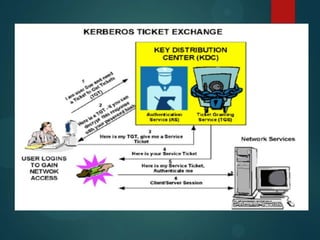
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol that was developed at MIT in the 1980s to allow nodes communicating over an insecure network to verify each other's identity. It uses tickets and session keys to allow clients and servers to communicate over a non-secure network and establish the identity of the users and servers. The Kerberos authentication process involves three main exchanges between the client, authentication server (KDC), and target server to authenticate users and allow access to services.