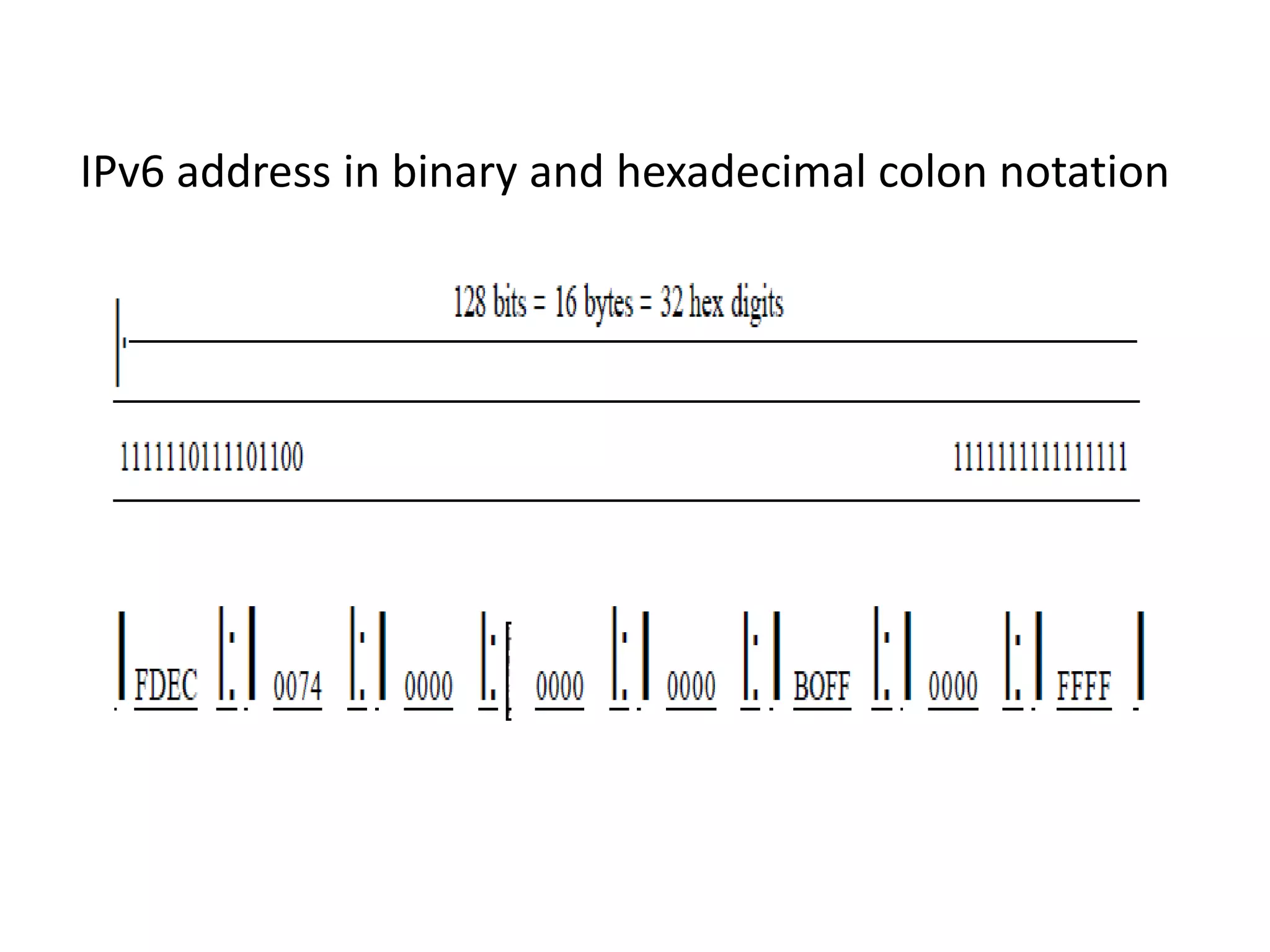
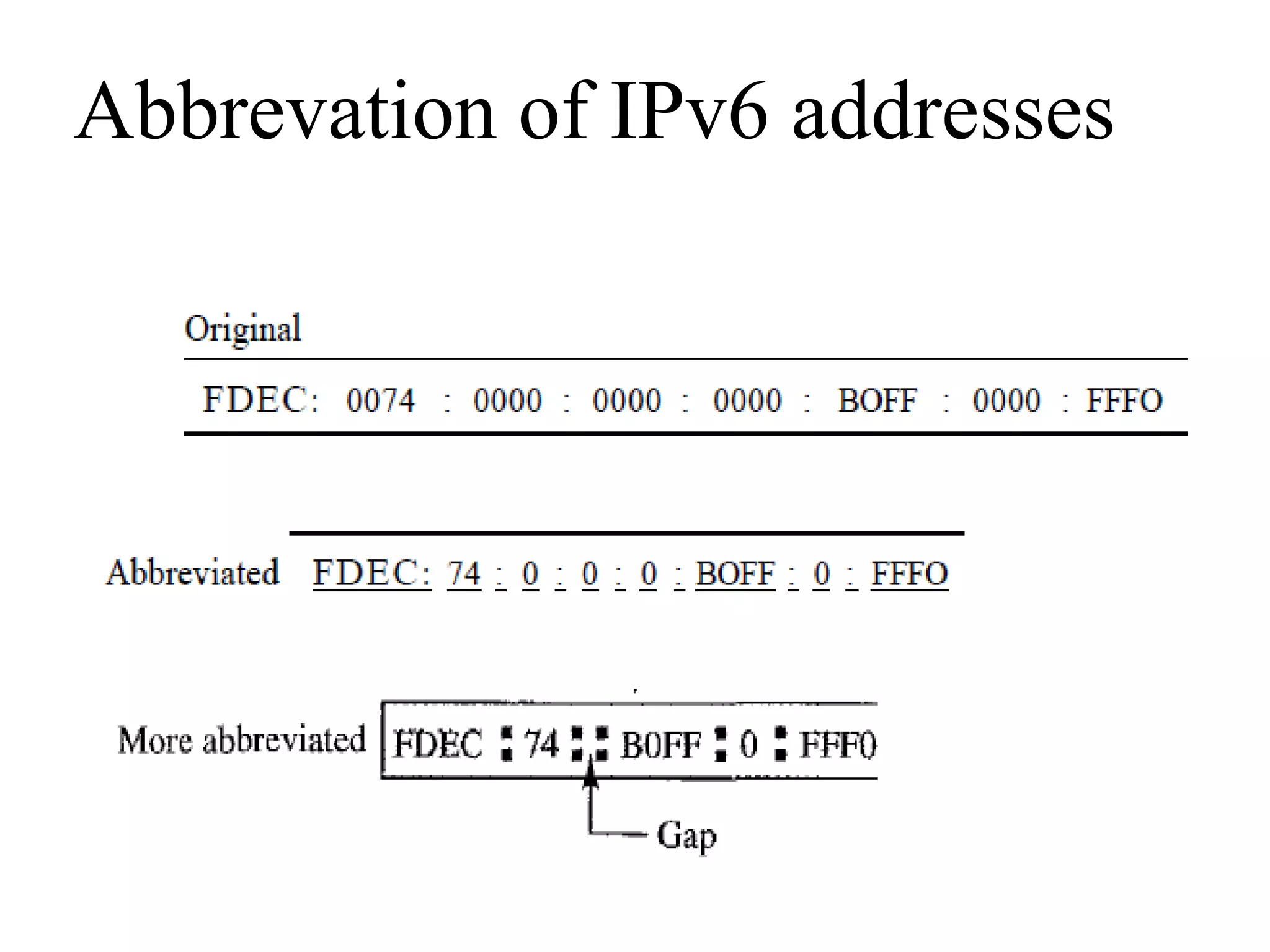
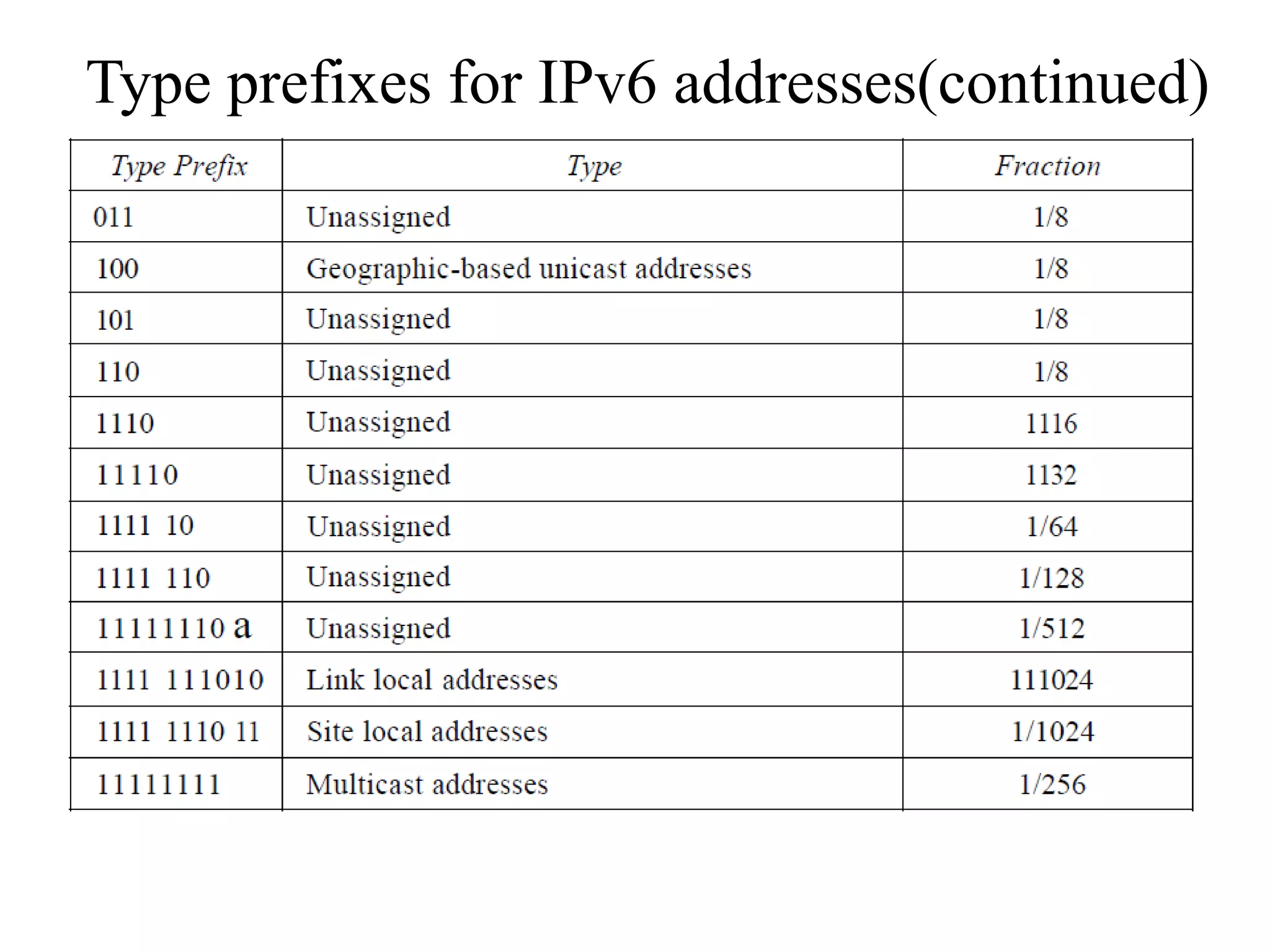
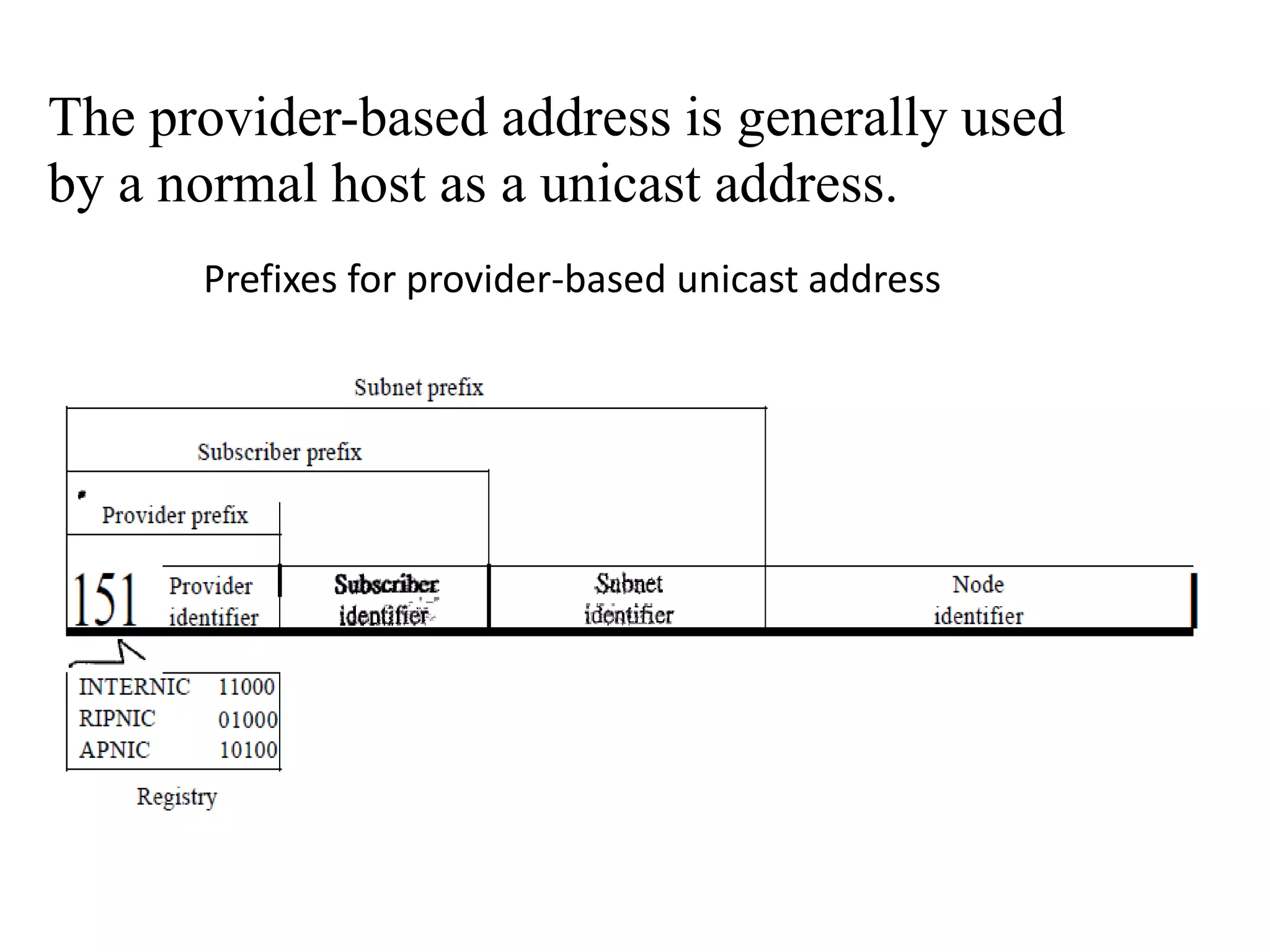
