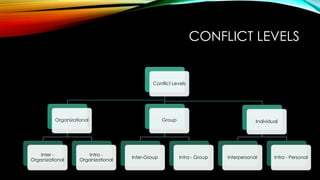
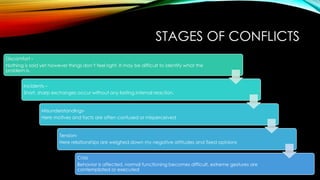
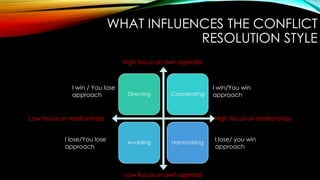
El documento detalla la naturaleza y las etapas de los conflictos, así como sus fuentes, síntomas y estilos de resolución. Los conflictos pueden surgir a diferentes niveles, incluyendo intra e interpersonales, e incluyen diversas dinámicas como la competencia por recursos limitados y la diversidad de objetivos. Se presentan estrategias para lograr resultados beneficiosos para ambas partes, enfatizando la importancia de la comunicación, la empatía y el compromiso en la resolución de conflictos.