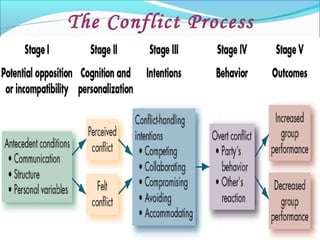
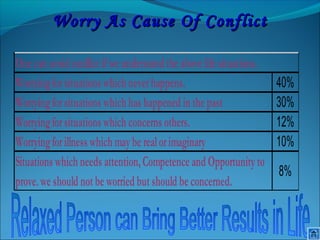
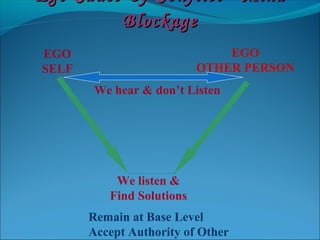
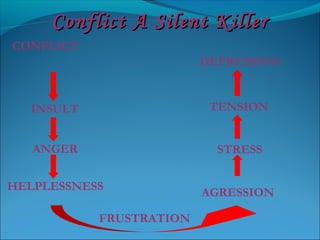
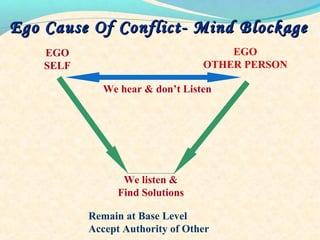
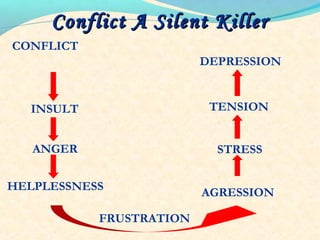
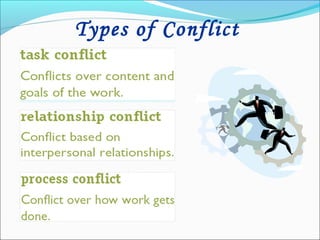
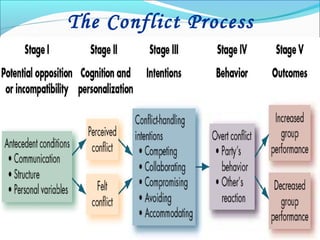
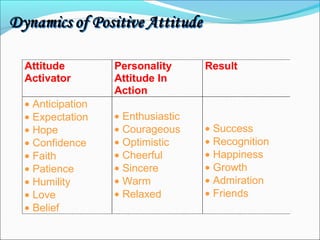
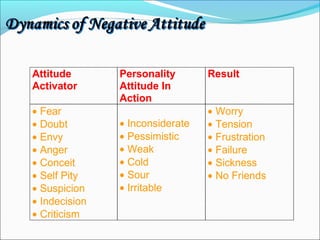
The document discusses the causes and types of conflict in the workplace. It states that conflict is a natural and sometimes beneficial part of organizations, arising from differences in personalities, perspectives, goals, and structural factors like ambiguous responsibilities. Conflict occurs when one party can negatively impact another, such as in supervisor-subordinate, team member, or customer interactions. The document outlines various reasons for conflict, including communication problems, power struggles, dissatisfaction with leadership, and organizational changes. It also distinguishes between constructive conflict that produces useful change and dysfunctional conflict that hinders performance and morale.




























































![ENERGY
WORRYWORRY
(Waste)(Waste)
RESPONSIBILITYRESPONSIBILITY
(Investment)(Investment)
20%20% 20%20% 60%60%
50%50% 50%50% NILNIL
MIND CAN’T FUNCTIONMIND CAN’T FUNCTION
100%100% 100%100%
FROM BODY’SFROM BODY’S
RESERVERESERVE
QUOTA OFQUOTA OF
ENERGYENERGY
FEELINGFEELING
[80%][80%]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conflictmanagement-130607000840-phpapp01/85/Conflict-management-67-320.jpg)