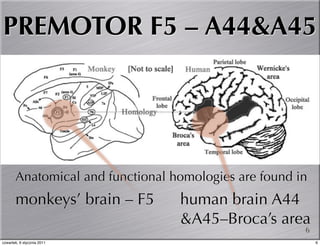
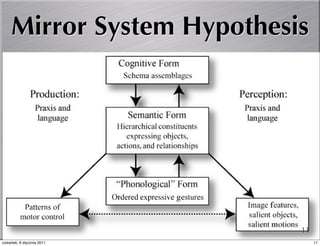
Mirror neurons help make meaning in communication in 3 key ways:
1) Mirror neurons fire both when we perform an action and when we observe another performing the same action, allowing us to understand others' intentions and have empathy.
2) Through mirroring others' gestures, words and actions in conversation, mirror neurons enable understanding without explicit meaning.
3) Mirror neurons are thought to have played a role in the evolution of language and culture by facilitating learning through imitation.