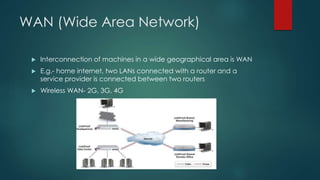
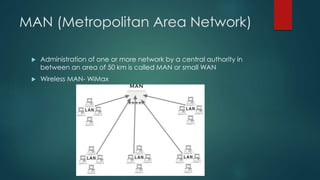
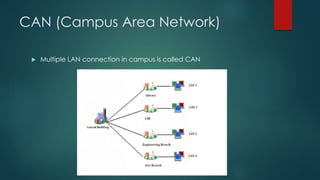
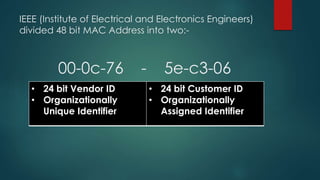
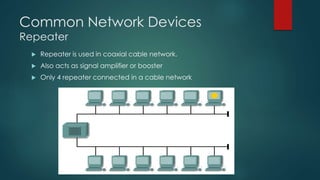
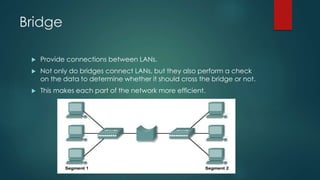
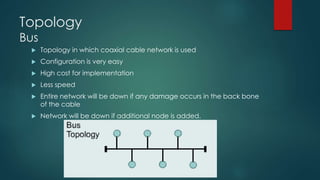
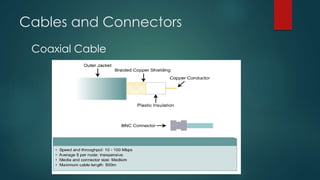
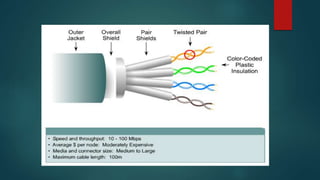
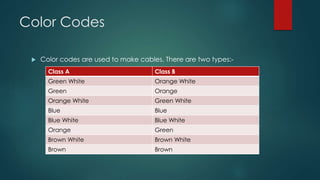
This document provides information about Cisco and the CCNA certification. It discusses Cisco as a company and their networking products. The CCNA certification focuses on routing, switching, security, service provider, and voice communication skills. The CCNA exam contains questions in drag and drop and simulation formats. The document also summarizes different types of computer networks, common networking devices, cable types, topologies and more.