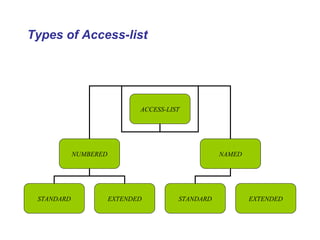
- Access control lists (ACLs) allow or deny network traffic passing through a router based on source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and port numbers.
- There are two main types of ACLs: standard ACLs which filter based on source IP addresses, and extended ACLs which filter on source/destination IP addresses, protocols, and port numbers.
- ACLs can be numbered or named, with named ACLs allowing selective editing of statements not possible with numbered ACLs.