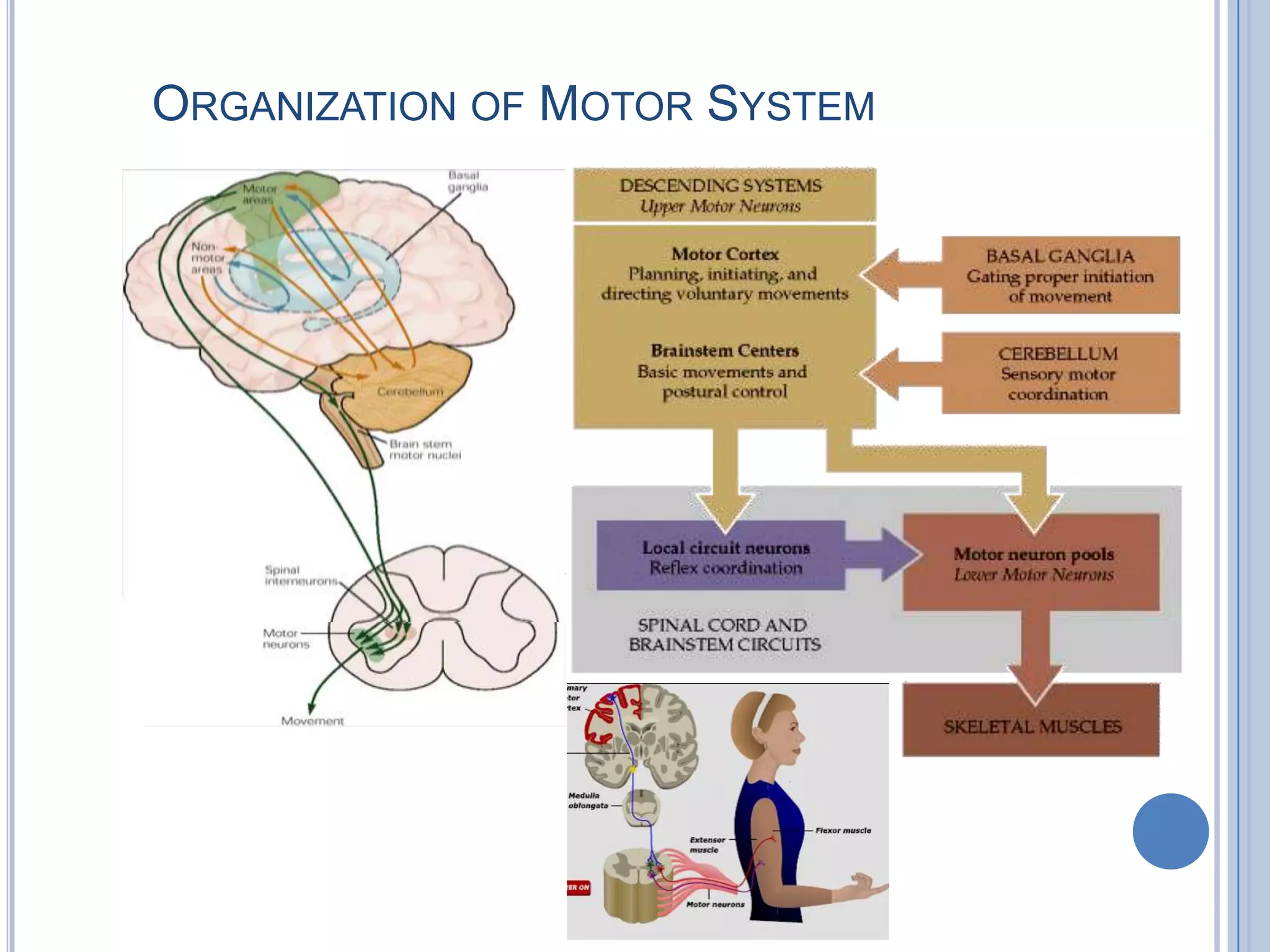
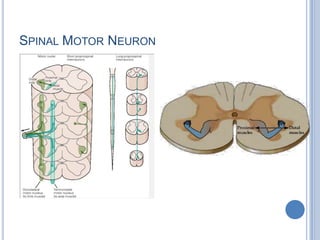
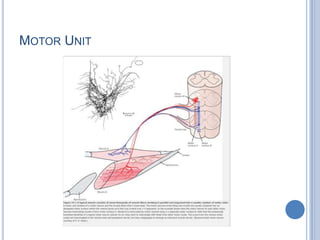
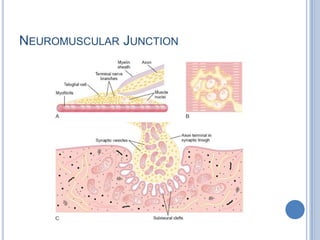
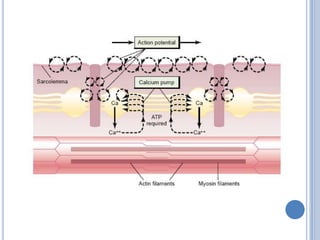
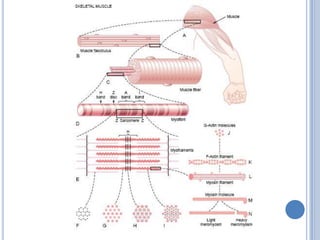
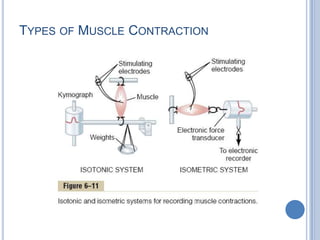
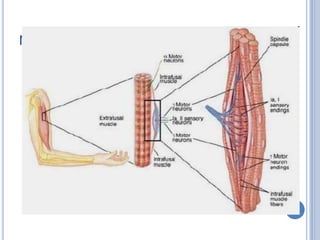
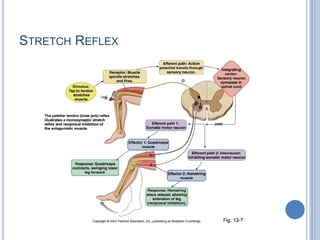
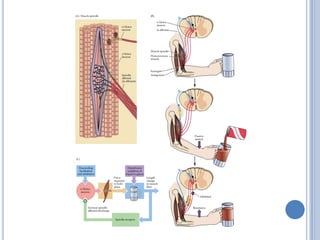
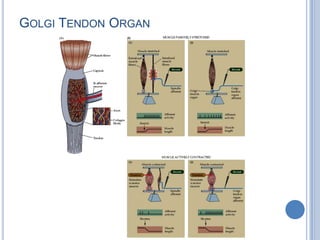
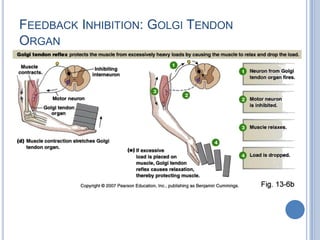
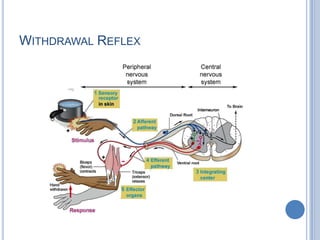
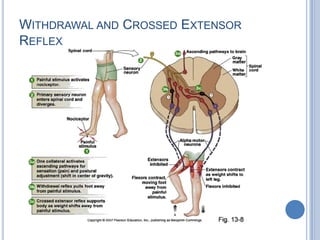
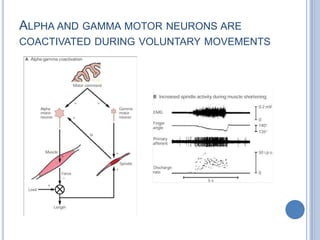
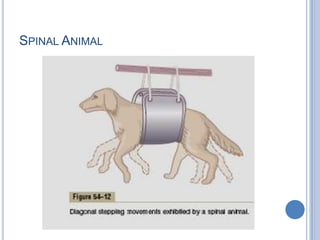