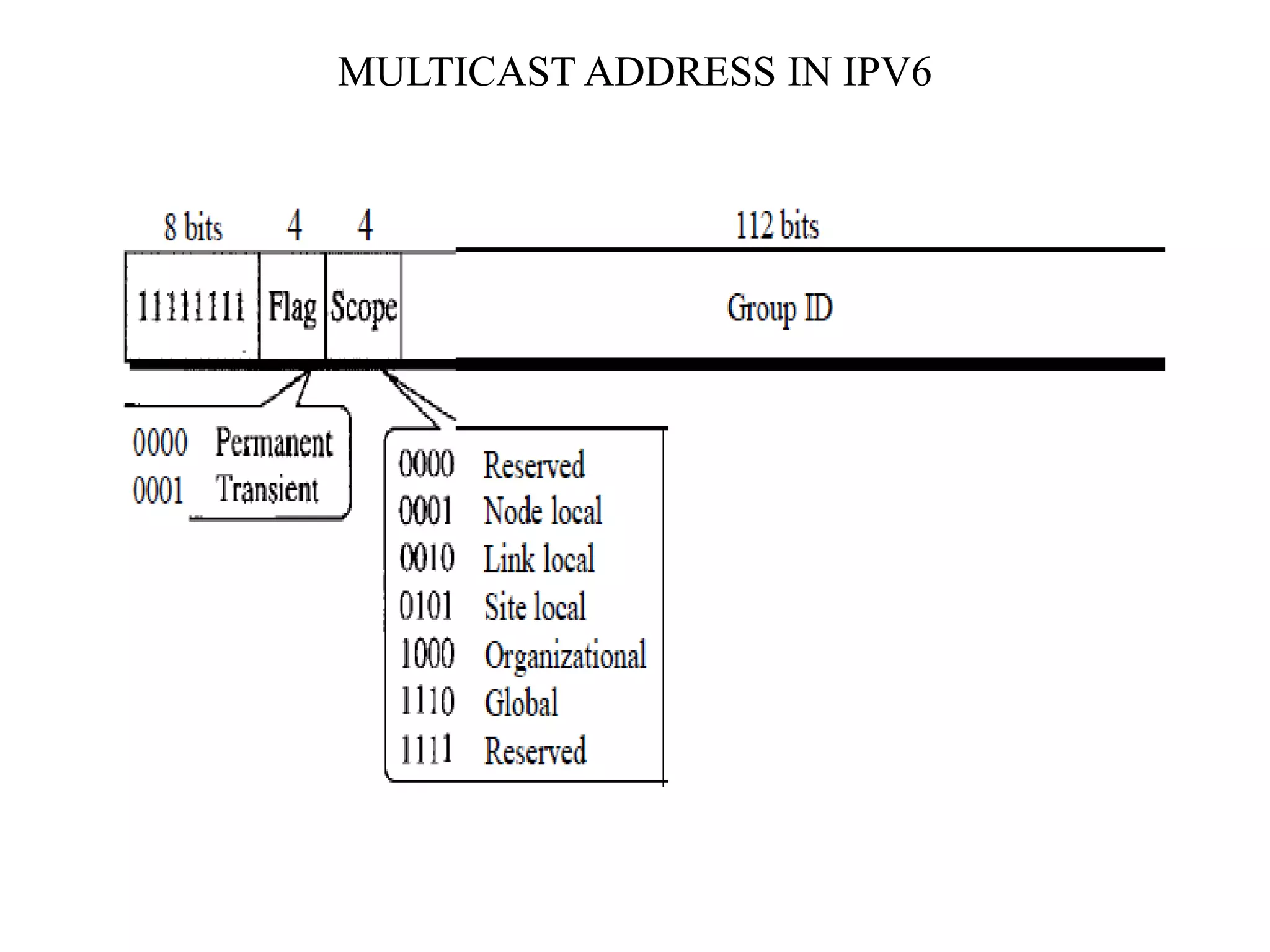
IPv6 addresses are 128-bit addresses used to identify nodes in an IPv6 network. They are conventionally written in hexadecimal colon notation, divided into eight sections of four hexadecimal digits each. IPv6 addresses have a hierarchical structure, with the type prefix in the first bits indicating the address category such as unicast, multicast, anycast, reserved, or local. Unicast addresses are used to identify a single interface, multicast for groups of interfaces, and anycast to select the nearest available node in a group.