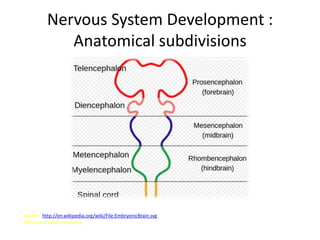
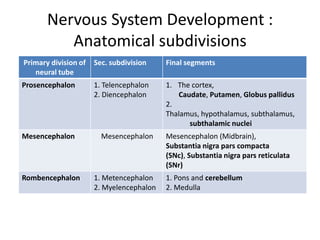
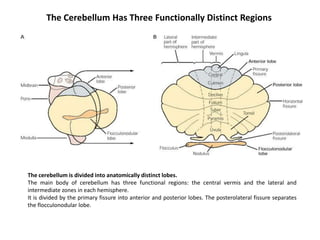
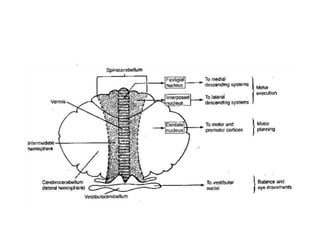
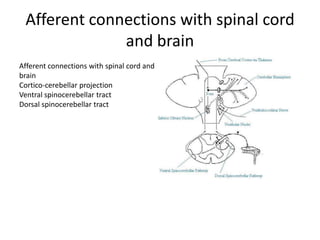
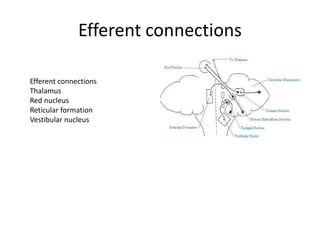
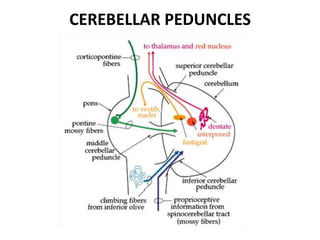
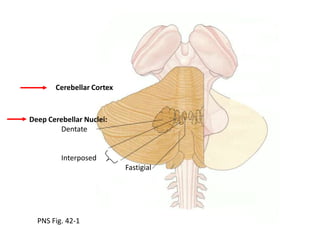
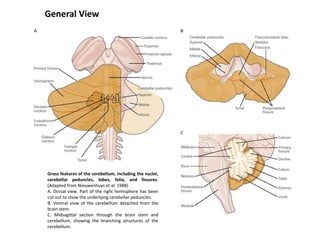
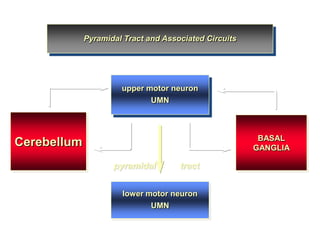
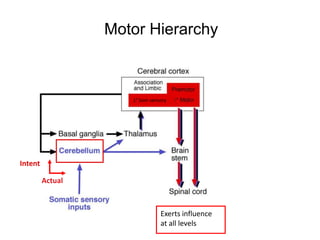
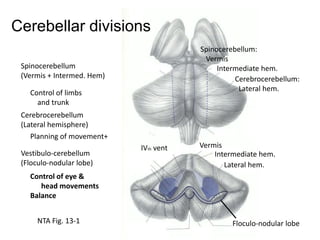
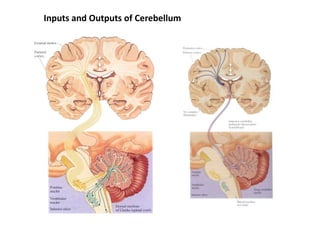
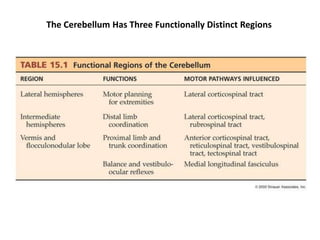
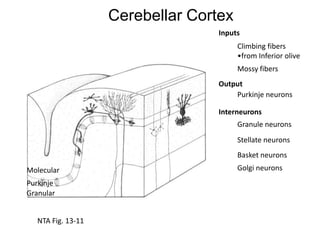
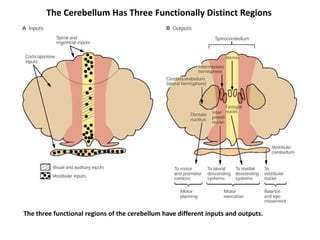
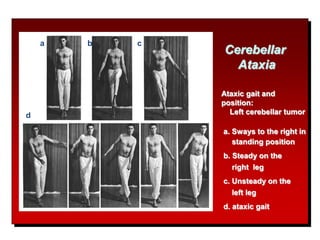
The document discusses the anatomy and functions of the cerebellum. It begins by outlining the embryonic development and subdivision of the nervous system. It then describes the three functionally distinct regions of the cerebellum - the vestibulocerebellum, spinocerebellum, and cerebrocerebellum - and their different inputs and outputs. The document also discusses the cerebellar peduncles, cortex, and nuclei. It outlines the roles of the cerebellum in motor control and coordination and describes clinical signs of cerebellar dysfunction such as ataxia.