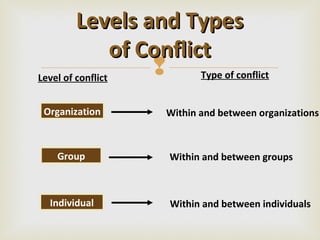
Conflict arises when individuals have differing views, interests or goals that they perceive as incompatible. There are various types and causes of conflict including interpersonal conflicts between individuals with different personalities, and intragroup conflicts within teams. The document outlines techniques for constructively resolving conflicts through open communication, understanding different perspectives, focusing on interests rather than positions, and finding solutions where all parties achieve their goals.