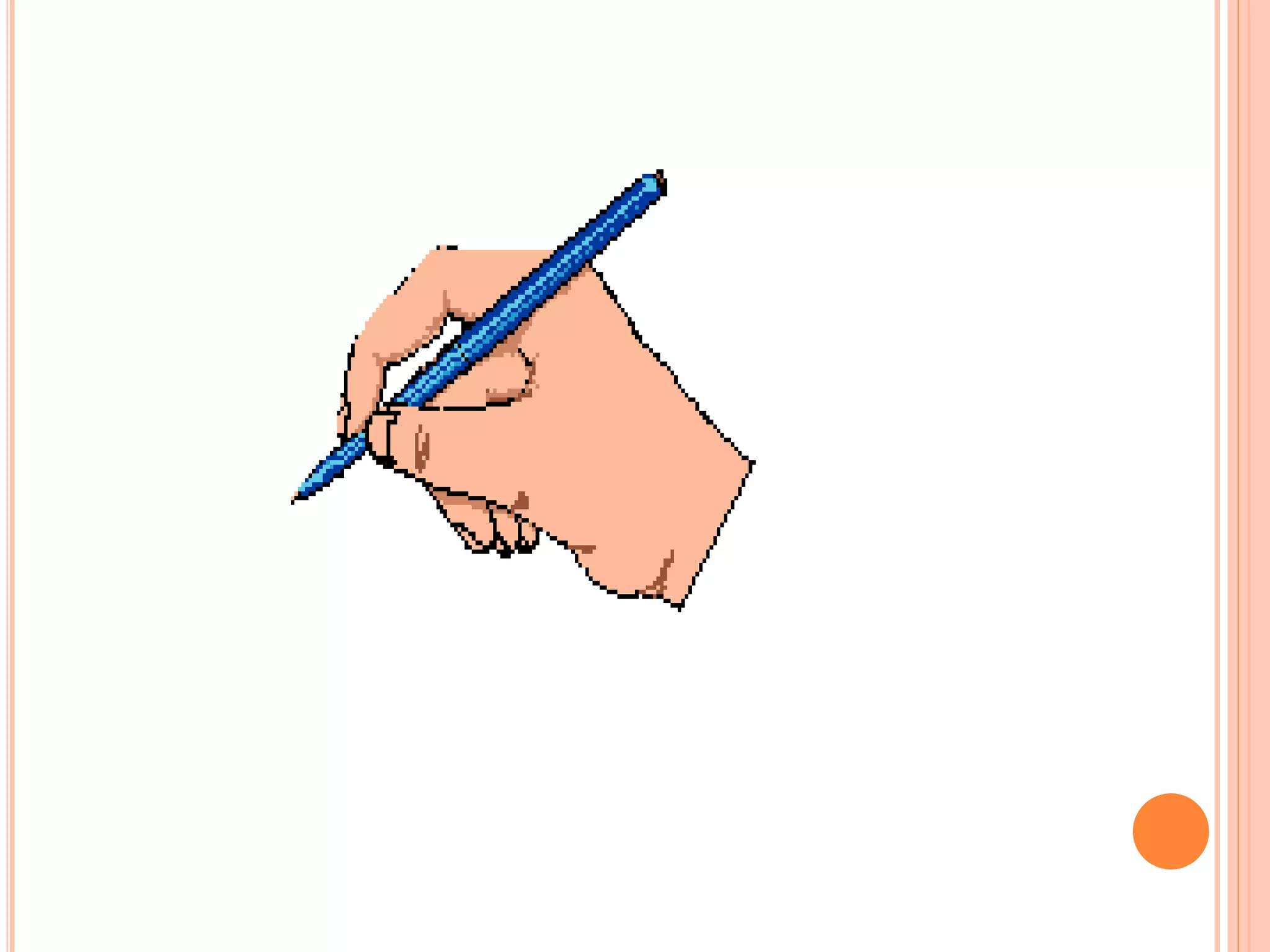
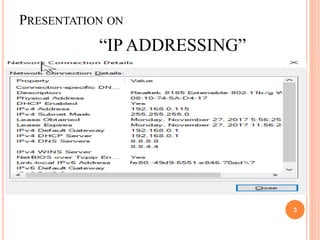
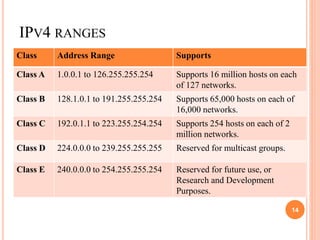
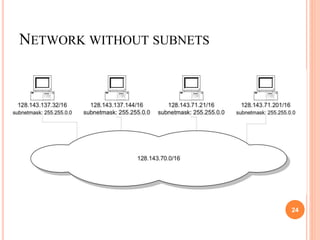
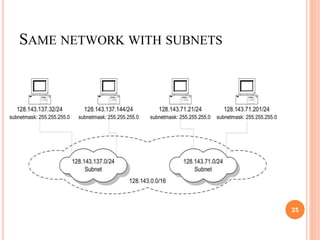
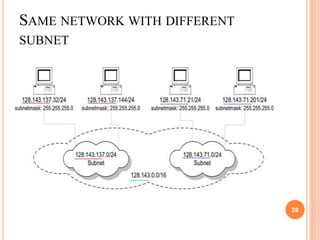
IPv4 and IPv6 are the two main versions of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses currently in use. IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers expressed in dotted decimal notation, while IPv6 addresses are longer 128-bit hexadecimal strings. IP addresses are assigned to identify machines on a network and allow communication and transfer of data between devices.