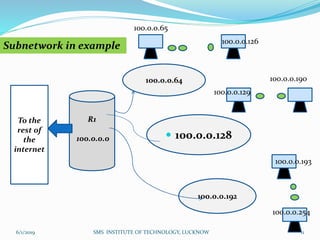
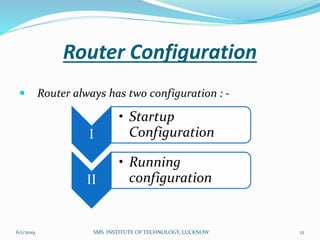
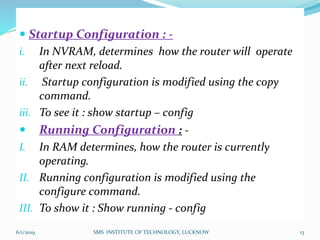
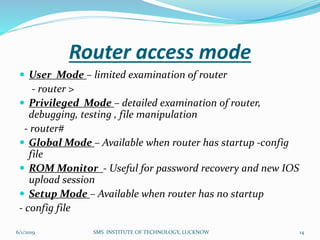
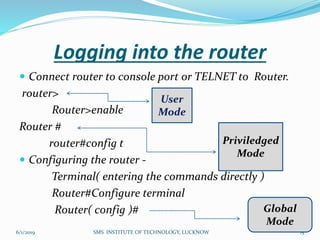
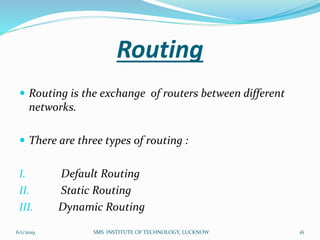
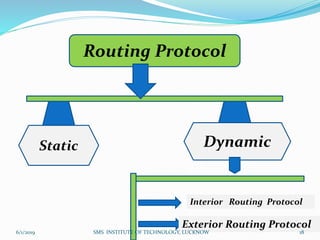
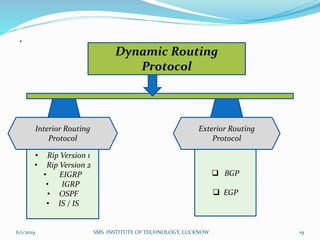
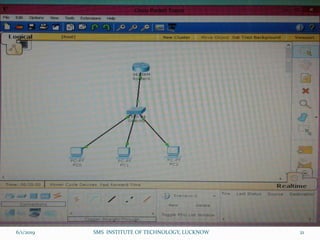
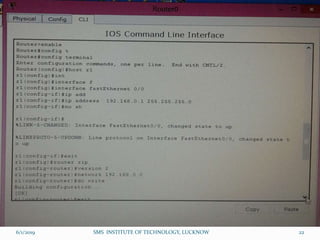
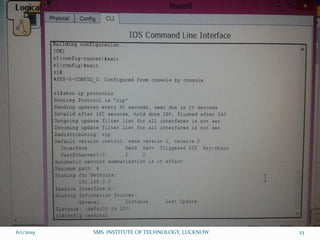
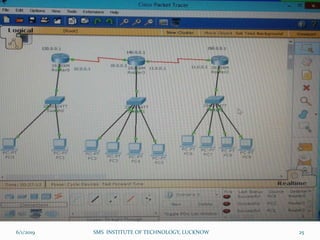
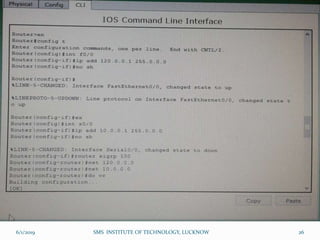
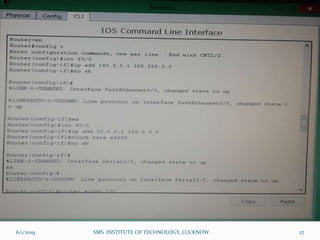
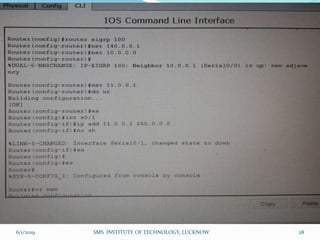
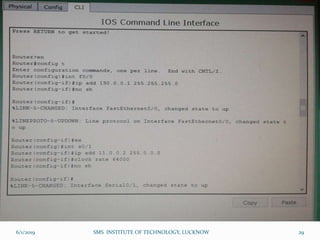
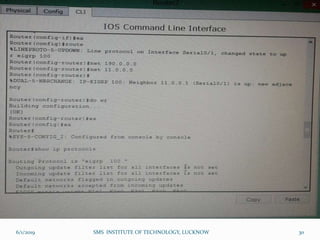
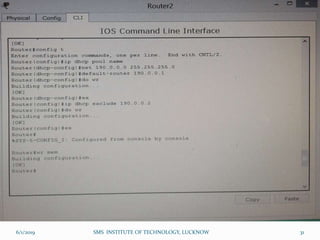
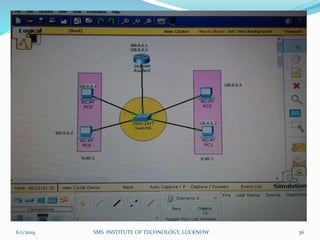
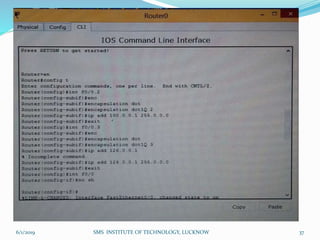
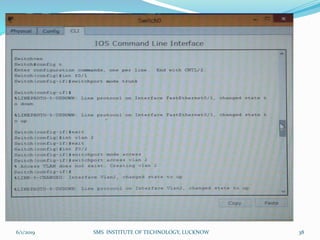
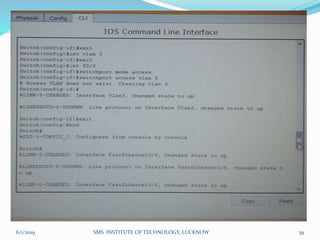
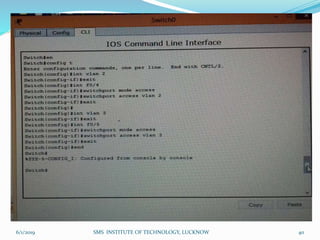
This document is a presentation on Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) and covers various topics related to networking, including types of networks (LAN, MAN, WAN), networking devices (like hubs, switches, routers), subnetting, routing protocols (RIP, EIGRP), and VLANs. It explains the configurations and types of routing, as well as the difference between routing protocols, and details the functions of routers and network access modes. The content emphasizes the importance of networking for communication and resource sharing.