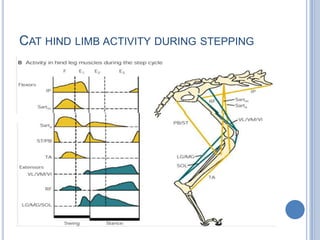
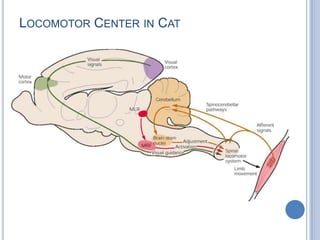
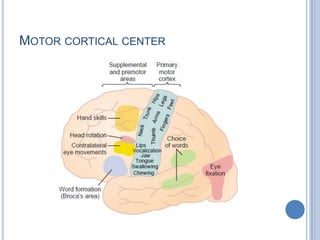
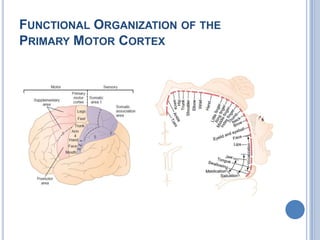
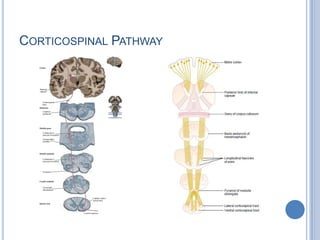
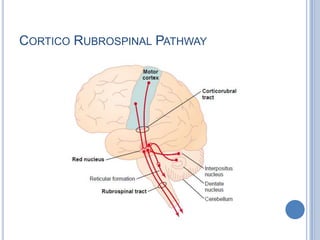
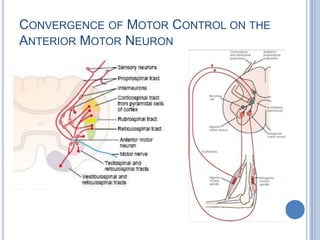
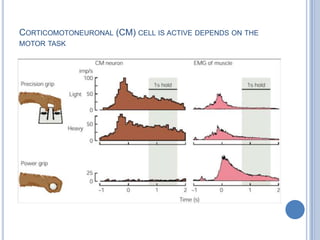
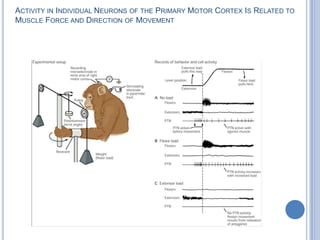
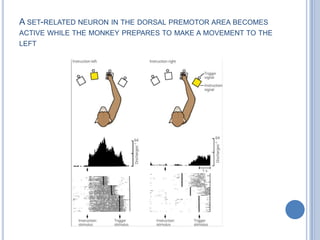
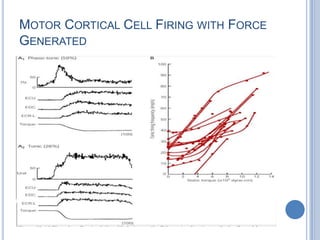
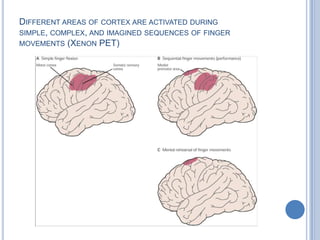
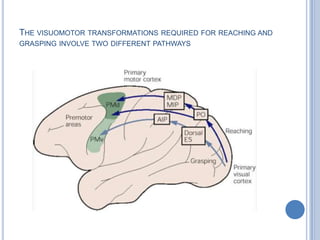
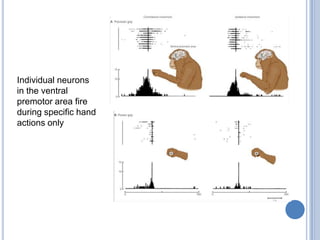
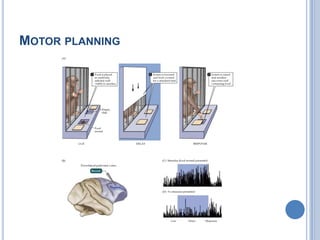
