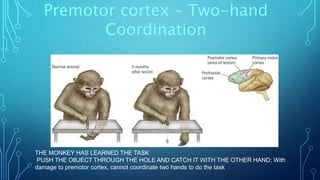
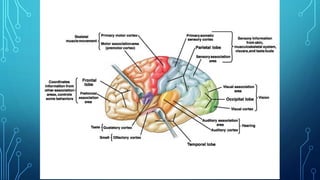
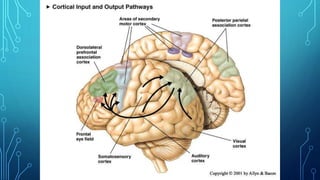
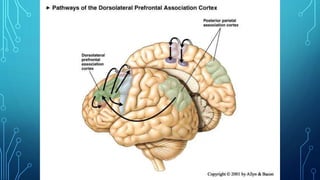
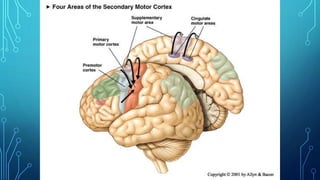
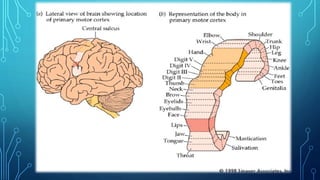
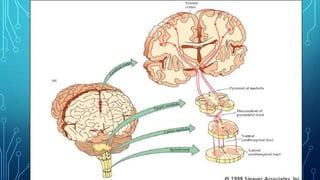
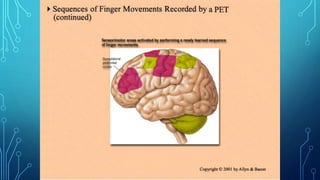
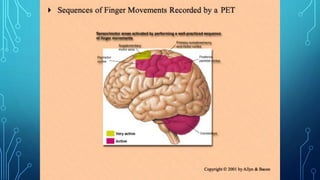
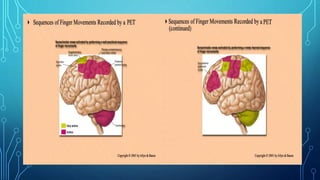
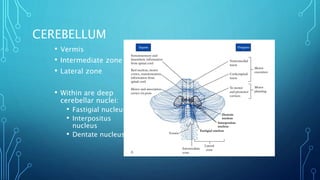
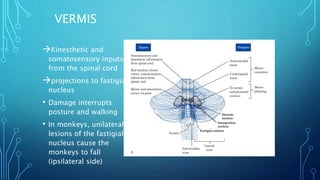
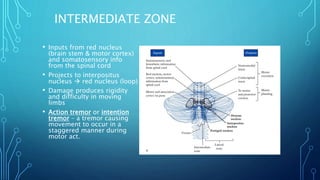
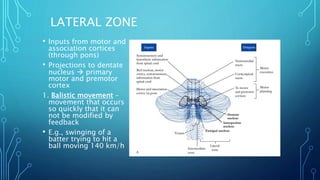
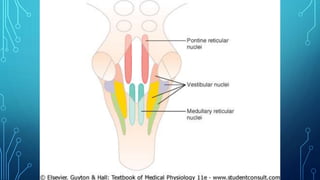
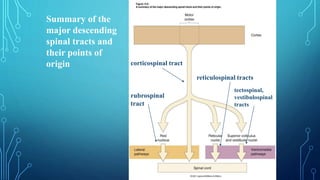
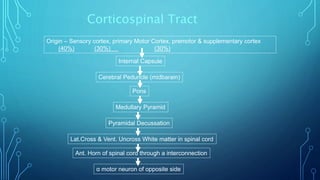
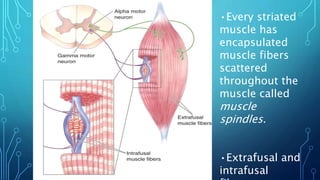
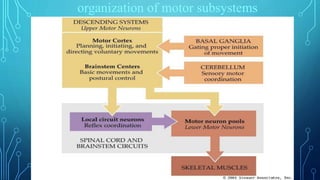
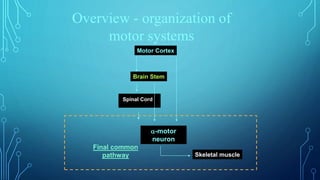
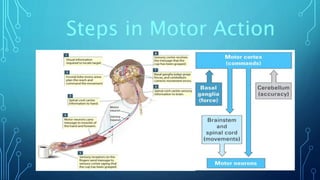
The document summarizes the key motor areas and pathways in the brain that control voluntary movement. It discusses the primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, and supplementary motor area that project to the spinal cord to control muscle movement. The basal ganglia and cerebellum also integrate with these motor areas to coordinate complex movements and ensure smooth motor execution. Damage to different motor areas can impact abilities like fine motor control, bimanual coordination, or lead to conditions like tremors or rigidity.