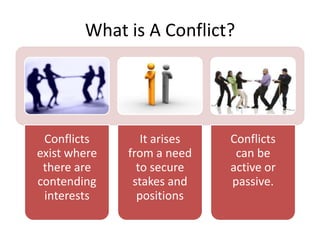
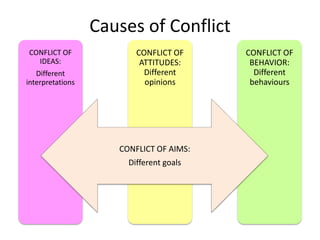
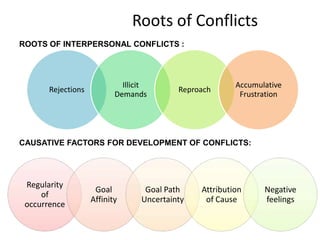
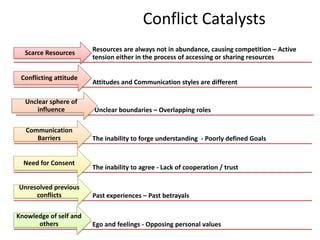
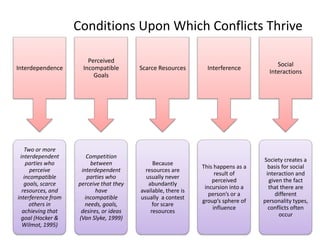
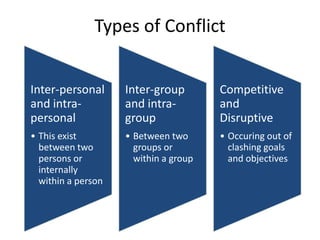
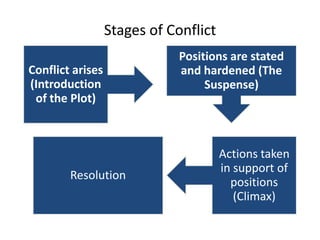
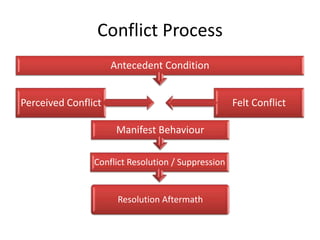
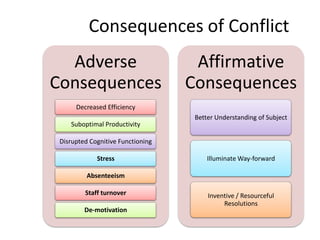
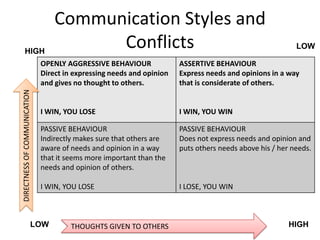
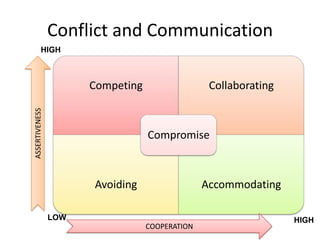
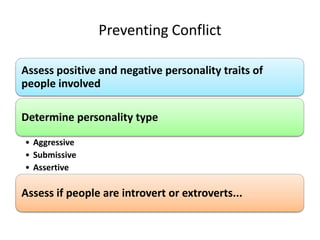
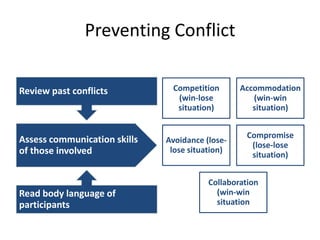
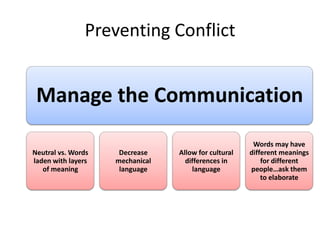
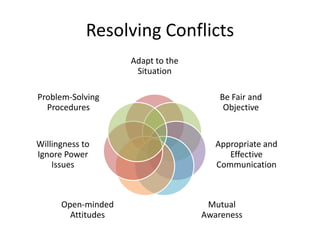
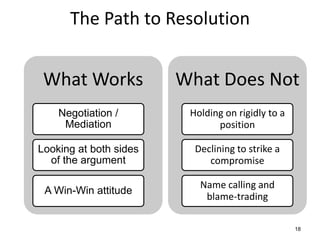
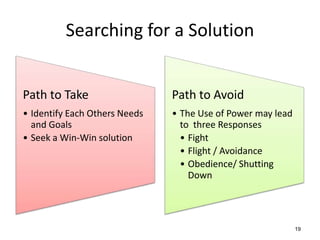
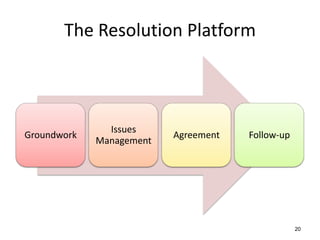
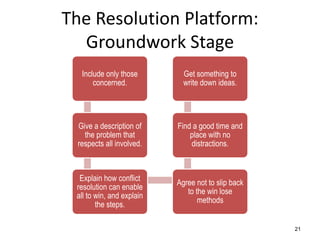
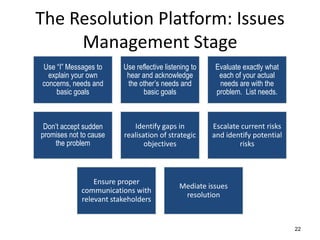
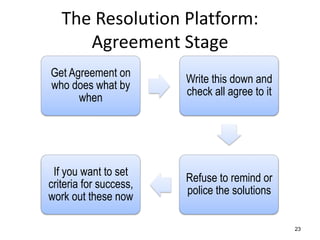
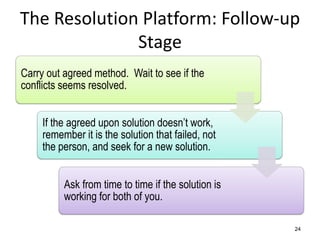
The document discusses the nature of conflict, various causes, types, and the resolution process. It highlights interpersonal and intrapersonal conflicts, stages of conflict, methods for conflict prevention, and effective communication strategies. The resolution platform includes groundwork, issues management, agreement, and follow-up stages to facilitate a win-win outcome.