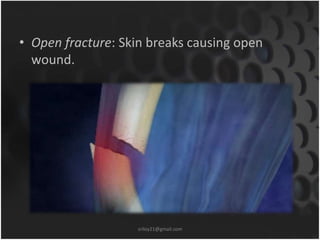
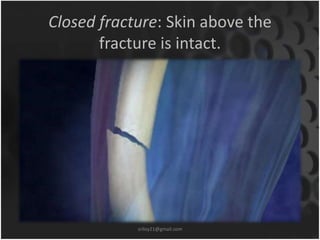
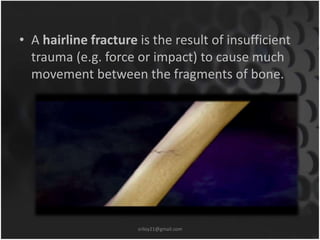
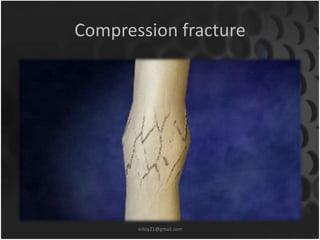
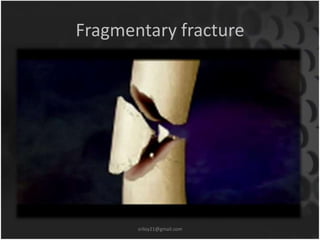
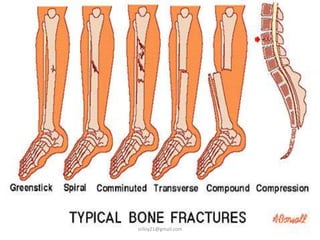
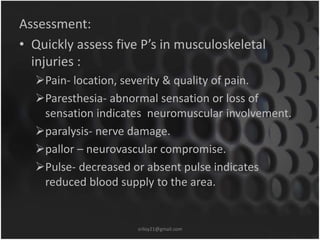
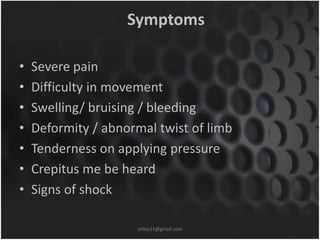
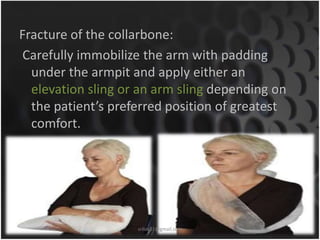
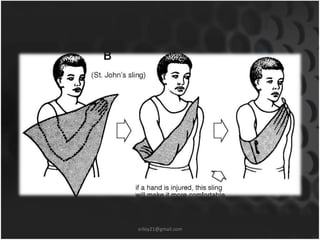
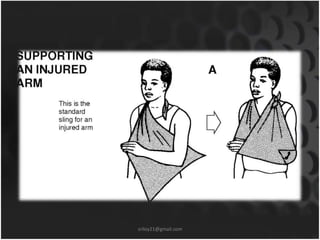
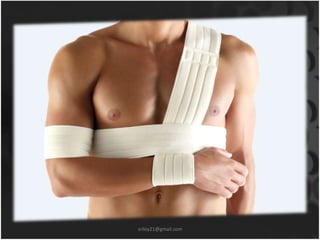
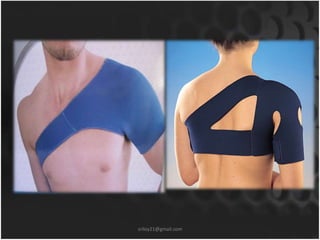
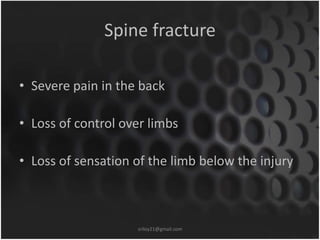
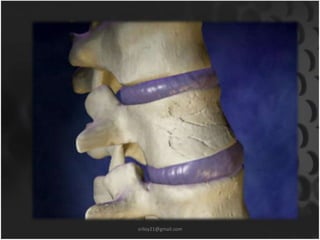
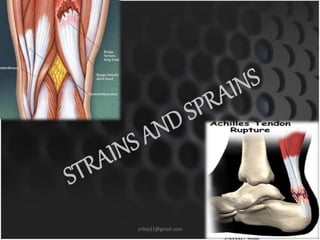
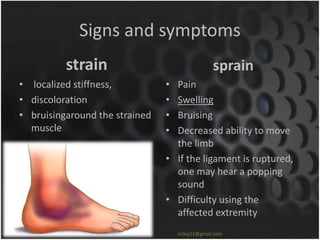
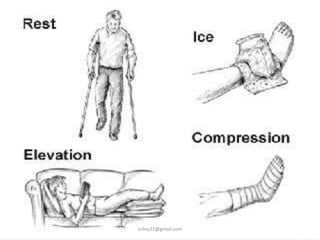
This document summarizes musculoskeletal injuries including strains, sprains, fractures, and dislocations. It defines strains as muscle or tendon injuries from overstretching and sprains as ligament injuries from overstretching. Signs of strains are localized stiffness, discoloration, and bruising, while signs of sprains are pain, swelling, bruising, decreased mobility, and sometimes a popping sound. Treatment for both involves RICE - rest, ice, compression, and elevation. The document also describes different types of fractures like closed versus open, stable versus unstable, and greenstick. First aid for fractures involves immobilization, preventing movement, and transport to the hospital.


![Cont…
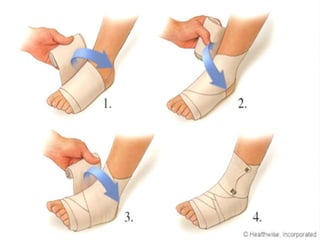
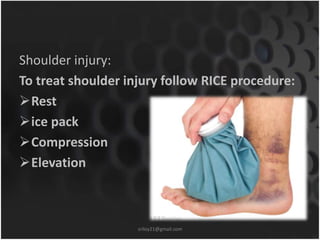
• Compression: Dressings, bandages, or ace-wraps should be
used to immobilize the sprain and provide support
– When wrapping the injury, more pressure should be applied at the far
end of the injury and decrease in the direction of the heart
– Compression should not cut off the circulation of the limb.[8]
• Elevation: Keeping the sprained joint elevated (in relation to
the rest of the body) will also help minimize swelling
sriloy21@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fracture-copy-141029104717-conversion-gate01/85/Fracture-copy-9-320.jpg)