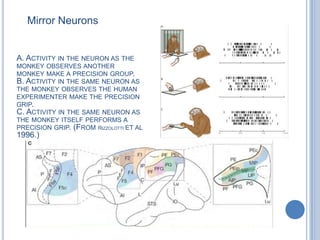
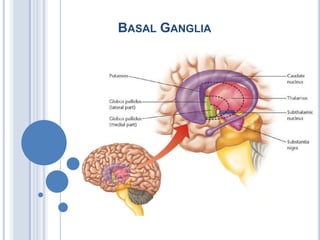
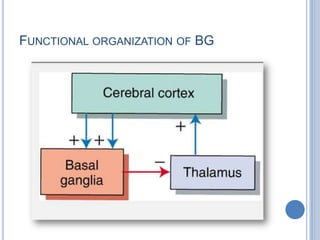
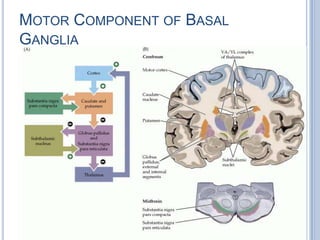
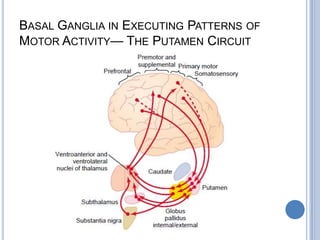
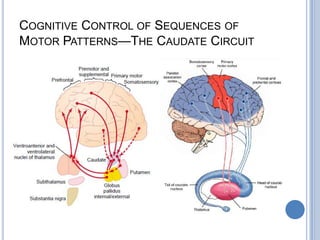
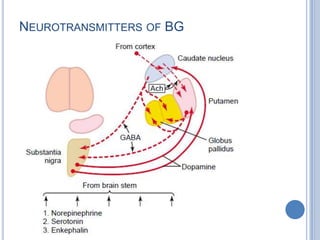
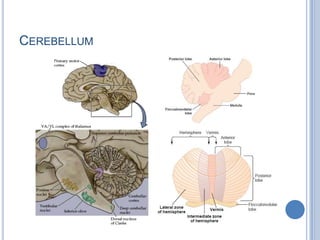
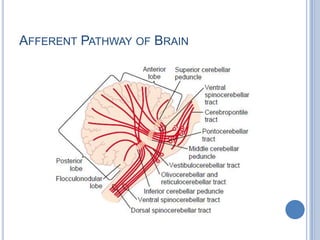
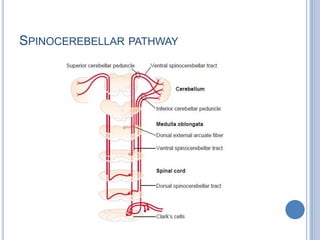
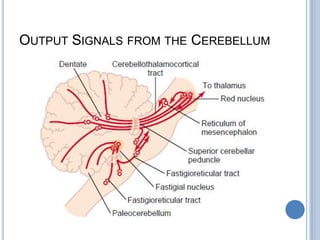
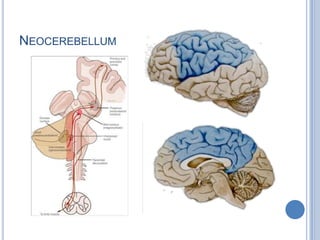
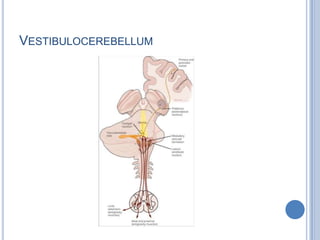
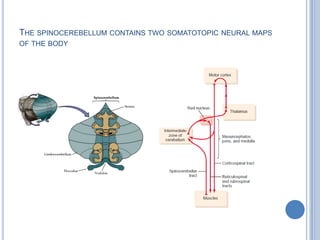
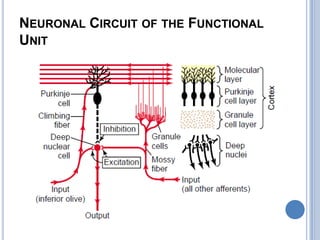
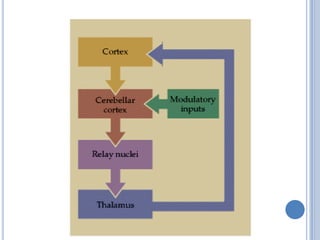
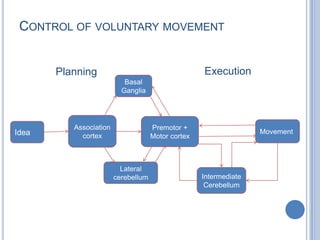
This document summarizes the organization and function of the motor system, including the spinal motor neuron, motor unit, neuromuscular junction, muscle spindles, stretch reflex, Golgi tendon organ, and feedback inhibition. It describes the role of alpha and gamma motor neurons in voluntary movements and locomotion. It discusses the primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and their involvement in motor planning, control, execution, learning, and adaptation. Key structures and pathways that converge on the anterior horn neuron to regulate precise movement are outlined.