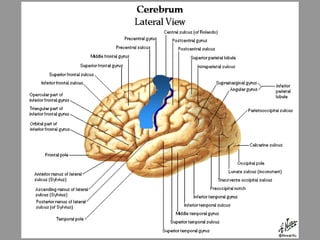
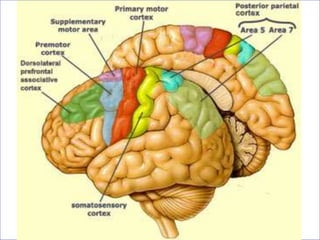
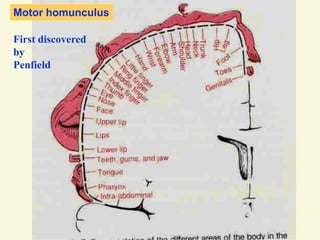
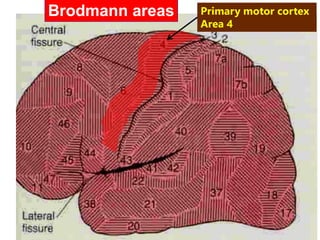
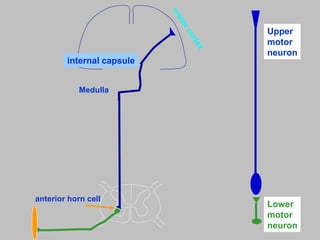
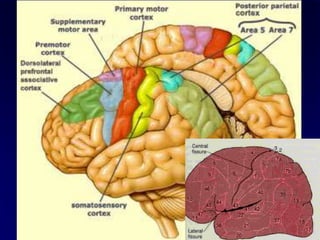
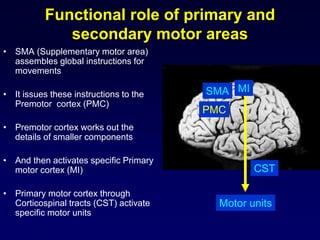
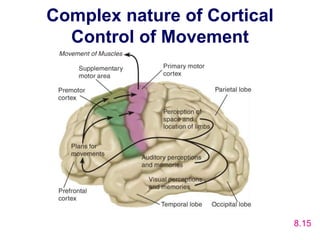
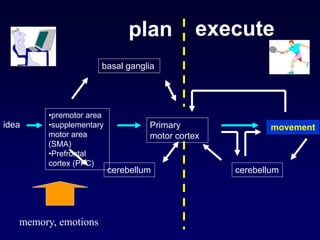
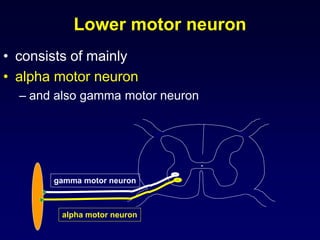
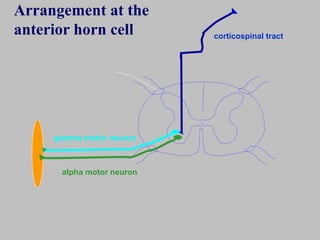
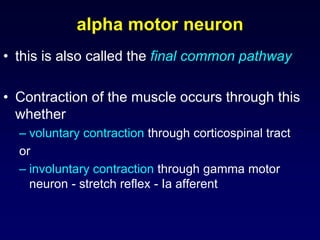
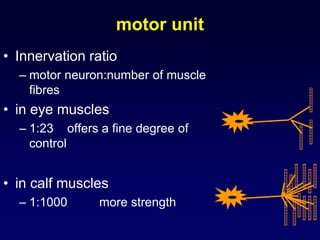
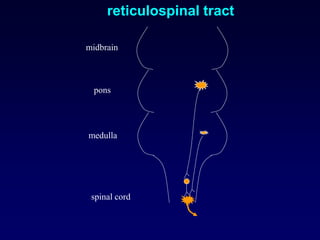
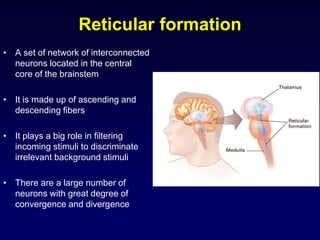
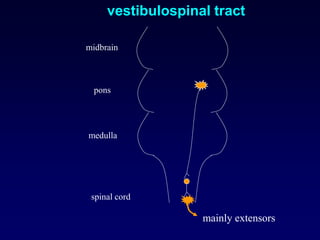
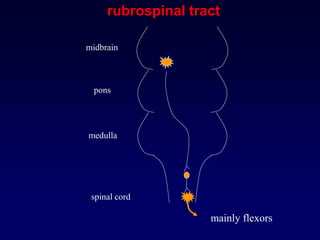
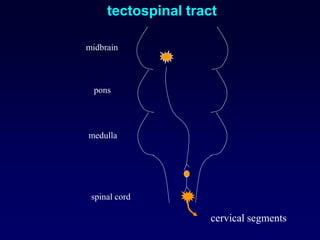
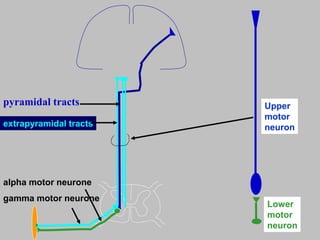
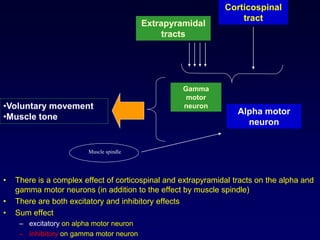
The motor system consists of upper motor neurons originating in the motor cortex and lower motor neurons originating in the spinal cord. The motor cortex is located in the frontal lobe and contains a somatotopic map called the motor homunculus. Primary motor areas like the primary motor cortex directly control muscle contraction, while secondary areas like the premotor cortex plan movements. Upper motor neurons descend through tracts like the corticospinal tract to synapse on lower motor neurons, which innervate muscles. Damage to different parts of the motor system can cause muscle weakness or changes in tone like spasticity or flaccidity.