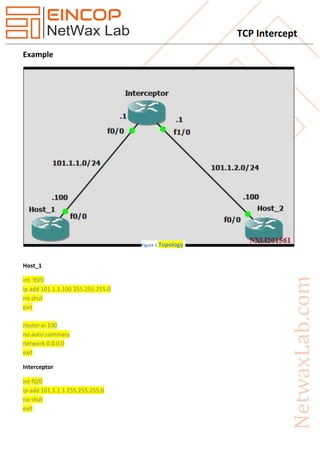
TCP intercept is designed to protect servers from denial-of-service attacks by capturing incoming TCP requests and acting as an intermediary between clients and the server. It can operate in two modes: 'intercept', where it actively buffers connections, and 'watch', where it observes connections without interfering. Configuration options include setting connection timeouts, thresholds for managing connections, and monitoring traffic to prevent excessive connection attempts.